Abstract
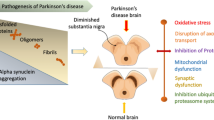
Idiopathic Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects approximately 1 % of the population over 55 years of age. The disease manifests itself through motor and nonmotor symptoms induced mainly by the neurodegeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc). The possible mechanisms involved in this pathology include mitochondrial dysfunction, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress. The present study evaluated the effects of the nonselective cyclooxygenase inhibitor ibuprofen on motor and depressive-like behavior induced by rotenone in rats. Rotenone (2.5 mg/kg, i.p., for 10 days) decreased tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactivity in the SNpc, and ibuprofen treatment (15 mg/kg, p.o., for 22 days) blocked this impairment. We also found that rotenone-induced motor deficits (hypolocomotion) and depressive-like behavior, and ibuprofen was able to reverse these deficits. In addition to motor and nonmotor behaviors, we evaluated oxidative stress induced by rotenone. Rotenone administration depleted glutathione levels in the hippocampus and reduced catalase activity in both the hippocampus and striatum. Post treatment with ibuprofen blocked the depletion of glutathione induced by rotenone and increased the basal levels of this antioxidant in the striatum. Ibuprofen also restored catalase activity. The neuroprotective effects of ibuprofen against toxicity induced by rotenone appear to be attributable to its antioxidant properties, in addition to cyclooxygenase inhibition.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarsland D, Pahlhagen S, Ballard CG, Ehrt U, Svenningsson P (2012) Depression in Parkinson’s disease: epidemiology, mechanisms and management. Nat Rev Neurol 8:35–47. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2011.189
Aebi H (1984) Catalase. In: Packer L (ed) Oxygen Radicals in Biological Systems (series title: Methods in Enzymology), vol 105. Academic Press, Orlando, pp 121–126
Alam A, Schmidt WJ (2002) Rotenone destroys dopaminergic neurons and induces parkinsonian symptoms in rats. Behav Brain Res 136:317–324. doi:10.1016/S0166-4328(02)00180-8
Aubin N, Curet O, Deffois A, Carter C (1998) Aspirin and salicylate protect against MPTP-induced dopamine depletion in mice. J Neurochem 71:1635–1642. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.71041635.x
Baker K, Marcus CB, Huffman K, Kruk H, Malfoy B, Doctrow SR (1998) Synthetic combined superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetics are protective as a delayed treatment in a rat stroke model: a key role for reactive oxygen species in ischemic brain injury. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 284:215–221
Betarbet R, Sherer TB, MacKenzie G, Garcia-Osuna M, Panov AV, Greenamyre TJ (2000) Chronic systemic pesticide exposure reproduces features of Parkinson’s disease. Nat Neurosci 3:1301–1306. doi:10.1038/81834
Blesa J, Phani S, Jackson-Lewis V, Przedborski S (2012) Classic and new models of Parkinson’s disease. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012:845618. doi:10.1155/2012/845618
Bové J, Perier C (2012) Neurotoxin-based models of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 211:51–76. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.10.057
Broadhurst PL (1960) Experiments in psychogenetics: applications of biometrical genetics to the inheritance of behaviour. In: Eysenck HJ (ed) Experiments in personality. Routledge and Kegan Paul, London, pp 52–71
Brunello N, Alboni S, Capone G, Benatti C, Blom JM, Tascedda F, Kriwin P, Mendlewicz J (2006) Acetylsalicylic acid accelerates the antidepressant effect of fluoxetine in the chronic escape deficit model of depression. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 21:219–225
Cabezas R, El-Bachá RS, Gonzáles J, Barreto GE (2012) Mitochondrial functions in astrocytes: neuroprotective implications from oxidative damage by rotenone. Neurosci Res 74:80–90. doi:10.1016/j.neures.2012.07.008
Cannon JR, Tapias VM, Na HM, Honick AS, Drolet RE, Greenamyre JT (2009) A highly reproducible rotenone model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 34:279–290. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2009.01.016
Casper D, Yaparpalvi U, Rempel N, Werner P (2000) Ibuprofen protects dopaminergic neurons against glutamate toxicity in vitro. Neurosci Lett 289:201–204. doi:10.1016/S0304-3940(00)01294-5
