Abstract
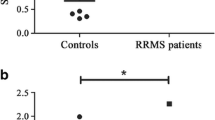
To investigate the concentrations of nitric oxide (NO) products (NOx) and arginase activity in acute neuroinflammation, we analyzed cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and plasma of clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) and relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) patients, who were divided into groups on the basis of clinical and radiological disease activity. The NOx levels, in both, CSF and plasma, were increased in CIS (p = 0.0015, p = 0.0014, respectively) and RRMS group (p = 0.002, p = 0.0019, respectively), while arginase activity approached low levels, in CIS (p = 0.009, p = 0.02, respectively) and RRMS group (p = 0.018, p = 0.034, respectively) compared to controls. The NOx levels were higher in CSF and plasma of CIS than in RRMS group (p = 0.065, p = 0.037, respectively), inverse to arginase activity which was higher, in CSF and plasma, in RRMS than in CIS group (p = 0.031, p = 0.02, respectively). The CSF and plasma NOx values positively correlated with the clinical disease activity in CIS (r = 0.09, p = 0.81; r = 0.45, p = 0.023, respectively) and RRMS group (r = 0.311, p = 0.04; r = 0.512, p = 0.01, respectively). Also, CSF and plasma arginase activity showed negative correlation with clinical disease activity in CIS (r = 0.39, p = 0.03; r = 0.1, p = 0.65, respectively) and RRMS group (r = 0.43, p = 0.03; r = 0.62, p = 0.015, respectively). The CSF NOx levels showed positive correlation with volume of acute radiological lesions of CNS in CIS (r = 0.25, p = 0.045) and RRMS group (r = 0.31, p = 0.04), while arginase activity showed the negative correlations in CIS (r = 0.41; p = 0.035) and RRMS group (r = 0.52, p = 0.022). The results support NO and arginase involvement in the pathogenesis of acute neuroinflammation, which determination may be useful as surrogate markers for clinical and radiological disease activity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acar G, Idiman F, Idiman E, Kırkalı G, Çakmakçı H, Özakbas S (2003) Nitric oxide as an activity marker in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 250:588–592
Ahn M, Lee C, Jung K, Kim H, Moon C, Sim KB, Shin T (2012a) Immunohistochemical study of arginase-1 in the spinal cords of rats with clip compression injury. Brain Res 1445:11–19
Ahn M, Yang W, Kim H, Jin JK, Moon C, Shin T (2012b) Immunohistochemical study of arginase-1 in the spinal cords of Lewis rats with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain Res 1453:77–86
Bansal V, Ochoa B (2003) Arginine availability, arginase, and the immune response. Curr Opin Clin Nutrit Met Care 6:223–228
Brettschneider J, Petzold A, Junker A, Tumani H (2006) Axonal damage markers in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with clinically isolated syndrome improve predicting conversion to definite multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 12:143–148
Broholm H, Andersen B, Wanscher B, Frederiksen JL, Rubin I, Pakkenberg B, Larsson HBW, Lauritzen M (2004) Nitric oxide synthase expression and enzymatic activity in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand 109:261–269
Bronte V, Zanovello P (2005) Regulation of immune responses by l-arginine metabolism. Nat Rev Immunol 5:641–654
Danilov AI, Andersson M, Bavand N, Wiklund NP, Olsson T, Brundin L (2003) Nitric oxide metabolite determinations reveal continuous inflammation in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 136:112–118
Durante W, Fruzsina K, Johnson FJ, Johnson RA (2007) Arginase: a critical regulator of nitric oxide synthesis and vascular function. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 34:906–911
El-Gayar S, Thuring-Nahler H, Pfeilschifter J, Rollinghoff M, Bogdan C (2003) Translational control of inducible nitric oxide synthase by IL-13 and arginine availability in inflammatory macrophages. J Immunol 171:4561–4568
Hill KE, Zollinger LV, Watt HE, Carlson NG, Rose JW (2004) Inducible nitric oxide synthase in chronic active multiple sclerosis plaques: distribution, cellular expression and association with myelin damage. J Neuroimmunol 151:171–179
