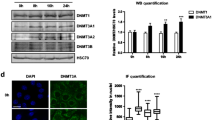
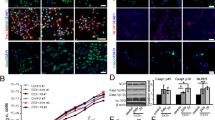
Abstract
Chronic alcohol consumption may cause neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders. Alcohol neurotoxicity is associated with the production of acetaldehyde and reactive oxygen species that induce oxidative DNA damage. However, the molecular mechanisms by which ethanol disturbs the DNA damage response (DDR), resulting in a defective DNA repair, remain unknown. Here, we have used cultured primary cortical neurons exposed to 50 or 100 mM ethanol for 7 days to analyze the ethanol-induced DDR. Ethanol exposure produced a dose-dependent generation of double strand breaks and the formation of DNA damage foci immunoreactive for the histone γH2AX, a DNA damage marker, and for the ubiquitylated H2A, which is involved in chromatin remodeling at DNA damage sites. Importantly, these DNA damage foci failed to recruit the protein 53BP1, a crucial DNA repair factor. This effect was associated with a drop in 53BP1 mRNA and protein levels and with an inhibition of global transcription. Moreover, ethanol-exposed neurons treated with ionizing radiation (2 Gy) also failed to recruit 53BP1 at DNA damage foci and exhibited a greater vulnerability to DNA lesions than irradiated control neurons. Our results support that defective DNA repair, mediated by the deficient expression and recruitment of 53BP1 to DNA damage sites, represents a novel mechanism involved in ethanol neurotoxicity. The design of therapeutic strategies that increase or stabilize 53BP1 levels might potentially promote DNA repair and partially compensate alcohol neurotoxicity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aschner M, Suñol C, Bal-Price A (2011) Cell Culture Techniques. Humana Press, Neuromethods
Baltanas F, Casafont I, Lafarga V, Weruaga E, Alonso JR, Berciano MT, Lafarga M (2011) Purkinje cell degeneration in pcd mice reveals large scale chromatin reorganization and gene silencing linked to defective DNA repair. J Biol Chem 286:28287–28302
Bothmer A, Robbiani DF, Feidahn N, Gazumyan A, Nussenzweig A, Nussenzweig MC (2010) 53PB1 regulates DNA resection and the choice between classical and alternative end joining during class switch recombination. J Exp Med 207:855–865
Callen E, di Virgilio M, Kruhlak MJ, Nieto-Soler M, Wong N, Chen HT, Faryabi RB, Polato F, Santos M, Starnes LM, Weserman DR, Lee JE, Tubbs A, Sleckman BP, Daniel JA, Ge K, Alt FW, Fernandez-Capetillo O, Nussenzweig MC, Nussenzweig A (2013) 53BP1 mediates productive and mutagenic DNA repair through distinct phosphoprotein interactions. Cell 153:1266–1280
Casafont I, Navascues J, Pena E, Lafarga M, Berciano MT (2006) Nuclear organization and dynamics of transcription sites in rat sensory ganglia neurons detected by incorporation of 5′-fluorouridine into nascent RNA. Neuroscience 140:453–462
Casafont I, Palanca A, Lafarga V, Berciano MT, Lafarga M (2011) Effect of ionizing radiation in sensory ganglion neurons: organization and dynamics of nuclear compartments of DNA damage/repair and their relationship with transcription and cell cycle. Acta Neuropathol 122:481–493
Cherian PP, Schenker S, Henderson GI (2008) Ethanol-mediated DNA damage and PARP-1 apoptotic responses in cultured fetal cortical neurons. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 32:1884–1892
Chu J, Tong M, de la Monte SM (2007) Chronic ethanol exposure causes mitocondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in immature central nervous system neurons. Acta Neuropathol 113:656–673
de la Monte SM, Kril JJ (2014) Human alcohol-related neuropathology. Acta Neuropathol 127:71–90
