Abstract
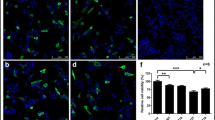
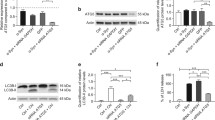
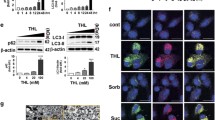
Alpha-synuclein (SNCA) oligomers have been reported to inhibit autophagy. Aminochrome-induced SNCA oligomers are neurotoxic, but the flavoenzyme DT-diaphorase prevents both their formation and their neurotoxicity. However, the possible protective role of DT-diaphorase against autophagy impairment by aminochrome-induced SNCA oligomers remains unclear. To test this idea, we used the cell line RCSN-3NQ7SNCA, with constitutive expression of a siRNA against DT-diaphorase and overexpression SNCA, and RCSN-3 as control cells. A significant increase in LC3-II expression was observed in RCSN-3 cells treated with 20 μM aminochrome and 10 μM rapamycin followed by a decrease in cell death compared to RCSN-3 cells incubated with 20 μM aminochrome alone. The incubation of RCSN-3NQ7SNCA cells with 20 μM aminochrome and 10 μM rapamycin does not change the expression of LC3-II in comparison with RCSN-3NQ7SNCA cells incubated with 20 μM aminochrome alone. The incubation of both cell lines preincubated with 100 nM bafilomycin and 20 μM aminochrome increases the level of LC3-II. Under the same conditions, cell death increases in both cell lines in comparison with cells incubated with 20 μM aminochrome. These results support the protective role of DT-diaphorase against SNCA oligomers-induced autophagy inhibition.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeliovich A, Schmitz Y, Farinas I, Choi-Lundberg D, Ho W, Castillo P, Shinsky N, Verdugo J, Armanini M, Ryan A et al (2000) Mice lacking α-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron 25:239–252
Arriagada C, Paris I, Sanchez de las Matas M, Martinez-Alvarado P, Cardenas S, Castaneda P, Graumann R, Perez-Pastene C, Olea-Azar C, Couve E (2004) On the neurotoxicity mechanism of leukoaminochrome o-semiquinone radical derived from dopamine oxidation: mitochondria damage, necrosis, and hydroxyl radical formation. Neurobiol Dis 16:468–477
Bellucci A, Zaltieri M, Navarria L, Grigoletto J, Missale C, Spano P (2012) From α-synuclein to synaptic dysfunctions: new insights into the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 1476:183–202
Bisaglia M, Mammi S, Bubacco L (2007) Kinetic and structural analysis of the early oxidation products of dopamine: analysis of the interactions with alpha-synuclein. J Biol Chem 282(21):15597–15605
Bisaglia M, Tosatto L, Munari F, Tessari I, de Laureto PP, Mammi S, Bubacco L (2010) Dopamine quinones interact with alpha-synuclein to form unstructured adducts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 394(2):424–428
Clayton DF, George JM (1998) The synucleins: a family of proteins involved in synaptic function, plasticity, neurodegeneration and disease. Trends Neurosci 21(6):249–254
Conway K, Rochet J, Bieganski R, Lansbury P (2001) Kinetic stabilization of the alpha-synuclein protofibril by a dopamine-alpha-synuclein adduct. Science 294:1346–1349
Crews L, Spencer B, Desplats P, Patrick C, Paulino A, Rockenstein E, Hansen L, Adame A, Galasko D, Masliah E (2010) Selective molecular alterations in the autophagy pathway in patients with Lewy body disease and in models of α-synucleinopathy. PLoS One 5(e):9313
Cuervo AM (2008) Autophagy and aging: keeping that old broom working. Trends Genet 24(12):604–12. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2008.10.002
Cuervo A, Stefanis L, Fredenburg R, Lansbury P, Sulzer D (2004) Impaired degradation of mutant alpha-synuclein by chaperonemediated autophagy. Science 305:1292–1295
