Abstract
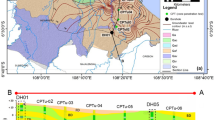
High amounts of iron, up to 14 mg/L, were found in groundwater samples from Marano Lagoon in the Friuli Venezia Giulia Plain (northeast Italy). In order to characterize groundwater hydrochemistry in the area, an investigation has been conducted on 35 wells that were monitored since 2006. Leaching tests were performed (under anaerobic conditions with deionized and saline waters) on two core samples in the area to study the iron release from soils to groundwater. Collected data indicated the main role of salinity in metal leaching and highlighted spatial correspondence between high levels of chloride and iron. To understand the mechanism of groundwater salinization, sulphate/chloride ratio has been investigated and a statistical relation between salinity, pH and iron was found. These data do not show any relation between past activities and high iron groundwater contents. High iron concentrations are diffuse in the whole area and therefore comparable to background values. Consequently, the study states that no remediation plan should have been made for iron concentrations in this area.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agenzia Regionale per la Protezione dell’Ambiente del Friuli Venezia Giulia Osservatorio Meteorologico Regionale [Environmental Protection Agency of Friuli Venezia Giulia meteorological observatory], rainfall data. http://www.osmer.fvg.it
Alloway BJ (1990) Heavy metals in soils. Blackie Academic and Professional, Glasgow, pp 12–25
Baldassi E, Tessarin A (2004) Torviscosa–Malisana. La storia [Torviscosa–Malisana. The Story] Associazione “Primi di Torviscosa”. Torviscosa 3–165. http://www.primiditorviscosa.it/fabbrica/origini.htm
Baumann T, Fruhstorfer P, Klein T, Niessner R (2006) Colloid and heavy metal transport at landfill sites in direct contact with groundwater. Water Res 40(14):2776–2786
Bone SE, Gonneaa ME, Charette MA (2006) Geochemical cycling of arsenic in a coastal aquifer. Environ Sci Technol 40(10):3275–3276
Botes PJ (2003) Investigation of mobility of trace elements in river sediments using ICP-OES. Dissertation, University of Pretoria 44–72. http://upetd.up.ac.za/thesis/available/etd-01182005-091457/unrestricted/00dissertation.pdf
Buss SR, Rivett MO, Morgan P, Bemment CD (2005) Attenuation of nitrate in the subsurface. Environment Agency Bristol England—Science Report SC030155/SR2: 11–71. http://publications.environment-agency.gov.uk/pdf/SCHO0605BJCS-e-e.pdf
Caprotti F (2006) Malaria and technological networks: medical geography in the Pontine Marshes, Italy, in the 1930s. Geogr J Royal Geogr Soc 172(2):145–155
Chapelle FH, Lovley DR (1992) Competitive exclusion of sulfate reduction by Fe(III)-reducing bacteria: a mechanism for producing discrete zones of high-iron ground water. Ground Water 30(1):29–36
Charette MA, Sholkovitz ER (2002) Oxidative precipitation of groundwater-derived ferrous iron in the subterranean estuary of a coastal bay. Geophys Res Lett 29(10):1–4. http://www.whoi.edu/science/MCG/groundwater/pubs/PDF/IronCurtain_GRL
Cucchi F, Brambati A (2003) La carta della vulnerabilità intrinseca delle falde contenute nelle aree di pianura della provincia di Udine Relazione Tecnica Generale [Intrinsic groundwater vulnerability map of the Upper Plain]. Department of Geological, Environmental and Marine Sciences, University of Trieste 17–18. http://www.provincia.udine.it/ambiente/difesadelsuolo/progetti/falde/Documents/Relazione_Generale.pdf
Cucchi F, Piano C (2001) Studies for the realization of the hydrogeological map of Friuli-Venezia Giulia. Ipogea 3(2000) GNDCI Pub. n°2030, LR4 57–71. http://www.gssg.it/modules/Downloads/data/ipogea/3/eng/Ipogea%203-5%20inglese.pdf
Cucchi F, Franceschini G, Zini L (2008) Hydrogeochemical investigations and groundwater provinces of the Friuli Venezia Giulia Plain aquifers, northern Italy. Env Geol 55(5):985–999
Del Frate A, Lombardo E, Monti G, Nosari M, Pastore V, Gardini P (2006) Modelling of surface water and groundwater interaction for remediation design at Torviscosa site. Studio Geotecnico Italiano. Dissertation, Provincia di Milano 1–13. http://www.provincia.milano.it/ambiente/bonifiche/doc/atti_2006_pastore_sgi.pdf
