Abstract
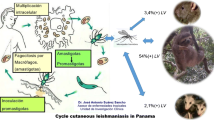
Cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) is endemic and a major health problem in 17 provinces out of 31 in Iran. This study aimed to determine vectors and reservoirs of the disease using molecular techniques in the borderline of Iran and Iraq. Sand flies and rodents were sampled using sticky paper traps and metal wire live traps, respectively, in the selected villages. About 10% of archived confirmed human positive slides was randomly checked for Leishmania by PCR–RFLP assay. The female sand flies were dissected in alcohol 96% in a sterile condition, the head and two segments of the abdomen end permanently mounted for identification and the remaining of body used for DNA extraction. The direct parasitological tests were carried out on the stained slides of rodents for Leishmania as well as PCR–RFLP assay used for molecular detection of parasite. A total of 2050 sand flies were identified comprising of Phlebotomus papatasi, Sergentomyia sintoni, Se. clydei, Se. mervynae, Se. theodori, Se. dentate and Se. iranica. The Ph. papatasi was ranked as a prevailing sand fly species. Molecular tests on female sand flies revealed infection of Ph. papatasi to Leishmania major. Direct parasitology and molecular tests confirmed of 20% infection to L. major among the sole rodents species “Tatera indica”. Due to wide dispersion of rodents colonies in the area and long favorite climate condition for sand flies, the CL foci will be provided the health risk for the religious tourists.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abai MA, Rassi Y, Imamian H, Fateh M, Mohebali M, Rafizadeh S (2007) PCR based on identification of vectors of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in Shahrood District, Central of Iran. Pak J Biol Sci 10(12):2061–2065
Abai MR, Oshaghi MA, Tajedin L, Rassi Y, Akhavan AA (2010) Geographical distribution and ecological features of the great gerbil subspecies in the main zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis foci in Iran. Asian Pac J Trop Med 3:800–803
Akhavan AA, Yaghoobi-Ershadi MR, Haibi F, Jafari R, Abdoli H, Arandian MH, Soleimani H, Zahraei-Ramazani AR, Mohebali M, Hajjaran H (2007) Emergence of cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania major in a new focus of southern Iran. J Arthropod-Borne Dis 1(1):1–8
Akhavan AA, Yaghoobi-Ershadi MR, Khamesipour A, Mirhendi H, Alimohammadian MH, Rassi Y, Arandian MH, Jafari R, Abdoli H, Shareghi N, Ghanei M, Jalali-Zand N (2010) Dynamics of Leishmania infection rates in Rhombomys opimus (Rodentia: Gerbillinae) population of an endemic focus of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in Iran. Bull Soc Pathol Exot 103(2):84–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13149-010-0044-1
Akhoundi M, Mohebali M, Asadi M, Mahmodi MR, Amraei K, Mirzaei A (2013a) Molecular characterization of Leishmania spp. in reservoir hosts in endemic foci of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in Iran. Folia Parasitol (Praha) 60(3):218–224
Akhoundi M, Baghaei A, Depaquit J, Parvizi P (2013b) Molecular characterization of Leishmania infection from naturally infected sand flies caught in a focus of cutaneous leishmaniasis (Eastern Iran). J Arthropod Borne Dis 7(2):122–131
Azizi K, Rassi Y, Moemenbellah-Fard MD (2010) PCR-based detection of Leishmania major kDNA within naturally infected Phlebotomus papatasi in southern Iran. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 104(6):440–442
Azizi K, Moemenbellah-Fard MD, Fakoorziba MR, Fekri S (2011) Gerbillus nanus (Rodentia: Muridae): a new reservoir host of Leishmania major. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 105(6):431–437. https://doi.org/10.1179/1364859411Y
Azizi K, Abedi F, Moemenbellah-Fard MD (2012a) Identification and frequency distribution of Leishmania (L.) major infections in sand flies from a new endemic ZCL focus in southeast Iran. Parasitol Res 111(4):1821–1826