Domert J, Sackmann C, Severinsson E, Agholme L, Bergström J, Ingelsson M, Hallbeck M (2016) Aggregated alpha-synuclein transfer efficiently between cultured human neuron-like cells and localize to lysosomes. PLoS One 11(12):e0168700. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0168700
Ebrahimi-Fakhari D, Cantuti-Castelvetri I, Fan Z, Rockenstein E, Masliah E, Hyman B, McLean P, Unni V (2011) Distinct roles in vivo for the ubiquitin-proteasome system and the autophagy-lysosomal pathway in the degradation of α-synuclein. J Neurosci 31:14508–14520
El-Agnaf OM, Jakes R, Curran MD, Middleton D, Ingenito R, Bianchi E, Pessi A, Neill D, Wallace A (1998) Aggregates from mutant and wild-type alpha-synuclein proteins and NAC peptide induce apoptotic cell death in human neuroblastoma cells by formation of beta-sheet and amyloid-like filaments. FEBS Lett 440(1–2):71–75
Emamzadeh FN (2016) Alpha-synuclein structure, functions, and interactions. J Res Med Sci 21:29
Emmanouilidou E, Stefanis L, Vekrellis K (2010) Cell-produced α-synuclein oligomers are targeted to, and impair, the 26S proteasome. Neurobiol Aging 31:953–968
George JM (2002) The synucleins. Genome Biol 3(1):REVIEWS3002
Giasson BI, Murray IV, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2001) A hydrophobic stretch of 12 amino acid residues in the middle of alpha-synuclein is essential for filament assembly. J Biol Chem 276(4):2380–2386
Gruden MA, Davydova TV, Narkevich VB, Fomina VG, Wang C, Kudrin VS, Morozova-Roche LA, Sewell RD (2014) Intranasal administration of alpha-synuclein aggregates: a Parkinson’s disease model with behavioural and neurochemical correlates. Behav Brain Res 263:158–168
Herrera A, Muñoz P, Steinbusch HW, Segura-Aguilar J (2017) Are dopamine oxidation metabolites involved in the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the nigrostriatal system in Parkinson’s disease? ACS Chem Neurosci. doi:10.1021/ acschemneuro.7b00034
Huenchuguala S, Muñoz P, Zavala P, Villa M, Cuevas C, Ahumada U, Graumann R, Nore B, Couve E, Mannervik B et al (2014) Glutathione transferase mu 2 protects glioblastoma cells against aminochrome toxicity by preventing autophagy and lysosome dysfunction. Autophagy 10:618–630
Ingelsson M (2016) Alpha-synuclein oligomers-neurotoxic molecules in Parkinson’s disease and other Lewy body disorders. Front Neurosci 10:408
Klionsky DJ, Abdelmohsen K, Abe A, Abedin MJ (2016) Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy 12:1–222
Lashuel HA, Hartley D, Petre BM, Walz T, Lansbury PT Jr (2002) Neurodegenerative disease: amyloid pores from pathogenic mutations. Nature 418, 291
Liu C, Corboy M, DeMartino G, Thomas P (2003) Endoproteolytic activity of the proteasome. Science 299:408–411
Lozano J, MuÑoz P, Nore B, Ledoux S, Segura-Aguilar J (2010) Stable expression of short interfering RNA for DTdiaphorase induces neurotoxicity. Chem Res Toxicol 23:1492–1496
Mak S, McCormack A, Manning-Bog A, Cuervo A, Di Monte D (2010) Lysosomal degradation of α-synuclein in vivo. J Biol Chem 285:13621–13629
Masliah E, Rockenstein E, Adame A, Alford M, Crews L, Hashimoto M, Seubert P, Lee M, Goldstein J, Chilcote T, Games D, Schenk D (2005) Effects of alpha-synuclein immunization in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuron 46:857–868
Muñoz P, Paris I, Sanders LH, Greenamyre JT, Segura-Aguilar J (2012) Overexpression of VMAT-2 and DT-diaphorase protects substantia nigra-derived cells against aminochrome neurotoxicity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822:1125–1136
Muñoz P, Cardenas S, Huenchuguala S, Briceño A, Couve E, Paris I, Segura-Aguilar J (2015) DT-diaphorase prevents aminochrome-induced alpha-synuclein oligomer formation and neurotoxicity. Toxicol Sci 145(1):37–47