Elder JF (1988) Metal biogeochemistry in surface-water systems; a review of principles and concepts. United States Geological Survey Circular 1013: 15–17. http://pubs.er.usgs.gov/djvu/CIR/circ_1013.djvu
Escolero O, Marín LE, Steinich B, Pacheco JA, Maldonado AM, Anzaldo JM (2005) Geochemistry of the hydrogeological reserve of Mérida Yucatán, Mexico. Geofisica Internacional 44(3):301–314. http://redalyc.uaemex.mx/redalyc/pdf/568/56844308.pdf
Feruglio D (1926) Progetto di bonifica della Bassa Friulana [Reclaim Project for the Lower Friulian Plain] Stabilimento Tipografico Friulano, Udine 1–144
Hageman PL (2006) U.S. Geological Survey field leach test for assessing water reactivity and leaching potential of mine wastes, soils, and other geologic and environmental materials. US Geol Sur 05(D03):1–7. http://pubs.usgs.gov/tm/2007/05D03/pdf/TM5-D3_508.pdf
Harbison J, Cox M (2002) Hydrological characteristics of groundwater in a subtropical coastal plain with large variations in salinity: Pimpama, Queensland, Australia. Hydrol Sci J (des Sciences Hydrologiques) 47(4):651–665. http://iahs.info/hsj/470/hysj_47_04_0651.pdf
International Organization for Standardization/International Electrotechnical Commission Ente Nazionale Italiano di Unificazione UNI CEI EN ISO/IEC 17025 (2005) General requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories. CEN/CENELEC 2nd edn 46–48
Johansson J (2005) Manganese solubility due to compaction in soils under corn and soybean. Dissertation, Lantbruks Universitet Sveriges 2–20. http://ex-epsilon.slu.se:8080/archive/00000658/01/Exarbete_J_Johansson.slutl.pdf
Kretzschmar R, Schäfer T (2005) Metal retention and transport on colloidal particles in the environment. Miner Soc Am 1(4):205–210
Kroeger KD, Swarzenski PW, Greenwood WMJ, Reich C (2007) Submarine groundwater discharge to Tampa Bay: nutrient fluxes and biogeochemistry of the coastal aquifer. Mar Chem 104(1–2):85–97
Kuma K (2004) Biogeochemistry of iron in seawater. Dissertation, Hokkaido University, pp 93–102. http://www.chikyu.ac.jp/AMORE/2004.3kyotoSympo/10.Kuma.pdf
Legambiente 2006 Stop al mercurio. La campagna italiana per la riconversione degli impianti cloro-soda [Stop mercury] Unpublished data, pp 37–44. http://www.verdenero.it/doc/2_stop_al_mercurio_dossier_legambiente.pdf
Martelli G, Granati C (2006) The confined aquifer system of Friuli Plain (North Eastern Italy): analysis of sustainable groundwater use. Italian J Eng Geol Environ Bologna 3(1):59–67
Martelli G, Roda C (1998) L’acquifero della bassa pianura friulana in comune di San Giorgio di Nogaro [The aquifer in San Giorgio di Nogaro, Lower Friuli Plain—NE Italy]. Quad Geol Appl Pitagora Ed Bologna 5(1):15–38
Martelli G, Granati C, Roda C (2003) Distribution of coarse-grained sediments in the Friuli alluvial plain (Northern Italy) from surface till the dept of 50 meters. Quad Geol Appl Pitagora Ed Bologna 2(1):131–146
McLean JE, Bledsoe BE (1992) Ground water issue. Behaviour of metals in soils. United States Environmental Protection Agency 1–25. http://www.epa.gov/ada/download/issue/issue14.pdf
Moore WS (1999) The subterranean estuary: a reaction zone of groundwater and seawater. Mar Chem 65(1–2):111–125
Mosetti F (1983) Sintesi sull’idrologia del Friuli Venezia Giulia [Summary of the Friuli Venezia Giulia hydrology]. Quad Ente Tutela Pesca Friuli Venezia Giulia Udine (6):167–263
Ouddane B, Skiker M, Fischer JC, Wartel M (1999) Distribution of iron and manganese in the Seine river estuary: approach with experimental laboratory mixing. J Environ Monit 1(5):489–496. http://www.rsc.org/delivery/_ArticleLinking/DisplayArticleForFree.cfm?doi=a903721g&JournalCode=EM
Park J, Sanford RA, Bethke CM (2006) Geochemical and microbiological zonation of the Middendorf aquifer, South Carolina. Chem Geol 230(1–2):88–104
Paul CJ, Puls RW (2007) Impact of turbidity on TCE and degradation products in ground water. Groundw Monit Remediat 17(1):128–133
Puls RW, Powell RM (2007) Acquisition of representative ground water quality samples for metals. Groundw Monit Remediat Natl Groundw Assoc 12(3):167–176. https://info.ngwa.org/GWOL/pdf/921856390.PDF
