Abstract
Purpose
The objective of the present study was to valorize the tiger tooth croaker (Otolithes ruber) fish head waste for the extraction of high value protein based component ‘gelatin’.
Methods
Gel strength, gelling and melting point and setting time, viscosity, turbidity, colour, emulsion activity and stability index and SDS–PAGE technique.
Results
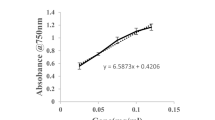
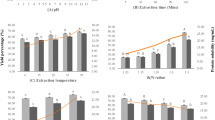
The gel strength of extracted croaker fish head waste gelatin was 45 g and had lower gelling (11 °C) and melting temperature (20.25 °C) and took more time (366 s) to gel at 11 °C compared to standard porcine gelatin of low bloom category. Colour analysis revealed that the whiteness and redness intensity of fish head waste gelatin were lower than the porcine gelatin. However, there was no significant difference in yellowness value between fish head waste gelatin prepared and porcine gelatin. The emulsion activity index of fish head waste gelatin decreased with increase in protein concentration. The SDS–PAGE analysis showed the presence of α-component and multiple low molecular weight peptides up to 45 kDa.
Conclusion
Croaker fish head waste could be utilized for extraction of gelatin of low bloom category. Appropriate changes could be incorporated in the process to obtain gelatin with higher gel strength.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
He, S., Franco, C., Zhang, W.: Process optimisation and physicochemical characterisation of enzymatic hydrolysates of proteins from co-products of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and Yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 47, 2397–2404 (2012)
Ruthu, Murthy, P.S., Rai, A.K., Bhaskar, N.: Fermentative recovery of lipids and proteins from freshwater fish head waste with reference to antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of protein hydrolysate. J. Food Sci. Technol. 51, 1884–1892 (2014)
Kasankala, L.M., Xue, Y., Weilong, Y., Hong, S.D., He, Q.: Optimization of gelatine extraction from grass carp (Catenopharyngodon idella) fish skin by response surface methodology. Bioresour. Technol. 98, 3338–3343 (2007)
Arnesen, J.A., Gildberg, A.: Extraction of muscle proteins and gelatine from cod head. Process Biochem. 41, 697–700 (2006)
Kołodziejska, I., Skierka, E., Sadowska, M., Kołodziejski, W., Niecikowska, C.: Effect of extracting time and temperature on yield of gelatin from different fish offal. Food Chem. 107, 700–706 (2008)
Ninan, G., Zynudheen, A.A.: Evaluation of quality and shelf life of two commercially important fish species viz., tiger tooth croaker (Otolithes ruber Bloch and Schneider) and flathead grey mullet (Mugil cephalus Linnaeus) in iced conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 84, 1035–1042 (2014)
AOAC: Official Methods of Analysis, 17th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington (2000)
BSI (British Standard Institution): Methods for sampling and testing gelatin. In: Physical and Chemical Methods. BSI, BS 757, London (1975)
Ninan, G., Joseph, J., Aliyamveettil, Z.A.: A comparative study on the physical, chemical and functional properties of carp skin and mammalian gelatins. J. Food Sci. Technol. 51, 2085–2091 (2014)
Cho, S.H., Jahncke, M.L., Chin, K.B., Eun, J.B.: The effect of processing conditions on the properties of gelatin from skate (Raja kenojei) skins. Food Hydrocoll. 20, 810–816 (2006)
Laemmli, U.K.: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 680–685 (1970)
Pearce, K.N., Kinsella, J.E.: Emulsifying properties of proteins: evaluation of a turbidimetric technique. J. Agric. Food Chem. 26, 716–723 (1978)
Zynudheen, A.A.: Utilization of fishery waste in India. In: Manual Prepared for the Awareness-Cum-Interactive Workshop on ‘Antibiotic, Pesticide and Insecticide Residue Contamination in Sea/Aqua Foods’ Organized by the Visakhapatnam Research Centre of Central Institute of Fisheries Technology on 6th Sept 2010 at Visakhapatnam, pp. 96–109 (2010)
Ghaly, A.E., Ramakrishnan, V.V., Brooks, M.S., Budge, S.M., Dave, D.: Fish processing wastes as a potential source of proteins, amino acids and oils: a critical review. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 5, 107–129 (2013)
Liu, H.Y., Han, J., Guo, S.D.: Characteristics of the gelatin extracted from Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) head bones. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 42, 540–544 (2009)