Chen H, Jacobs E, Schwarzschild MA, McCullough ML, Calle EE, Thun MJ, Ascherio A (2005) Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug use and the risk for Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 58:963–967. doi:10.1002/ana.20682
Choi WS, Palmiter RD, Xia Z (2011) Loss of mitochondrial complex I activity potentiates dopamine neuron death induced by microtubule dysfunction in a Parkinson’s disease model. J Cell Biol 192:873–882. doi:10.1083/jcb.201009132
Clausen A, Xu X, Bi X, Baudry M (2012) Effects of the superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetic EUK-207 in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease: protection against and interruption of progression of amyloid and tau pathology and cognitive decline. J Alzheimer Dis 30:183–208. doi:10.3233/JAD-2012-111298
Dauer W, Przedborski S (2003) Parkinson’s disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron 39:889–909. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(03)00568-3
Dhillon AS, Tarbutton GL, Levin JL, Plotkin GM, Lowry LK, Nalbone JT, Shepherd S (2008) Pesticide/environmental exposures and Parkinson’s disease in East Texas. J Agromed 13:37–48. doi:10.1080/10599240801986215
Esposito E, Di Matteo V, Benigno A, Pierucci M, Crescimanno G, Di Giovanni G (2007) Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs in Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 205:295–312. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2007.02.008
Feng ZH, Wang TG, Li DD, Fung P, Wilson BC, Liu B, Ali SF, Langenbach R, Hong JS (2002) Cyclooxygenase-2-deficient mice are resistant to 1-methyl-4-phenyl1, 2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced damage of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. Neurosci Lett 329:354–358. doi:10.1016/S0304-3940(02)00704-8
Fleming SM, Zhu C, Fernagut PO, Mehta A, DiCarlo CD, Seaman RL, Chesselet MF (2004) Behavioral and immunohistochemical effects of chronic intravenous and subcutaneous infusions of varying doses of rotenone. Exp Neurol 187:418–429. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2004.01.023
Gao R, Yuan Z, Zhao Z, Gao X (1998) Mechanism of pyrogallol autoxidation and determination of superoxide dismutase enzyme activity. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg 45:41–45. doi:10.1016/S0302-4598(98)00072-5
Gao X, Chen H, Schwarzschild MA, Ascherio A (2011) Use of ibuprofen and risk of Parkinson disease. Neurology 76:863–869. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e31820f2d79
He Y, Imam SZ, Dong Z, Jankovic J, Ali SF, Appel SH, Le W (2003) Role of nitric oxide in rotenone-induced nigro-striatal injury. J Neurochem 86:1338–1345. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01938.x
Hirsch EC, Jenner P, Przedborski S (2013) Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Movement Disord 28:24–30. doi:10.1002/mds.25032
Hoglinger GU, Féger J, Prignet A, Michel PP, Parain K, Champy P, Ruberg M, Oertel WH, Hirsch EC (2003) Chronic systemic complex I inhibition induces a hypokinetic multisystem degeneration in rats. J Neurochem 84:491–502. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01533.x
Hou JG, Lai EC (2007) Non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Int J Gerontol 1:53–64
Hsieh Y, Mounsey RB, Teismann P (2011) MPP+-induced toxicity in the presence of dopamine is mediated by COX-2 through oxidative stress. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 384:157–167. doi:10.1007/s00210-011-0660-8
Huang J, Liu H, Gu W, Yan Z, Xu Z, Yang Y, Zhu X, Li Y (2006) A delivery strategy for rotenone microspheres in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Biomaterials 27:937–946. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.07.005
Jiang Z, Hunt JV, Wolf SP (1992) Ferrous ion oxidation in the presence of xylenol orange for detection of lipid hydroperoxide in low density lipoprotein. Anal Biochem 202:384–389. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(92)901
Kim WG, Mohney RP, Wilson B, Jeohn GH, Liu B, Hong JS (2000) Regional difference in susceptibility to lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity in the rat brain: role of microglia. J Neurosci 20:6309–6316
Klivenyi P, Andreassen OA, Ferrante RJ, Dedeoglu A, Mueller G, Lancelot E, Bogdanov M, Andersen JK, Jiang D, Beal MF (2000) Mice deficient in cellular glutathione peroxidase show increased vulnerability to malonate, 3-nitropropionic acid, and 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine. J Neurosci 20:1–7