Rijkenberg MJA, Gerringa LJA, Velzeboer I, Timmermans KR, Buma AGJ, De Baar HJW (2005) Iron-binding ligands in Dutch estuaries are not affected by UV induced photochemical degradation. Mar Chem 100(1,2):11–23. http://www.rug.nl/fwn/onderzoek/instituten/esrig/oe/publications/artikelen/bumamarchem1002006.pdf
Ryu J, Dahlgren RA, Gao S, Tanji KK (2004) Characterization of redox processes in shallow groundwater of Owens Dry Lake, California. Environ Sci Technol 38(22):5950–5957
Sánchez-Martos F, Pulido-Bosch A, Molina Sánchez L, Vallejos-Izquierdo A (2001) Identification of the origin of salinization in groundwater using minor ions (Lower Andarax, Southeast Spain). Sci Total Environ 297(1–3):43–58
Schnapp JT (1997) The fabric of modern times. Univ Chicago Press Crit Inq 24(1):191–245
Spiteri C, Regnier P, Slomp CP, Charette MA (2005) pH-dependent iron oxide precipitation in a subterranean estuary. J Geochem Explor 88:399–403
Stefanini S, Cucchi F (1977) Gli acquiferi del sottosuolo della provincia di Udine (The aquifers in the Udine province). Quad Istit Ricerca Sulle Acque 34(6):131–147 Centro Nazionale Ricerca P/368 Roma
Testa JM, Charette MA, Sholkovitz ER, Allen MC, Rago A, Herbold CW (2002) Dissolved iron cycling in the subterranean estuary of a Coastal Bay: Waquoit Bay, Massachusetts. Estuar Freshw Biogeochem, The Biol Bull 203:255–256. http://www.biolbull.org/cgi/reprint/203/2/255
Thayalakumaran T, Charlesworth P, Bristow K (2004) Assessment of the geochemical environment in the lower Burdekin aquifer: implications for the removal of nitrate through denitrification. Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation CSIRO Land and Water Technical Report 32/04, pp 1–37. http://www.clw.csiro.au/publications/technical2004/tr32-04.pdf
Tihansky AB (2005) Effects of aquifer heterogeneity on ground-water flow and chloride concentrations in the Upper Floridian Aquifer near and within an active pumping well field, West-Central Florida. Dissertation, United States Geological Survey Science in Florida Orlando, pp 1–74. http://pubs.usgs.gov/sir/2004/5268/pdf/sir20045268.pdf
United States Environmental Protection Agency (1996) Low stress (low flow) purging and sampling procedure for the collection of ground water samples from monitoring wells. United States Environmental Protection Agency 1–13. http://www.epa.gov/region6/6pd/qa/qadevtools/mod5_sops/groundwater/sampling/r1_lowflow.pdf
Ussher SJ, Achterberg EP, Worsfold PJ (2004) Marine Biogeochemistry of Iron. Environ Chem 1(2):67–80
Weber L, Völker C, Schartau M, Wolf-Gladrow DA (2005) Modeling the speciation and biogeochemistry of iron at the Bermuda Atlantic Time-series study site. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 19 GB1019 1–23. http://epic.awi.de/Publications/Web2005a.pdf
Weber L, Völker C, Oschlies A, Burchard H (2007) Iron profiles and speciation of the upper water column at the Bermuda Atlantic time-series Study site: a model based sensitivity study. Biogeosciences (4):689-706. http://www.biogeosciences.net/4/689/2007/bg-4-689-2007.pdf
Whittemore DO (2004) Geochemical identification of source of salinity in groundwaters of the high plains aquifer south of McPherson, Kansas. Kansas Geological Survey open file report 2004-62, pp 1–21. http://www.kgs.ku.edu/Hydro/Publications/2004/OFR04_62/index.html
Whittemore DO, Grieve ER, Young DP, Wilson BB (2005) Water quality in the high plains aquifer and the Cimarron River in seaward and Meade Counties, Kansas. Kansas Geol Sur 1–27. http://www.kgs.ku.edu/HighPlains/OHP/2005_27.pdf
Wu J, Luther GW III (1994) Size-fractionated iron concentrations in the water column of the western North Atlantic Ocean. Am Soc Limnol Oceanogr 39(5):1119–1129
Acknowledgments
We thank the ARPA Department of Pordenone for TOC analyses and the Geology Department of the University of Trieste for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pezzetta, E., Lutman, A., Martinuzzi, I. et al. Iron concentrations in selected groundwater samples from the lower Friulian Plain, northeast Italy: importance of salinity. Environ Earth Sci 62, 377–391 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0533-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0533-3