Abstract
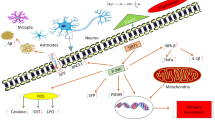
The development of agents that affect two or more relevant targets has drawn considerable attention in treatment of AD. Diallyl disulfide (DADS), an active principle of garlic, has been reported to prevent APP processing by amyloidogenic pathway. Recently, we have reported a new series of DADS derivatives and our findings revealed that compound 7k and 7l could provide good templates for developing new multifunctional agents for AD treatment. Thus, the present study was constructed to investigate the neuroprotective effect of DADS analogues (7k and 7l) against Aβ-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells and in ameliorating the cognition deficit induced by scopolamine in rat model. The results indicated that compound 7k and 7l significantly inhibited Aβ1–42-induced neuronal cell death by inhibiting ROS generation. Moreover, they prevented apoptosis, in response to ROS, by restoring normal Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. Furthermore, it was observed that scopolamine-induced memory impairment was coupled by alterations in neurotransmitters, acetylcholinesterase activity and oxidative stress markers. Histological analysis revealed severe damaging effects of scopolamine on the structure of cerebral cortex and hippocampus. Administration of compounds 7k and 7l at 5 mg/kg significantly reversed scopolamine-induced behavioural, biochemical, neurochemical and histological changes in a manner comparable to standard donepezil. Together the present findings and previous studies indicate that compounds 7k and 7l have neuroprotective and cognition-enhancing effects, which makes them a promising multi-target candidate for addressing the complex nature of AD.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anandatheerthavarada HK, Biswas G, Robin M-A, Avadhani NG (2003) Mitochondrial targeting and a novel transmembrane arrest of Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein impairs mitochondrial function in neuronal cells. J Cell Biol 161(1):41–54
Bartus RT (2000) On neurodegenerative diseases, models, and treatment strategies: lessons learned and lessons forgotten a generation following the cholinergic hypothesis. Exp Neurol 163(2):495–529
Behl C, Davis J, Cole GM, Schubert D (1992) Vitamin E protects nerve cells from amyloid β protein toxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 186(2):944–950
Bihaqi SW, Singh AP, Tiwari M (2012) Supplementation of Convolvulus pluricaulis attenuates scopolamine-induced increased tau and Amyloid precursor protein (AβPP) expression in rat brain. Indian J Pharmacol 44(5):593
Blake M, Krawczyk M, Baratti Boccia M (2014) Neuropharmacology of memory consolidation and reconsolidation: insights on central cholinergic mechanisms. J Physiol Paris 108(4):286–291
Blokland A, Schreiber R, Prickaerts J (2006) Improving memory: a role for phosphodiesterases. Curr Pharm Des 12(20):2511–2523
Boldogh I, Kruzel ML, Colostrinin TM (2008) An oxidative stress modulator for prevention and treatment of age-related disorders. J Alzheimer’s Dis 13:303–321
Bores GM, Huger FP, Petko W, Mutlib AE, Camacho F, Rush DK, Selk DE, Wolf V, Kosley R, Davis L (1996) Pharmacological evaluation of novel Alzheimer’s disease therapeutics: acetylcholinesterase inhibitors related to galanthamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 277(2):728–738
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1):248–254
Buckingham SD, Jones AK, Brown LA, Sattelle DB (2009) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor signalling: roles in Alzheimer’s disease and amyloid neuroprotection. Pharmacol Rev 61(1):39–61
Canal CE, Chang Q, Gold PE (2007) Amnesia produced by altered release of neurotransmitters after intraamygdala injections of a protein synthesis inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104(30):12500–12505