Lapointe N, St-Hilaire M, Martinoli MG, Blanchet J, Gould P, Rouillard C, Cicchetti F (2004) Rotenone induces non-specific nervous system and systemic toxicity. FASEB J 18:717–719. doi:10.1096/fj.03-0677fje
Linnoila M, Whorton AR, Rubinow DR, Cowdry RW, Ninan PT, Waters RN (1983) CSF prostaglandin levels in depressed and schizophrenic patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 40:405–406. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1983.01790040059008
Lucki I (1997) The forced swimming test as a model for core and component behavioral effects of antidepressant drugs. Behav Pharmacol 8:523–532
Luo C, Rajput AH, Akhtar S, Rajput A (2007) α-Synuclein and tyrosine hydroxylase expression in acute rotenone toxicity. Int J Mol Med 19:517–521
Madathil SK, Karuppagounder SS, Mohanakumar KP (2013) Sodium salicylate protects against rotenone-induced Parkinsonism in rats. Synapse 67:502–514. doi:10.1002/syn.21658
Marklund S, Marklund G (1974) Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem 47:469–474. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03714.x
Michel TM, Pulschen D, Thome J (2012) The role of oxidative stress in depressive disorders. Curr Pharm Des 18:5890–5899
Mikova O, Yakimova R, Bosmans E, Kenis G, Maes M (2001) Increased serum tumor necrosis factor alpha concentrations in major depression and multiple sclerosis. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 11:203–208
Minghetti L (2004) Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in inflammatory and degenerative brain diseases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63:901–910
Morais LH, Lima MMS, Martynhak BJ, Santiago R, Takahashi TT, Ariza D, Barbiero JK, Andreatini R, Vital MABF (2012) Characterization of motor, depressive-like and neurochemical alterations induced by a short-term rotenone administration. Pharmacol Rep 64:1081–1090
Moreira CG, Barbiero JK, Ariza D, Dombrowski PA, Sabioni P, Bortolanza M, Da Cunha C, Vital MA, Lima MM (2012) Behavioral, neurochemical and histological alterations promoted by bilateral intranigral rotenone administration: a new approach for an old neurotoxin. Neurotox Res 21:291–301. doi:10.1007/s12640-011-9278-3
Morioka N, Kumagai K, Morita K, Kitayama S, Dohi T (2004) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs potentiate 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+)-induced cell death by promoting the intracellular accumulation of MPP+ in PC12 cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. doi:10.1124/jpet.104.065300
Mosley RL, Hutter-Saunders JA, Stone DK, Gendleman HE (2012) Inflammation and adaptive immunity in Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2:a009381. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a009381
Muller N, Schwarz MJ, Dehning S, Douhe A, Cerovecki A, Goldstein-Muller B, Spellmann I, Hetzel G, Maino K, Kleindienst N, Muller HJ, Arolt V, Riedel M (2006) The cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib has therapeutic effects in major depression: results of a double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled, add-on pilot study to reboxetine. Mol Psychiatry 11:680–684. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001805
Muller N, Myint A, Schwarz MJ (2011) Inflammatory biomarkers and depression. Neurotox Res 19:308–318. doi:10.1007/s12640-010-9210-2
O’Banion MK (1999) Cyclooxygenase-2: molecular biology, pharmacology, and neurobiology. Crit Rev Neurobiol 13:45–82
Paxinos G, Watson C (1997) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 3rd edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Phillis JW, Horrocks LA, Farooqui AA (2006) Cyclooxygenases, lipoxygenases, and epoxygenases in CNS: their role and involvement in neurological disorders. Brain Res Rev 52:201–243. doi:10.1016/j.brainresrev.2006.02.002
Phinney AL, Andringa G, Bol JG, Wolters EC, van Muiswinkel FL, van Dam AM, Drukarch B (2006) Enhanced sensitivity of dopaminergic neurons to rotenone-induced toxicity with aging. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 12:228–238. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2005.12.002
Porsolt RD, Anton G, Blavet N, Jalfre M (1978) Behavioural despair in rats: a new model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Eur J Pharmacol 47:379–391. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(78)90118-8
Reneric JP, Bouvard M, Stinus L (2002) In the rat forced swimming test, chronic but not subacute administration of dual 5-HT/NA antidepressant treatments may produce greater effects than selective drugs. Behav Brain Res 136:521–532. doi:10.1016/S0166-4328(02)00203-6
