Abstract
Introduction
Extraction of teeth is followed by resorption of the residual alveolar ridge that continues throughout life resulting in loss of alveolar height and width. Of the numerous techniques that have been used to arrest post extraction alveoloar ridge resorption, the placement of a graft material inside the socket immediately after extraction has been mostly followed. Type 1 collagen is one of the commonly used graft material that prevent resorption by providing dimensional stability to the socket. Bisphosphonates are an anti-osteoclastic drug that prevent resorption by disrupting the membrane ruffling of the osteoclasts. Alendronate a bisphosphonate, is primarily used in diseases with bone loss. It has been used to reduce active bone resorption significantly without interfering with bone mineralization and quality. The need for the study is to examine the inhibitory effect of alendronate on residual ridge resorption when applied locally in combination with type I collagen on alveolar bone immediately following tooth extraction.
Materials and Methods
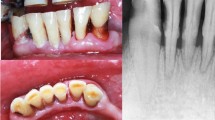
Twenty patients with age between 30 and 65 years were selected from the out patient department of The Oxford Dental College and Hospital. The patients were divided into two groups. In the first group after extraction of teeth from premolar to midline the sockets were irrigated with saline and sutured. On the left side type I collagen sponge was placed and sutured. In the other group the right side was treated the same way after extraction as in first group where as in the left side sockets type I collagen soaked in 20 mg/ml of alendronate was placed and sutured. Patients were evaluated clinically for any local irritation as well as radiologically with orthopantomograph X-rays were taken immediately after the extraction, 1 month after extraction and 4 months after extraction to determine the amount of bone loss prevented.
Results
The statistically significant bone loss prevented by the collagen alone was 22.8 % and in collagen with alendronate group was 44.38 % at the end of 4 months.
Conclusion
Type I collagen soaked with alendronate when placed in the socket immediately after extraction of teeth prevents post-extraction alveolar ridge resorption.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altundal H, Guvener O (2004) The effect of alendronate on resorption of the alveolar bone following tooth extraction. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 33:286–293
Sowmya NK, Tarun Kumar AB, Mehta DS (2010) Clinical evaluation of regenerative potential of type I collagen membrane along with xenogenic bone graft in the treatment of periodontal intrabony defects assessed with surgical re-entry and radiographic linear and densitometric analysis. J Indian Soc Periodontol 14(1):23–29
Knezovic-Zlataric D, Celebic A, Lazic B (2002) Resorptive changes of maxillary and mandibular bone structures in removable denture wearers. Acta Stomat Croat 36:261–265
Wong RWK, Rabie ABM (2003) Statin collagen grafts used to repair defects in the parietal bone of rabbits. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 41:244–248
Kaynak Deniz, Meffert Roland, Günhan Meral, Günhan Ömer, Özkaya Özay (2000) A histopathological investigation on the effects of the bisphosphonate alendronate on resorptive phase following mucoperiosteal flap surgery in the mandible of rats. J Periodontol 71:790–796
Binderman I, Adut M, Yaffe A (2000) Effectiveness of local delivery of alendronate in reducing alveolar bone loss following periodontal surgery in rats. J Periodontol 71:1236–1240
Yaffe A, Golomb G, Breuer E, Binderman I (2000) The effect of topical delivery of novel bisacylphosphonates in reducing alveolar bone loss in the rat model. J Periodontol 71:1607–1612
Yaffe A, Herman A, Bahar H, Binderman I (2003) Combined local application of tetracycline and bisphosphonate reduces alveolar bone resorption in rats. J Periodontal 74:1038–1042
Monjo M, Rubert M, Wohlfahrt JC, Ronolt HJ, Ellingsen JE, Lyngstadaas SP (2008) In vivo performance of absorbable collagen sponges with rosuvastatin in critical-size cortical bone defects. Acta Biomater 6(4):1405–1412
Spolidorio LC, Marcantonio E Jr, Spolidorio DMP, Nassar CA, Nassar PO, Marcantonio RA, Rossa C Jr (2007) Alendronate therapy in cyclosporine-induced alveolar bone loss in rats. J Periodont Res 42:466–473
Huges DE, Macdonald BR, Russel RGG, Gowen M (1989) Inhibition of osteoclast like cell formation by bisphosphonates in long term cultures of human bone marrow. 83: 1930–1935
AAOMS Position Paper (2007) American association of oral and maxillofacial surgeons position paper on bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65:369–376
Jeal W, Barradell LB, Mctavish D (1997) Alendronate: a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Drugs Mar 53(3):415–434
Rodan GA, Fleisch HA (1996) Bisphosphonates: mechanism of action. J Clin Invest 97(12):2692–2696
Rogers MJ, Frith JC, Luckman SP, Coxon FP, Benford HL, Monkkonen J, Auriola S, Chilton KM, Russell RGG (1999) Molecular mechanism of action of bisphosphonates. Bone 24(5 Supplement):73S–79S
Sato M, Grazer W, Endo N, Akins R, Simmons H, Thompson DD, Golub E, Rodan GA (1991) Bisphosphonate action: alendronate localization in rat bone and effects on osteoclast ultrastructure. J. Clin. Invest 88:2095–2105
Yaffe A, Iztkovich M, Earon Y, Alt I, Lilov R, Binderman I (1997) Local delivery of an amino bisphosphonate prevents the resorptive phase of alveolar bone following mucoperiosteal flap surgery in rats. J Periodontol 68:884–889
Yaffe A, Binderman I, Breuer E, Pinto T, Golomb G (1999) Disposition of alendronate following local delivery in a rat jaw. J Periodontol 70:893–895
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix



Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Sarkar, A., Singhvi, N., Shetty, J.N. et al. The Local Effect of Alendronate with Intra-alveolar Collagen Sponges on Post Extraction Alveolar ridge Resorption: A Clinical Trial. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 14, 344–356 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-014-0633-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-014-0633-9