Castellano C, Cabib S, Puglisi-Allegra S (1996) Psychopharmacology of memory modulation: evidence for multiple interaction among neurotransmitters and hormones. Behav Brain Res 77(1):1–21
Cavalli A, Bolognesi ML, Minarini A, Rosini M, Tumiatti V, Recanatini M, Melchiorre C (2008) Multi-target-directed ligands to combat neurodegenerative diseases. J Med Chem 51(3):347–372
Cecchi C, Fiorillo C, Baglioni S, Pensalfini A, Bagnoli S, Nacmias B, Sorbi S, Nosi D, Relini A, Liguri G (2007) Increased susceptibility to amyloid toxicity in familial Alzheimer’s fibroblasts. Neurobiol Aging 28(6):863–876
Chen J, Long Y, Han M, Wang T, Chen Q, Wang R (2008) Water-soluble derivative of propolis mitigates scopolamine-induced learning and memory impairment in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 90(3):441–446
Choi DY, Lee YJ, Lee SY, Lee YM, Lee HH, Choi IS, Oh KW, Han SB, Nam SY, Hong JT, (2012) Attenuation of scopolamine-induced cognitive dysfunction by obovatol. Arch Pharm Res 35(7):1279–1286
Chyan Y-J, Poeggeler B, Omar RA, Chain DG, Frangione B, Ghiso J, Pappolla MA (1999) Potent neuroprotective properties against the Alzheimer β-amyloid by an endogenous melatonin-related indole structure, indole-3-propionic acid. J Biol Chem 274(31):21937–21942
Cummings JL, Doody R, Clark C (2007) Disease-modifying therapies for Alzheimer disease challenges to early intervention. Neurology 69(16):1622–1634
Dringen R, Gutterer JM, Hirrlinger J (2000) Glutathione metabolism in brain. Eur J Biochem 267(16):4912–4916
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7(2):88–95
Flohé L, Günzler WA (1984) Assays of glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol 105(1):14–120
Fukui K, Omoi NO, Hayasaka T, Shinnkai T, Suzuki S, Abe K, Urano S (2002) Cognitive impairment of rats caused by oxidative stress and aging, and its prevention by vitamin E. Ann NY Acad Sci 959(1):275–284
Giacobini E (1998) Cholinergic foundations of Alzheimer’s disease therapy. J Physiol Paris 92(3):283–287
Giacobini E (2002) Long-term stabilizing effect of cholinesterase inhibitors in the therapy of Alzheimer’disease. J Neural Transm Suppl 62:181–187
Giridharan VV, Thandavarayan RA, Konishi T (2011) Amelioration of scopolamine induced cognitive dysfunction and oxidative stress by Inonotus obliquus–a medicinal mushroom. Food Funct 2(6):320–327
Gupta VB, Indi SS, Rao KSJ (2009) Garlic extract exhibits antiamyloidogenic activity on amyloid‐beta fibrillogenesis: relevance to Alzheimer's disease. Phytother Res 23(1):111–115
Hensley K, Hall N, Subramaniam R, Cole P, Harris M, Aksenov M, Aksenova M, Gabbita SP, Wu JF, Carney JM (1995) Brain regional correspondence between Alzheimer’s disease histopathology and biomarkers of protein oxidation. J Neurochem 65(5):2146–2156
Huber SJ, Shulman HG, Paulson GW, Shuttleworth EC (1989) Dose-dependent memory impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 39(3):438
Iversen SD (1998) The pharmacology of memory. Comptes Rendus de l’Académie des Sciences-Series III-Sciences de la Vie 321(2):209–215
Jollow D, Mitchell J, Zampaglione NA, Gillette J (1974) Bromobenzene-induced liver necrosis. Protective role of glutathione and evidence for 3,4-bromobenzene oxide as the hepatotoxic metabolite. Pharmacology 11(3):151–169
Khatri M, Rai SK, Alam S, Vij A, Tiwari M (2009) Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of new arylpiperazines N-[4-[4-(aryl) piperazine-1-yl]-phenyl]-amine derivatives: putative role of 5-HT1A receptors. Bioorg Med Chem 17(5):1890–1897
Leuner K, Müller WE, Reichert AS (2012) From mitochondrial dysfunction to amyloid beta formation: novel insights into the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 46(1):186–193
Levine RL, Garland D, Oliver CN, Amici A, Climent I, Lenz A-G, Ahn B-W, Shaltiel S, Stadtman ER (1990) Determination of carbonyl content in oxidatively modified proteins. Methods Enzymol 186:464–478