Sanders LH, Greenamyre JT (2013) Oxidative damage to macromolecules in human Parkinson disease and the rotenone model. Free Radic Bio Med. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.01.003
Sandrini M, Vitale G, Pini LA (2002) Effect of rofecoxib on nociception and the serotonin system in the rat brain. Inflamm Res 51:154–159. doi:10.1007/pl00000287
Santiago RM, Barbieiro J, Lima MM, Dombrowski PA, Andreatini R, Vital MA (2010) Depressive-like behaviors alterations induced by intranigral MPTP, 6-OHDA, LPS and rotenone models of Parkinson’s disease are predominantly associated with serotonin and dopamine. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 34:1104–1114. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.06.004
Schuler F, Casida JE (2001) Functional coupling of PSST and ND1 subunits in NADH: ubiquinone oxidoreductase established by photo affinity labeling. Biochim Biophys Acta 1506:79–87. doi:10.1016/S0005-2728(01)00183-9
Sedlak J, Lindsay RH (1968) Estimation of total protein-bound and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissues with Ellman’s reagent. Anal Biochem 25:192–205
Sherer TB, Kim J, Betarbet R, Greenamyre JT (2003) Subcutaneous rotenone exposure causes highly selective dopaminergic degeneration and α-synuclein aggregation. Exp Neurol 179:9–16. doi:10.1006/exnr.2002.8072
Soliman Y, Jackson T, Mazzio E, Soliman KFA (2009) The effects of piroxicam in the attenuation of MPP+/MPTP toxicity in vitro and in vivo. Neurochem Res 34:304–310. doi:10.1007/s11064-008-9779-5
Tanner CM, Kamel F, Ross GW, Hoppin JA, Goldman SM, Orell M, Marras C, Bhudhikanok GS, Kasten M, Chade AR, Comyns K, Richards MB, Meng C, Priestley B, Fernandez HH, Cambi F, Umbach DM, Blair A, Sandler DP, Langston JW (2011) Rotenone, paraquat, and Parkinson’s disease. Environ Health Persp 119:866–872. doi:10.1289/ehp.1002839
Teismann P (2012) COX-2 in the neurodegenerative process of Parkinson’s disease. Biofactors 38:395–397. doi:10.1002/biof.1035
Teismann P, Tieu K, Choi DK, Wu DC, Naini A, Hunot S, Vila M, Jackson-Lewis V, Przedborski S (2003a) Cyclooxygenase-2 is instrumental in Parkinson’s disease neurodegeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:5473–5478. doi:10.1073/pnas.0837397100
Teismann P, Vila M, Choi DK, Tieu K, Wu DC, Jackson-Lewis V, Przedborski S (2003b) COX-2 and neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 991:272–277. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb07482.x
Thakur P, Nehru B (2013) Anti-inflammatory properties rather than anti-oxidant capability is the major mechanism of neuroprotection by sodium salicylate in a chronic rotenone model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 231:420–431. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.11.006
Wilkinson BL, Cramer PE, Varvel NH, Reed-Geaghan E, Jiang Q, Szabo A, Herrup K, Lamb BT, Landreth GE (2012) Ibuprofen attenuates oxidative damage through NOX2 inhibition in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 33:197.e21–197.332. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.06.014
Winterbourn CC (1993) Superoxide as an intracellular radical sink. Free Radic Biol Med 14:85–90. doi:10.1016/0891-5849(93)90512-S
Yaron I, Shirazi I, Judovich R, Levartovsky D, Caspi D, Yaron M (1999) Fluoxetine and amitriptyline inhibit nitric oxide, prostaglandin E2, and hyaluronic acid production in human synovial cells and synovial tissue cultures. Arthritis Rheum 42:2561–2568. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(199912)42:12<2561:AID-ANR8>3.0.CO;2-U
Zhu C, Vourc’h P, Fernagut PO, Fleming SM, Lacan S, Dicarlo CD, Seaman RL, Chesselet MF (2004) Variable effects of chronic subcutaneous administration of rotenone on striatal histology. J Comp Neurol 478:418–426. doi:10.1002/cne.20305
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from CNPq, CAPES, and REUNI, which had no further role in the study design, in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of the data, in writing the report, or in the decision to submit the paper for publication. MABFV is a recipient of a CNPq fellowship.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaminelli, T., Gradowski, R.W., Bassani, T.B. et al. Antidepressant and Antioxidative Effect of Ibuprofen in the Rotenone Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Neurotox Res 26, 351–362 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-014-9467-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-014-9467-y