Ramakrishnan, V.V., Ghaly, A.E., Brooks, M.S., Budge, S.M.: Extraction of proteins from mackerel fish processing waste using Alcalase enzyme. J. Bioprocess. Biotech. (2013). doi:10.4172/2155-9821.1000130
Arvanitoyannis, I.S., Kassaveti, A.: Fish industry waste: treatments, environmental impacts, current and potential uses. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 43, 726–745 (2008)
Khiari, Z., Rico, D., Martin-Diana, A.B., Barry-Ryan, C.: The extraction of gelatine from mackerel (Scomber scombrus) heads with the use of different organic acids. J. Fish. Sci. Com. 5, 52–63 (2011)
Koli, J.M., Basu, S., Nayak, B.B., Patange, S.B., Pagarkar, A.U., Gudipati, V.: Functional characteristics of gelatin extracted from skin and bone of Tiger-toothed croaker (Otolithes ruber) and Pink perch (Nemipterus japonicus). Food Bioprod. Process. 90, 555–562 (2012)
Wainewright, F.W.: Physical tests for gelatin and gelatin products. In: Ward, A.G., Courts, A. (eds.) The Science and Technology of Gelatin, pp. 507–534. Academic, New York (1977)
Badii, F., Howell, N.K.: Fish gelatin: structure, gelling properties and interaction with egg albumen proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 20, 630–640 (2006)
Leuenberger, B.H.: Investigation of viscosity and gelation properties of different mammalian and fish gelatins. Food Hydrocoll. 5, 353–361 (1991)
Karim, A.A., Bhat, R.: Fish gelatin: properties, challenges, and prospects as an alternative to mammalian gelatins. Food Hydrocoll. 23, 563–576 (2009)
Silva, R.D., Bandeira, S., Petry, F.C., Pinto L.A.: Effect of bone particle size of carp (Cyprinus carpio) heads in gelatin extraction. Repositorio.furg.br (2011)
Choi, S.S., Regenstein, J.M.: Physicochemical and sensory characteristics of fish gelatin. J. Food Sci. 65, 194–199 (2000)
Johnston-Banks, F.A.: Gelatine. In: Harris, P. (ed.) Food Gels, pp. 233–289. Springer, Netherlands (1990)
Lassoued, I., Jridi, M., Nasri, R., Dammak, A., Hajji, M., Nasri, M., Barkia, A.: Characteristics and functional properties of gelatin from thornback ray skin obtained by pepsin-aided process in comparison with commercial halal bovine gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 41, 309–318 (2014)
Silva, R.S., Bandeira, S.F., Pinto, L.A.: Characteristics and chemical composition of skins gelatin from cobia (Rachycentron canadum). LWT Food Sci. Technol. 57, 580–585 (2014)
Muyonga, J.H., Cole, C.G.B., Duodu, K.G.: Extraction and physico-chemical characterisation of Nile perch (Lates niloticus) skin and bone gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 18, 581–592 (2004)
Hailing, P.J., Walstra, P.: Protein stabilized foams and emulsions. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 15, 155–203 (1981)
Ahmad, M., Benjakul, S.: Characteristics of gelatin from the skin of unicorn leatherjacket (Aluterus monoceros) as influenced by acid pretreatment and extraction time. Food Hydrocoll. 25, 381–388 (2011)
Nagarajan, M., Benjakul, S., Prodpran, T., Songtipya, P., Kishimura, H.: Characteristics and functional properties of gelatin from splendid squid (Loligo formosana) skin as affected by extraction temperatures. Food Hydrocoll. 29, 389–397 (2012)
Ktari, N., Jridi, M., Nasri, R., Lassoued, I., Ayed, H.B., Barkia, A., Nasri, M.: Characteristics and functional properties of gelatin from zebra blenny (Salaria basilisca) skin. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 58, 602–608 (2014)
Gómez-Guillén, M.C., Turnay, J., Fernández-Díaz, M.D., Ulmo, N., Lizarbe, M.A., Montero, P.: Structural and physical properties of gelatin extracted from different marine species: a comparative study. Food Hydrocoll. 16, 25–34 (2002)
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Director, ICAR-Central Institute of Fisheries Technology, Cochin, Kerala, India for providing the necessary facilities. The authors also wish to express their gratitude to technical staff of Fish Processing Division for the support given during the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elavarasan, K., Kumar, A., Uchoi, D. et al. Extraction and Characterization of Gelatin from the Head Waste of Tiger Tooth Croaker (Otolithes ruber). Waste Biomass Valor 8, 851–858 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9639-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9639-5