Azizi K, Moemenbellah-Fard MD, Kalantari M, Fakoorziba MR (2012b) Molecular detection of Leishmania major kDNA from wild rodents in a new focus of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in an Oriental region of Iran. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 12(10):844–850. https://doi.org/10.1089/vbz.2011.0872
Azizi K, Fakoorziba MR, Jalali M, Moemenbellah-Fard MD (2012c) First molecular detection of Leishmania major within naturally infected Phlebotomus salehi from a zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis focus in southern Iran. Trop Biomed 29(1):1–8
Azizi K, Askari MB, Kalantari M, Moemenbellah-Fard MD (2016) Molecular detection of Leishmania parasites and host blood meal identification in wild sand flies from a new endemic rural region, south of Iran. Pathog Glob Health 110(7–8):303–309
Bakhshi H, Oshaghi MA, Abai MR, Rassi Y, Akhavan AA, Sheikh Z, Mohtarami F, Saidi Z, Mirzajani H, Anjomruz M (2013) Molecular detection of Leishmania infection in sand flies in border line of Iran–Turkmenistan: restricted and permissive vectors. Exp Parasitol 135(2):382–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2013.07.020
Darvishi M, Yaghoobi-Ershadi MR, Shahbazi F, Akhavan AA, Jafari R, Soleimani H, Yaghoobi-Ershadi N, Khajeian M, Darabi H, Arandian MH (2015) Epidemiological study on sand flies in an endemic focus of cutaneous leishmaniasis, Bushehr city, southwestern Iran. Front Public Health 3:14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2015.00014
Edrissian GH, Ghorbani M, Tahvildar-Bidruni GH (1975) Meriones persicus, another probable reservoir of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in Iran. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 69(5–6):517–519
Etemad A (1978) Mammals of Iran, rodents and identification Key, vol 1. Natural Resource Protection and Human Environment Association Press, Tehran (in Persian)
Feiz Haddad MH, Ghasemi E, Maraghi S, Tavala M (2016) Identification of Leishmania species isolated from human cutaneous leishmaniasis in Mehran, Western Iran using Nested PCR. Iran J Parasitol 11(1):65–72
Hajjaran H, Mohebali M, Alimoradi S, Abai MR, Edrissian GH (2009) Isolation and characterization of pathogenic Leishmania turanica from Nesokia indica (Rodentia, Muridae) by PCR–RFLP and ITS1 sequencing in Iran. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 103(11):1177–1179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trstmh.2008.08.016
Jafari R, Najafzadeh N, Sedaghat MM, Parvizi P (2013) Molecular characterization of sandflies and Leishmania detection in main vector of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in Abarkouh district of Yazd province, Iran. Asian Pac J Trop Med 6(10):792–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1995-7645(13)60140-6
Javadian E, Mesghali A (1974) Studies on cutaneous leishmaniasis in Khuzestan, Iran. Part I. The leptomonad infection of sandflies. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales 67(5):513–516
Javadian E, Nadim A, Tahvildare-Bidruni GH, Asefi V (1976) Epidemiology of cutaneous leishmaniasis in Iran: B. Khorassan Part V: report on a focus of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in Esferayen. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales 69(2):140–143
Javadian E, Jalali-Galousang A, Seyedi Rashti MA (1997) Sandflies of Ilam province, west of Iran with description of two new species from the Genus Phlebotomus: Ph. ilami and Ph. nadimi. Iran J Public Health 26:13–20
Javadian E, Dehestani M, Nadim A, Rassi Y, Tahvildar-Bidruni GH, Seyedi-Rashti MA, Shadmehr A (1998) Confirmation of Tatera indica (Rodentia: Gerbilidae) as the main host of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in the west of Iran. Iran J Public Health 27(1–2):55–60
Kassiri H, Javadian E, Abdigoudarzi M (2011) Natural Leishmania infection in Meriones hurrianae and Tatera indica (Rodentia: Cricetidae: Gerbillinae) in Sistan-Baluchistan province, southeastern of Iran. Adv Stud Biol 6:247–256
Kassiri H, Naddaf SR, Mohebali M, Javadian E (2012a) Molecular characterization of Leishmania infection in sand flies from Sistan and Baluchistan province, southeastern Iran. Jundishapur J Microbiol 5(2):430–433