Deitrich R, Zimatkin S, Pronko S (2006) Oxidation of ethanol in the brain and its consequences. Alcohol Res Health 29:266–273
Doil C, Mailand N, Bekker-Jensen S, Menard P, Larsen DH, Pepperkok R, Ellenberg J, Panier S, Durocher D, Bartek J, Lukas J, Lukas C (2009) RNF168 binds and amplifies ubiquitin conjugates on damaged chromosomes to allow accumulation of repair proteins. Cell 136:435–446
Eckardt MJ, File SE, Gessa GL, Grant KA, Guerri C, Hoffman PL, Kalant H, Koob GF, Li TK, Tabakoff B (1998) Effects of moderate alcohol consumption on the central nervous system. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:998–1040
Escribano-Diaz C, Durocher D (2013) DNA repair pathway choice-a PTIP of the hat to 53BP1. EMBO Rep 8:665–666
Fernandez-Capetillo O, Lee A, Nussenzweig M, Nussenzweig A (2004) H2AX: the histone guardian of genome. DNA Repair 3:959–967
Gonzalez-Suarez I, Redwood AB, Grotsky GA, Neumann MA, Cheng EH, Stewart CL, Dusso A, Gonzalo S (2011) A new pathway that regulates 53BP1 stability implicates Cathepsin L and vitamin D in DNA repair. EMBO J 30:3383–3396
Goodlett CR, Horn KH, Zhou FC (2005) Alcohol teratogenesis: mechanism of damage and strategies for intervention. Exp Biol Med 230:394–406
Grotzky DA, Gonzalez-Suarez I, Novell A, Neumann MA, Yaddanapudi SC, Croke M, Martinez-Alonso M, Redwood AB, Ortega-Martinez S, Feng Z, Lerma E, Ramón y Cajla T, Zhang J, Matias-Guiu X, Dusso A, Gonzalo S (2013) BRCA1 loss activates cathepsin L-mediated degradation of 53BP1 in breast cancer cells. J Cell Biol 200:187–202
Guo Y, Chen Y, Carreon S, Qiang M (2012) Chronic intermittent ethanol exposure and its removal induce a different miRNA expression pattern in primary cortical neuronal cultures. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 36:1058–1066
Hetman M, Vashishta A, Rempala G (2010) Neurotoxic mechanisms of DNA damage: focus on transcriptional inhibition. J Neurochem 114:1537–1549
Iborra JF, Pombo A, Jackson DA, Cook PR (1996) Active RNA polymerases are localized within discrete transcription factories in human nuclei. J Cell Sci 109:1427–1436
Jorgensen S, Schotta G, Sorensen CS (2013) Histone H4 lysine 20 methylation: key player in epigenetic regulation of genomic integrity. Nucleic Acid Res 41:2797–2806
Kofman AV, Kim J, Park SY, Dupart E, Letson C, Bao Y, Ding K, Chen Q, Schiff D, Larner J, Abounader R (2013) microRNA-34a promotes DNA damage and mitotic catastrophe. Cell Cycle 12:3500–3511
Kruman II, Henderson GI, Bergeson SE (2012) DNA damage and neurotoxicity of chronic alcohol abuse. Exp Biol Med 237:740–747
Lamarche F, Gonthier B, Signorini N, Eysseric H, Barret L (2003) Acute exposure of cultured neurones to ethanol results in reversible DNA single-strand breaks; whereas chronic exposure causes loss of cell viability. Alcohol 38:550–558
Lamarche F, Gonthier B, Signorini N, Eysseric H, Barret L (2004) Impact of ethanol and acetaldehyde on DNA and cell viability of cultured neurones. Cell Biol Toxicol 20:361–374
Lieber MR (2010) The mechanism of double-strand DNA break repair by the nonhomologous DNA end-joining pathway. Ann Rev Biochem 79:181–211
Marín MP, Esteban-Pretel G, Ponsoda X, Romero AM, Ballestín R, López C, Megías L, Timoneda J, Molowny A, Canales JJ, Renau-Piqueras J (2010) Endocytosis in cultured neurons is altered by chronic alcohol exposure. Toxicol Sci 115:202–213
May PA, Gossage JP, Kalberg WO, Robinson LK, Buckley D, Manning M, Hoyme HE (2009) Prevalence and epidemiologic characteristics of FASD from various research methods with an emphasis on recent in-school studies. Dev Disabil Res Rev 15:176–192