Ibragic S, Sofic E, Suljic E, Avdagic N, Bajraktarevic A, Tahirovic I (2012) Serum nitric oxide concentrations in patients with multiple sclerosis and patients with epilepsy. J Neural Transm 119:7–11
Jolivalt CG, Howard RB, Chen LS, Mizisin AP, Lai CS (2003) A novel nitric oxide scavenger in combination with cyclosporine A ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis progression in mice. J Neuroimmunol 138(1–2):56–64
Kahl KG, Zielasek J, Uttenthal LO, Rodrigo J, Toyka KV, Schmidt HH (2003) Protective role of the cytokine-inducible isoform of nitric oxide synthase induction and nitrosative stress in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis of the DA rat. J Neurosci Res 73:198–205
Kahl KG, Schmidt HHW, Jung S, Sherman P, Toyka KV, Zielasek J (2004) Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice with a targeted deletion of the inducible nitric oxide synthase gene: increased T-helper 1 response. Neurosci Lett 358(1):58–62
Kapoor R, Davies M, Blaker PA, Hall SM, Smith KJ (2003) Blockers of sodium and calcium entry protect axons from nitric oxide-mediated degeneration. Ann Neurol 53(2):174–180
Kepka-Lenhart D, Mistry SK, Wu G, Morris SM (2000) Arginase I: a limiting factor for nitric oxide and polyamine synthesis by activated macrophages? Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 279:R2237–R2242
Kim H, Ahn M, Choi S, Kim M, Sim KB, Kim J, Moon C, Shin T (2013) Potential role of fibronectin in microglia/macrophage activation following cryoinjury in the rat brain: an immunohistochemical study. Brain Res 1502:11–19
King NE, Rothenberg ME, Zimmermann N (2004) Arginine in asthma and lung inflammation. J Nutr 134:2830S–2836S
Kuhlmann T, Lingfeld G, Bitsch A, Schuchardt J, Bruck W (2002) Acute axonal damage in multiple sclerosis is most extensive in early disease stages and decreases over time. Brain 125:2202–2212
Kurtzke JF (1983) Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclero-sis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 33:1444–1452
Lassmann H (2003) Axonal injury in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:695–697
Lee J, Ryu H, Ferrante RJ, Morris SM Jr, Ratan RR (2003) Translational control of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression by arginine can explain the arginase paradox. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:4843–4848
Li H, Meininger CJ, Hawker JR, Haynes TE, Kepka-Lenhart D, Mistry SK, Morris SM Jr, Wu G (2001) Regulatory role of arginase I and II in nitric oxide, polyamine, and proline synthesis in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 280:E75–E82
Ljubisavljevic S, Stojanovic I, Pavlovic R, Sokolovic D, Pavlovic D, Cvetkovic T, Stevanovic I (2012) Modulation of nitric oxide synthase by arginase and methylated arginines during the acute phase of experimental multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 318(1–2):106–111
Ljubisavljevic S, Stojanovic I, Vojinovic S, Stojanov D, Stojanovic S, Cvetkovic T, Savic D, Pavlovic D (2013a) The patients with clinically isolated syndrome and relapsing remitting multiples sclerosis show different levels of advanced protein oxidation products and reduced thiols content in sera and CSF. Neurochem Int 62(7):988–997
Ljubisavljevic S, Stojanovic I, Vojinovic S, Stojanov D, Stojanovic S, Kocic G, Savic D, Cvetkovic T, Pavlovic D (2013b) Cerebrospinal fluid and plasma oxidative stress biomarkers in different clinical phenotypes of neuroinflammatory acute attacks. Conceptual accession: from fundamental to clinic. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33:767–777
Lublin FD, Reingold SC (1996) Defining the clinical course of multiple sclerosis: results of an international survey— National Multiple Sclerosis Society (USA) Advisory Committee on Clinical Trials of New Agents in Multiple Sclerosis. Neurology 46:907–911
