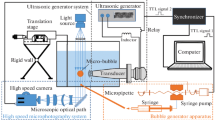
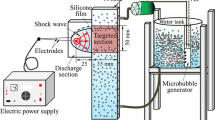
Abstract
This paper reports the observation and analysis of the microbubble motion induced by an underwater shock wave. In the analysis, Herring’s bubble motion equation was numerically solved using an experimental shock wave pressure profile. The pressure attenuation of the rebound shock wave of a microbubble was also estimated by numerical simulation. The motion behaviors of the microbubbles during their interaction with an electric discharge shock wave, such as their rebound, shock wave generation, and microjet formation, were observed by magnified visualization. To improve the observation accuracy, spatial positioning control of the microbubbles was employed. The experimentally determined time variation of the diameter of the microbubbles when they collapsed spherically was in agreement with the results of the numerical analyses, and the latter also revealed a very high pressure of the rebound shock wave. There were, however, discrepancies between the experimental and analytical results for non-spherical collapse. It is thought that spherical collapse produces stronger rebound shock waves and that the probability of such collapse increases with decreasing diameter of the bubble. In addition, it was demonstrated that single and multiple microbubbles moved vigorously after interaction with a shock wave and the latter coalesced into a single bubble within several hundred microseconds.
Graphical Abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe A, Kanai K, Mimura H, Nishio S, Ishida H ( 2007) Study on application of shock waves generated by micro bubbles to the treatment of ships’ ballast water. In: Proceedings 26th international symposium on shock wave. pp 869–874
Abe A, Mimura H (2013) Sterilization of ships’ ballast water, Chapter 11 of bubble dynamics and shock waves. In: Delale CF (ed) Shock wave science and technology reference library. vol 8. Springer, New York, pp 339–362
Class NK (2014) Latest information of approval of ballast water management system
Ding Z, Gracewski SM (1996) The behavior of a gas cavity impacted by a weak or strong shock wave. J Fluid Mech 309:183–209
Fukuda S, Wan B, Abe A (2012) Analytical estimation of microbubble motion exposed to discontinuous pressure change. In: Proceedings 28th international symposium on shock waves, Part 12, pp 909–914
Harten A (1985) Implicit total variation diminishing (TVD) schemes for steady-state calculations. J Comput Phys 57:327–360
Herring C (1941) Theory of the pulsations of the gas bubble produced by an underwater explosion. OSRD, Rep. 236
International Maritime Organization (2004) International convention for the control and management of ships’ ballast water and sediments
Maeno S, Wang J, Fukuda S, Abe A (2013) Observation and analysis of microbubble motion induced by an under water shock wave, 29th international symposium on shock waves, No. 0246-000026
Wolfrum B, Kurz T, Mettin R, Lauterborn W (2003) Shock wave induced interaction of microbubbles and boundaries. Phys Fluids 15(10):2916–2922
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by JSPS KAKENHI (Grant Numbers 22360367 and 25630405). The authors would like to express their gratitude to Messrs. Satoshi Matsumura and Akira Hirami of Nac Inc., Messrs. Takaaki Mizushima and Hiroyuki Usui of Nobby Tech. Ltd., and Mr. Katsuhiro Takayama of Photoron Co. for their technical assistance in the visualization processes of the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abe, A., Wang, J., Shioda, M. et al. Observation and analysis of interactive phenomena between microbubbles and underwater shock wave. J Vis 18, 437–447 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-014-0257-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-014-0257-7