McKinnon PJ (2009) DNA repair deficiency and neurological disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:100–112
Misso G, Di Martino MT, De Rosa G, Farooqi AA, Lombardi A, Campani V, Zarone MR, Gullà A, Tagliaferri P, Tassone P, Caraglia M (2014) Mir-34: a new weapon against cancer? Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 3:e194
Noon AT, Goodarzi AA (2011) 53BP1-mediated DNA double strand break repair: Insert bad pun here. DNA Repair 10:1071–1076
Olive PL, Banáth JP (2006) The comet assay: a method to measure DNA damage in individual cells. Nat Protoc 1:23–29
Pandey SC, Ugale R, Zhang H, Tang L, Prakash A (2008) Brain chromatin remodeling: a novel mechanism of alcoholism. J Neurosci 28:3729–3737
Panier S, Boulton SJ (2014) Double strand break repair: 53BP1 comes into focus. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:7–18
Price PJ, Brewer GJ (2001) Serum-free media for neural cell cultures. Adult and embryonic. In: Fedoroff S, Richardson A (eds) Protocols for neural cell culture. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 255–264
Rass U, Ahel I, West SC (2007) Defective DNA repair and neurodegeneration disease. Cell 130:991–1004
Redwood AB, Perkins SM, Vanderwaal RP, Feng Z, Biehl KJ, Gonzalez-Suarez I, Morgado-Palacín L, Shi W, Sage J, Roti-Roti JL, Stewart CL, Zhang J, Gonzalo S (2011) A dual role for A-type lamins in DNA double-strand breaks repair. Cell Cycle 10:3652–3657
Romero AM, Renau-Piqueras J, Pilar Marín M, Timoneda J, Berciano MT, Lafarga M, Esteban-Pretel G (2013) Chronic alcohol alters dendritic spine development in neurons in primary culture. Neurotox Res 24:532–548
Romero AM, Renau-Piqueras J, Marín MP, Esteban-Pretel G (2015) Chronic alcohol exposure affects the cell components involved in membrane traffic in neuronal dendrites. Neurotox Res 27:43–54
Rulten SL, Hodder E, Ripley TL, Stephens DN, Mayne LV (2008) Alcohol induces DNA damage and the Fanconi anemia D2 protein implicating FANCD2 in the DNA damage response pathway in brain. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 32:1186–1196
Schultz LB, Chehab NH, Malikzay A, Halazonetis TD (2000) p53 binding protein 1 (53BP1) is an early participant in the cellular response to DNA double strand-breaks. J Cell Biol 151:1381–1390
Streissguth AP, Barr HM, Sampson PD, Bookstein FL (1994) Prenatal alcohol and offspring development: the first fourteen years. Drug Alcohol Depend 36:89–99
Valenzuela CF, Morton RA, Diaz MR, Topper L (2012) Does moderate drinking harm the fetal brain? Insights from animal models. Trends Neurosci 35:284–292
Wang B, Matsuoka S, Carpenter PB, Elledge SJ (2002) 53BP1, a mediator of the DNA damage checkpoint. Science 298:1435–1438
Yang ES, Wang H, Jiang G, Nowsheen S, Fu A, Hallahan DE, Xia F (2009) Lithium-mediated protection of hippocampal cells involves enhancement of DNA-PK-dependent repair in mice. J Clin Invest 119:1124–1135
Funding
“Dirección General de Investigación” of Spain (BFU2011-23983), and “Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red sobre Enfermedades Neurodegenerativas (CIBERNED; CB06/05/0037)” from Spain. “Ministerio de Educación, Cultura y Deporte” (FPU AP2009-3393) from Spain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Romero, A.M., Palanca, A., Ruiz-Soto, M. et al. Chronic Alcohol Exposure Decreases 53BP1 Protein Levels Leading to a Defective DNA Repair in Cultured Primary Cortical Neurons. Neurotox Res 29, 69–79 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-015-9554-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-015-9554-8