Kassiri H, Sharifinia N, Jalilian N, Shemshad K (2012b) Epidemiological aspects of cutaneous leishmaniasis in Ilam province, west of Iran (2000–2007). Asian Pac J Trop Dis 2:S382–S386
Kassiri H, Naddaf SR, Javadian EA, Mohebali M (2013) First report on isolation and characterization of Leishmania major from Meriones hurrianae (Rodentia: Gerbillidae) of a rural cutaneous leishmaniasis focus in southeastern Iran. Iran Red Crescent Med J 15(9):789–793. https://doi.org/10.5812/ircmj.6974
Kavarizadeh F, Khademvatan S, Vazirianzadeh B, Feizhaddad MH, Zarean M (2017) Molecular characterization of Leishmania parasites isolated from sandflies species of a zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in Musiyan south west Iran. J Parasit Dis 41(1):274–281
Kermanjani A, Akhlaghi L, Oormazdi H, Hadighi H (2017) Isolation and identification of cutaneous leishmaniasis species by PCR–RFLP in Ilam province, the west of Iran. J Parasit Dis 41(1):175–179
Mehrabani D, Motazedian MH, Oryan A, Asgari Q, Hatam GR, Karamian M (2007) A search for the rodent hosts of Leishmania major in the Larestan region of southern Iran: demonstration of the parasite in Tatera indica and Gerbillus sp., by microscopy, culture and PCR. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 101(4):315–322
Mesghali A, Seyedi-Rashti MA, Nadim A (1967) Epidemiology of cutaneous leishmaniasis in Iran. II. Natural leptomonad infection of sand flies in the Meshed and Lotfabad areas. Bull Soc Pathol Exot 60(6):514–518
Mirzaei A, Rouhani S, Taherkhani H, Farahmand M, Kazemi B, Hedayati M, Baghaei A, Davari B, Parvizi P (2011) Isolation and detection of Leishmania species among naturally infected Rhombomis opimus, a reservoir host of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in Turkemen Sahara, North East of Iran. Exp Parasitol 129(4):375–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2011.08.020
Moemenbellah-Fard MD, Kalantari M, Rassi Y, Javadian E (2003) The PCR-based detection of Leishmania major infections in Meriones libycus (Rodentia: Muridae) from southern Iran. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 97(8):811–816
Mohammadi S, Parvizi P (2016) Simultaneous morphological and molecular characterization of Tatera indica in Southwestern Iran. J Arthropod Borne Dis 10(1):55–64
Mohammadi S, Vazirianzadeh B, Fotouhi-Ardakani R, Alaee Novin E, Amirkhani A, Samii J, Esmaeili Rastaghi AR, Parvizi P (2016) Tatera indica (Rodentia: Muridae) as the prior concern and the main reservoir host of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis on the border of Iran and Iraq. Jundishapur J Microbiol 10(1):e42452. https://doi.org/10.5812/jjm.42452
Mohebali M, Motazedian MH, Parsa F, Hajjaran H, Yaghoobi-Ershadi MR (2002) Identification of Leishmania species from different parts of Iran using a random amplified polymorphic DNA in humans, animal reservoirs and vectors. Med J Islam Repub Iran 15(34):243–246
Mohebali M, Javadian E, Yaghoobi-Ewrshadi MR, Akhavan AA, Hajjaran H, Abai MR (2004) Characterization of Leishmania infection in rodents from endemic areas of the Islamic Republic of Iran. East Mediterr Health J 10(4–5):591–598
Motazedian MH, Noyes H, Maingon R (2002) Leishmania and Sauroleishmania: the use of random amplified polymorphic DNA for identification of parasites from vertebrates and invertebrates. Exp Parasitol 83(1–4):10–16
Motazedian MH, Mehrabani D, Oryan A, Asgari Q, Karamian M, Kalantari M (2006) Life cycle of cutaneous leishmaniasis in Larestan, southern Iran. Iran J Clin Infect Dis 1(3):137–143
Motazedian MH, Parhizkari M, Mehrabani D, Hatam G, Asgari Q (2010) First detection of Leishmania major in Rattus norvegicus from Fars Province, Southern Iran. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 10(10):969–975. https://doi.org/10.1089/vbz.2008.0214
Nadim A, Faghih M (1968) Epidemiology of cutaneous leishmaniasis in the Isfahan province of Iran, I. The reservoir, II. The human disease. J Trop Med Hyg 62:534–542
Nadim A, Seyedi-Rashti MA (1971) A brief review of the epidemiology of various types of leishmaniasis in Iran. Acta Med Iran 14:99–106