Li S-Y, Wang X-B, Xie S-S, Jiang N, Wang KD, Yao H-Q, Sun H-B, Kong L-Y (2013) Multifunctional tacrine–flavonoid hybrids with cholinergic, β-amyloid-reducing, and metal chelating properties for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Med Chem 69:632–646
Liang K, McGaugh JL, Yao H-Y (1990) Involvement of amygdala pathways in the influence of post-training intra-amygdala norepinephrine and peripheral epinephrine on memory storage. Brain Res 508(2):225–233
Liu T, Xia Z, Zhang W-W, Xu J-R, Ge X-X, Li J, Cui Y, Qiu Z-B, Xu J, Xie Q (2013) Bis (9)-(−)-nor-meptazinol as a novel dual-binding AChEI potently ameliorates scopolamine-induced cognitive deficits in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 104:138–143
Loizzo MR, Tundis R, Menichini F, Menichini F (2008) Natural products and their derivatives as cholinesterase inhibitors in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders: an update. Curr Med Chem 15(12):1209-1228
Loo DT, Copani A, Pike CJ, Whittemore ER, Walencewicz AJ, Cotman CW (1993) Apoptosis is induced by beta-amyloid in cultured central nervous system neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90(17):7951–7955
Manral A, Saini V, Meena P, Tiwari M (2015) Multifunctional novel diallyl disulfide (DADS) derivatives with β-amyloid-reducing, cholinergic, antioxidant and metal chelating properties for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg Med Chem 23(19):6389–6403
Meister A (1988) Glutathione metabolism and its selective modification. J Biol Chem 263(33):17205–17208
Melo JB, Agostinho P, Oliveira CR (2003) Involvement of oxidative stress in the enhancement of acetylcholinesterase activity induced by amyloid beta-peptide. Neurosci Res 45(1):117–127
Morgan D, Munireddy S, Alamed J, DeLeon J, Diamond DM, Bickford P, Hutton M, Lewis J, McGowan E, Gordon MN (2008) Apparent behavioral benefits of tau overexpression in P301L tau transgenic mice. J Alzheimer’s Dis JAD 15(4):605
Morice E, Billard J-M, Denis C, Mathieu F, Betancur C, Epelbaum J, Giros B, Nosten-Bertrand M (2007) Parallel loss of hippocampal LTD and cognitive flexibility in a genetic model of hyperdopaminergia. Neuropsychopharmacology 32(10):2108–2116
Nalini K, Karanth K, Rao A, Aroor A (1992) Effects of piracetam on retention and biogenic amine turnover in albino rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 42(4):859–864
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95(2):351–358
Pachauri SD, Tota S, Khandelwal K, Verma P, Nath C, Hanif K, Shukla R, Saxena J, Dwivedi AK (2012) Protective effect of fruits of Morinda citrifolia L. on scopolamine induced memory impairment in mice: a behavioral, biochemical and cerebral blood flow study. J Ethnopharmacol 139(1):34–41
Park CH, Lee YJ, Lee SH, Choi SH, Kim HS, Jeong SJ, Kim SS, Suh YH (2000) Dehydroevodiamine· HCl prevents impairment of learning and memory and neuronal loss in rat models of cognitive disturbance. J Neurochem 74(1):244–253
Pepeu G, Giovannini MG, Bracco L (2013) Effect of cholinesterase inhibitors on attention. Chem Biol Interact 203(1):361–364
Pollack SJ, Sadlerl IJ, Hawtin SR, Tailor VJ, Shearman MS (1995) Sulfated glycosammnoglycans and dyes attenuate the neurotoxic effects of β-amyloid in rat PC12 cells. Neurosci Lett 184:113–116
Rai SK, Sharma M, Tiwari M (2009) Inhibitory effect of novel diallyldisulfide analogs on HMG-CoA reductase expression in hypercholesterolemic rats: CREB as a potential upstream target. Life Sci 85(5):211–219
Schlumpf M, Lichtensteiger W, Langemann H, Waser PG, Hefti F (1974) A fluorometric micromethod for the simultaneous determination of serotonin, noradrenaline and dopamine in milligram amounts of brain tissue. Biochem Pharmacol 23(17):2437–2446
Selkoe DJ (2001) Clearing the brain's amyloid cobwebs. Neuron 32(2):177–180
Serrano-Pozo A, Frosch MP, Masliah E, Hyman BT (2011) Neuropathological alterations in Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Med 1(1):a006189