Marchetti B, Morale MC, Brouwer J, Tirolo C, Testa N, Caniglia S, Barden N, Amor S, Smith PA, Dijkstra CD (2002) Exposure to a dysfunctional glucocorticoid receptor from early embryonic life programs the resistance to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis via nitric oxide-induced immunosuppression. J Immunol 168(11):5848–5859
Moncada S, Bolanos JP (2006) Nitric oxide, cell bioenergetics and neurodegeneration. J Neurochem 97:1676–1689
Mori M, Gotoh T (2004) Arginine metabolic enzymes, nitric oxide and infection. J Nutr 134:2820S–2825S
Navaro-Gonzalvez JA, Garcia-Benayas C, Arenas J (1998) Semiautomated measurement of nitrate in biological fluids. Clin Chem 44:679–681
Nicholson B, Manner CK, Kleeman J, MacLeod CL (2001) Sustained nitric oxide production in macrophages requires the arginine transporter CAT2. J Biol Chem 276:15881–15885
Polman CH, Reingold SC, Banwell B, Clanet M, Cohen JA, Filippi M, Fujihara K, Havrdova E, Hutchinson M, Kappos L, Lublin FD, Montalban X, O’Connor P, Sandberg-Wollheim M, Thomp-son AJ, Waubant E, Weinshenker B, Wolinsky JS (2011) Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 Revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann Neurol 69(2):292–302
Porembska Z, Kedra M (1975) Early diagnosis of myocardial infarction by arginase activity determination. Clin Chim Acta 60:355–361
Rejdak K, Eikelenboom MJ, Petzold A, Thompson EJ, Stelmasiak Z, Lazeron RH, Barkhof F, Polman CH, Uitdehaag BM, Giovannoni G (2004) CSF nitric oxide metabolites are associated with activity and progression of multiple sclerosis. Neurology 63:1439–1445
Rejdak K, Petzold A, Stelmasiak Z, Giovannoni G (2008) Cerebrospinal fluid brain specific proteins in relation to nitric oxide metabolites during relapse of multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 14:59–66
Rodríguez-Sáinz MC, Sánchez-Ramón S, de Andrés C, Rodríguez-Mahou M, Muñoz-Fernández MA (2002) Th1/Th2 cytokine balance and nitric oxide in cerebrospinal fluid and serum from patients with multiple sclerosis. Eur Cytokine Netw 13(1):110–114
Roghani M, Mahboudi F, Saharian MA, Etemadifar M, Esfahani AN, Nahrevanian H, Elahi E (2010) Concentrations of nitric oxide metabolites in the serum of Iranian multiple sclerosis patients. J Neurol Sci 294:92–94
Shin T, Ahn M, Matsumoto Y (2012) Mechanism of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats: recent insights from macrophages. Anat Cell Biol 45(3):141–148
Shin T, Ahn M, Matsumoto Y, Moon C (2013a) Mechanism of experimental autoimmune neuritis in Lewis rats: the dual role of macrophages. Histol Histopathol 28(6):679–684
Shin T, Ahn M, Moon C, Kim S, Sim KB (2013b) Alternatively activated macrophages in spinal cord injury and remission: another mechanism for repair? Mol Neurobiol 47(3):1011–1019
Smith KJ, Lassmann H (2002) The role of nitric oxide in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol 1(4):232–241
Staykova MA, Paridaen JT, Cowden WB, Willenborg DO (2005) Nitric Oxide Contributes to Resistance of the Brown Norway Rat to Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Am J Pathol 166(1):147–157
Xu L, Hilliard B, Carmody RJ, Tsabary G, Shin H, Christianson DW, Chen YH (2003) Arginase and autoimmune inflammation in the central nervous system. Immunol 110:141–148
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grant from the scientific project number 41018 financed by the Ministry of Education and Science, Republic of Serbia. Authors thank Svetlana Stojanovic, Milena Krsmanovic, Slobodan Vojinovic, and Dragan Stojanov, for the support in the clinical and laboratory work and Zorica Tomic, for the technical support in blood and CSF collection.
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest exists for any of the authors listed in the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ljubisavljevic, S., Stojanovic, I., Pavlovic, R. et al. The Importance of Nitric Oxide and Arginase in the Pathogenesis of Acute Neuroinflammation: Are Those Contra Players with the Same Direction?. Neurotox Res 26, 392–399 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-014-9470-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-014-9470-3