Nadim A, Tahvildar-Bidruni GH (1977) Epidemiology of cutaneous leishmaniasis in Iran. B. Khorassan, part VI: cutaneous leishmaniasis in Neishabur, Iran. Bull Soc Pathol Exot 70:171–177
Nadim A, Seyedi-Rashti MA, Mesghali A (1968) Epidemiology of cutaneous leishmaniasis in Turkemen Sahara, Iran. J Trop Med Hyg 71:238–239
Nadim A, Mesghali A, Javadian E (1977) Cutaneous leishmaniasis in southern Iran. Ecology des leishmaniasis No. 239
Oshaghi MA, Yaghobi-Ershadi MR, Abbassi M, Parvizi P, Akhavan AA, Rahimi Foroshani A, Zahraei AR, Rassi Y, Mohtarami F (2008) Detection of Leishmania major in naturally infected sand flies using semi nested-PCR. Iran J Public Health 37(4):59–64
Parvizi P, Ready PD (2008) Nested PCRs and sequencing of nuclear ITS-rDNA fragments detect three Leishmania species of gerbils in sand flies from Iranian foci of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis. Trop Med Int Health 13:1159–1171
Parvizi P, Moradi G, Akbari G, Farahmand M, Ready PD, Piazak N, Assmar M, Amirkhani A (2008) PCR detection and sequencing of parasite ITS-rDNA gene from reservoirs host of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in central Iran. Parasitol Res 103(6):1273–1278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-1124-z
Parvizi P, Akhoundi M, Mirzaei H (2012) Distribution, fauna and seasonal variation of sandflies, simultaneous detection of nuclear internal transcribed spacer ribosomal DNA gene of Leishmania major in Rhombomys opimus and Phlebotomus papatasi, in Natanz district in central part of Iran. Iran Biomed J 16(2):113–120
Parvizi P, Alaeenovin E, Kazerooni PA, Ready PD (2013) Low diversity of Leishmania parasites in sandflies and the absence of the great gerbil in foci of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in Fars province, southern Iran. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 107(6):356–362. https://doi.org/10.1093/trstmh/trt027
Pourmohammadi B, Motazedian MH, Kalantari M (2008) Rodent infection with Leishmania in a new focus of human cutaneous leishmaniasis, in northern Iran. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 102(2):127–133. https://doi.org/10.1179/136485908X252223
Rab MA, Azmi FA, Iqbal J, Hamid J, Ghafoor A, Burney MI, Seyedi-Rashti MA (1986) Cutaneous leishmaniasis in Baluchistan reservoir host and sand fly vector in Uthal, Lasbella. J Pak Med Assoc 36:134–138
Rafizadeh S, Saraei M, Abai MR, Oshaghi MA, Mohebali M, Peymani A (2016) Molecular detection of Leishmania major and L. turanica in Phlebotomus papatasi and first natural infection of Ph. salehi to L. major in northeast of Iran. J Arthropod Borne Dis 10(2):141–147
Rassi Y, Hanafi-Bojd AA (2006) Sand flies (leishmaniasis vectors) with pictorial identification key. Noavaran-e-elm Press, Tehran, Iran, pp 156–169
Rassi Y, Jalali M, Javadian E, Motazedian MH (2001) Confirmation of Meriones libycus (Rodentia: Gerbillidae) as the main reservoir host of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in Arsanjan, Fars Province, south of Iran (1999–2000). Iran J Public Health 30(3–4):143–144
Rassi Y, Kaverizadeh F, Javadian E, Mohebali M (2004) First report on natural promastigote infection of Phlebotomus caucasicus in a new focus of visceral leishmaniasis in north west of Iran. Iran J Public Health 33(4):70–72
Rassi Y, Javadian E, Amin M, Rafizadeh S, Vatandoost H, Motazedian H (2006) Meriones libycus is the main reservoir of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in South Islamic Republic of Iran. East Mediterr Health J 12(3–4):475–477
Rassi Y, Abai MR, Javadian E, Rafizadeh S, Imamian H, Mohebali M, Fateh M, Hajjaran H, Ismaili K (2008a) Molecular data on vectors and reservoir hosts of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in central Iran. Bull Soc Pathol Exot 101(5):425–428
Rassi Y, Sofizadeh A, Abai MR, Oshaghi MA, Rafizadeh S, Mohebail M, Mohtarami F, Salahi R (2008b) Molecular detection of Leishmania major in the vectors and reservoir hosts of cutaneous leishmaniasis in Kalaleh district, Golestan province, Iran. Iran J Arthropod-Borne Dis 2:21–27