Sharma M, Tiwari M, Chandra R (2004) Bis [3-(4′-substituted phenyl)prop-2-ene] disulfides as a new class of antihyperlipidemic compounds. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14(21):5347–5350
Sharma DK, Manral A, Saini V, Singh A, Srinivasan B, Tiwari M (2012) Novel diallyldisulfide analogs ameliorate cardiovascular remodeling in rats with L-NAME-induced hypertension. Eur J Pharmacol 691(1):198–208
Smith IK, Vierheller TL, Thorne CA (1988) Assay of glutathione reductase in crude tissue homogenates using 5,5′-dithiobis (2-nitrobenzoic acid). Anal Biochem 175(2):408–413
Steele T, Hodges D, Levesque T, Locke K, Sandage B (1996) The D1 agonist dihydrexidine releases acetylcholine and improves cognition in rats. Ann NY Acad Sci 777(1):427–430
Stone WS, Croul CE, Gold PE (1988) Attenuation of scopolamine-induced amnesia in mice. Psychopharmacology 96(3):417–420
Sugaya K, Giacobini E, Chiappinelli V (1990) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes in human frontal cortex: changes in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci Res 27(3):349–359
The Organisation of Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) The OECD Guideline for Testing of Chemical (2001) 407 repeated dose oral toxicity-rodent: 28-day or 14-day study. OECD, Paris, pp 1–7
Tuppo EE, Arias HR (2005) The role of inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37(2):289–305
Vasudevan M, Parle M (2006) Pharmacological actions of Thespesia populnea relevant to Alzheimer’s disease. Phytomedicine 13(9):677–687
Vizi ES, Harsing LG, Zimanvi I, Gaal G (1985) Release and turnover of noradrenaline in isolated median eminence: lack of negative feedback modulation. Neurosci 16(4):907–916
Walton NM, Shin R, Tajinda K, Heusner CL, Kogan JH, Miyake S, Chen Q, Tamura K, Matsumoto M (2012) Adult neurogenesis transiently generates oxidative stress. PLoS One 7(4):e35264
Wang R-G, Zhu X-Z (2003) Subtoxic concentration of manganese synergistically potentiates 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. Brain Res 961(1):131–138
Wang X, Wang Z-H, Wu Y-Y, Tang H, Tan L, Wang X, Gao X-Y, Xiong Y-S, Liu D, Wang J-Z (2013) Melatonin attenuates scopolamine-induced memory/synaptic disorder by rescuing EPACs/miR-124/Egr1 pathway. Mol Neurobiol 47(1):373–381
Weinstock M (1995) The pharmacotherapy of Alzheimer’s disease based on the cholinergic hypothesis: an update. Neurodegeneration 4(4):349–356
Xia Y, Cheng S, He J, Liu X, Tang Y, Yuan H, He L, Lu T, Tu B, Wang Y (2011) Effects of subchronic exposure to benzo [a] pyrene (B [a] P) on learning and memory, and neurotransmitters in male Sprague–Dawley rat. Neurotoxicology 32(2):188–198
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, Kim CN, Ibrado AM, Cai J, Peng TI, Jones DP, Wang X (1997) Prevention of apoptosis by Bcl-2: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked. Sci 275(5303): 1129–1132
Yu BP, Yang R (1996) Critical evaluation of the free radical theory of aging. Ann Ny Acad Sci 786(1):1–11
Zhou W, Fukumoto S, Yokogoshi H (2009) Components of lemon essential oil attenuate dementia induced by scopolamine. Nutr Neurosci 12(2):57–64
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to gratefully acknowledge scientific contributions from Prof. Vani Brahmachari. Financial assistance from the University of Delhi is acknowledged. The authors gratefully acknowledge Dr. Dipti Prasad, DIPAS, New Delhi, for providing necessary facilities to conduct behavioural experiments. Apra Manral wishes to acknowledge the Senior Research Fellowship awarded by the University Grants Commission—Govt. of India. The facilities provided by ACBR and the University of Delhi are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manral, A., Meena, P., Saini, V. et al. DADS Analogues Ameliorated the Cognitive Impairments of Alzheimer-Like Rat Model Induced by Scopolamine. Neurotox Res 30, 407–426 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-016-9625-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-016-9625-5