Nakamura K, Nemani V, Wallender E, Kaehlcke K, Ott M, Edwards R (2008) Optical reporters for the conformation of α-synuclein reveal a specific interaction with mitochondria. J Neurosci 28:12305–12317
Norris E, Giasson B, Hodara R, Xu S, Trojanowski J, Ischiropoulos H, Lee V (2005) Reversible inhibition of alpha-synuclein fibrillization by dopaminochrome-mediated conformational alterations. J Biol Chem 280:21212–21219
Ottolini D, Calí T, Szabò I, Brini M (2017) Alpha-synuclein at the intracellular and the extracellular side: functional and dysfunctional implications. Biol Chem 398(1):77–100
Paris I, Lozano J, Cardenas S, Perez-Pastene C, Saud K, Fuentes P, Caviedes P, Dagnino-Subiabre A, RaismanVozari R, Shimahara T (2008) The catecholaminergic RCSN-3 cell line: a model to study dopamine metabolism. Neurotox Res 13:221–230
Paris I, Perez-Pastene C, Cardenas S, Iturriaga-Vasquez P, Muñoz P, Couve E, Caviedes P, Segura-Aguilar J (2010) Aminochrome induces disruption of actin, alpha-, and beta-tubulin cytoskeleton networks in substantia-nigra-derived cell line. Neurotox Res 18:82–92
Paris I, Muñoz P, Huenchuguala S, Couve E, Sanders LH, Greenamyre JT, Caviedes P, Segura-Aguilar J (2011) Autophagy protects against aminochrome-induced cell death in substantia nigra-derived cell line. Toxicol Sci 121:376–388
Petrucci S, Ginevrino M, Valente EM (2016) Phenotypic spectrum of alpha-synuclein mutations: new insights from patients and cellular models. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 22(Suppl 1):S16–S20
Segura-Aguilar J, Paris I, Muñoz P, Ferrari E, Zecca L, Zucca F (2014) Protective and toxic roles of dopamine in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 129:898–915
Segura-Aguilar J, Muñoz P, Paris I (2016) Aminochrome as new preclinical model to find new pharmacological treatment that stop the development of Parkinson’s disease. Curr Med Chem 23:346–359
Spillantini M, Crowther R, Jakes R, Hasegawa M, Goedert M (1998) Alpha-synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:6469–6473
Ulmer TS, Bax A (2005) Comparison of structure and dynamics of micelle-bound human alpha-synuclein and Parkinson disease variants. J Biol Chem 280(52):43179–43187
Van Laar V, Mishizen A, Cascio M, Hastings T (2009) Proteomic identification of dopamine-conjugated proteins from isolated rat brain mitochondria and SH-SY5Y cells. Neurobiol Dis 34:487–500
Volles M, And Lansbury P (2003) Zeroing in on the pathogenic form of alpha-synuclein and its mechanism of neurotoxicity in Parkinson’s disease. Biochemistry 42:7871–7878
Xilouri M, Brekk O, Stefanis L (2013) Alpha-synuclein and protein degradation systems: a reciprocal relationship. Mol Neurobiol 47:537–551
Xu Y, Stokes A, Roskoski R, Vrana K (1998) Dopamine in the presence of tyrosinase covalently modifies and inactivates tyrosinase hydroxylase. J Neurosci Res 54:691–697
Yu W, Dorado B, Figueroa H, Wang L, Planel E, Cookson M, Clark L, Duff K (2009) Metabolic activity determines efficacy of macroautophagic clearance of pathological oligomeric α-synuclein. Am J Pathol 175:736–747
Zafar KS, Siegel D, Ross D (2006) A potential role for cyclized quinones derived from dopamine, DOPA, and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid in proteasomal inhibition. Mol Pharmacol 70:1079–1086
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by FONDECYT # 1100165. RCSN-3 cells are made available by P. Caviedes upon request (pcaviede@med.uchile.cl).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muñoz, P.S., Segura-Aguilar, J. DT-diaphorase Protects Against Autophagy Induced by Aminochrome-Dependent Alpha-Synuclein Oligomers. Neurotox Res 32, 362–367 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-017-9747-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-017-9747-4