Rassi Y, Oshaghi MA, Azani SM, Abai MR, Rafizadeh S, Mohebai M, Mohtarami F, Zeinali MK (2010) Molecular detection of Leishmania infection due to Leishmania major and Leishmania turanica in the vectors and reservoir host in Iran. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 11(2):145–150. https://doi.org/10.1089/vbz.2009.0167
Rassi Y, Saghafipour Reza AM, Oshaghi MA, Rafizadeh S, Mohebali M, Yaghoobi-Ershadi MR, Mohtarami F, Farzinnia B (2011) Phlebotomus papatasi and Meriones libycus as the vector and reservoir host of cutaneous leishmaniasis in Qomrood District, Qom Province, central Iran. Asian Pac J Trop Med 4(2):97–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1995-7645(11)60045-X
Rassi Y, Karami H, Abai MR, Mohebali M, Bakhshi H, Oshaghi MA, Rafizadeh S, Bagherpoor Hagigi H, Hosseini A, Gholami M (2013) First detection of Leishmania infantum DNA in wild caught Phlebotomus papatasi in endemic focus of cutaneous leishmaniasis, south of Iran. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 3(10):825–829
Rassi Y, Abai MR, Rafizadeh S (2015) Molecular confirmation of main vector and reservoir host of cutaneous leishmaniasis in new focus of disease in south of Iran. J Entomol Zool Stud 3(1):140–143
Rouhani S, Mirzaei A, Spotin A, Parvizi P (2014) Novel identification of Leishmania major in Hemiechinus auritus and molecular detection of this parasite in Meriones libycus from an important foci of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in Iran. J Infect Public Health 7(3):210–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2013.12.002
Salam N, Mohammed Al-Shaqha W, Azzi A (2014) Leishmaniasis in the Middle East: incidence and epidemiology. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 8(10):e3208. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0003208
Seyedi-Rashti MA, Nadim A (1967) Epidemiology of cutaneous leishmaniasis in Iran. B. Khorasan area, I. The reservoirs. J Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales 60:510–514
Shirmohammadi H, Kayedi MH, Abai MR, Zahraie Ramazani A, Moradi M, Mohebali M, Rafizadeh S, Rassi Y (2017) First molecular detection of Leishmania major DNA within Meriones persicus in new focus of cutaneous leishmaniasis in Lorestan Province, West of Iran. J Entomol Zool Stud 5(2):1187–1190
Shirzadi MR, Gouya MM (2010) National guidelines for cutaneous leishmaniasis surveillance in Iran. Publication of the Zoonoses Control Department, Minstry of Health and Medical Education, Tehran, Iran, pp 1–78 (in Persian)
Tashakori M, Ajdary S, Kariminia A et al (2003) Characterization of Leishmania species and L. major strains in different endemic areas of leishmaniasis in Iran. Iran Biomed J 7:43–50
Vahabi A, Rassi Y, Oshaghi MA, Sayyadi M, Rafizadeh S (2016) Detection of Leishmania major DNA within wild caught Phlebotomus papatasi and species composition of sand flies in endemic focus of cutaneous leishmaniasis, in western Iran. J Parasit Dis 40(1):69–74
Vazirianzadeh B, Saki J, Jahanifard E, Zarean M, Amraee K, Navid Pour S (2013) Isolation and Identification of Leishmania species from sandflies and rodents collected from Roffaye district, Khuzestan province, southwest of Iran. Jundishapur J Microbiol 6(6):e10025. https://doi.org/10.5812/jjm.10025
World Health Organization (2000) Epidemiological aspects control of the leishmaniasis. WHO Tech Rep Ser 793:41–46
World Health Organization (2010) Control of the Leishmaniases. World Health Org Tech Rep Ser 949:22–26
World Health Organization (2017) Leishmaniasis: epidemiological situation. http://www.who.int/leishmaniasis/burden/en. Accessed 22 June 2017
Yaghoobi-Ershadi MR (2012a) Phlebotomine sand flies (Diptera: Psychodidae) in Iran and their role on Leishmania transmission. J Arthropod Borne Dis 6(1):1–17
Yaghoobi-Ershadi MR (2012b) Phlebotomine sand flies (Diptera: Psychodidae) in Iran and their role on Leishmania Transmission. J Arthropod-Borne Dis 6(1):1–17
Yaghoobi-Ershadi MR, Javadian E (1996) Epidemiological study of reservoir hosts in an endemic area of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in Iran. Bull World Health Organ 74:587–590
Yaghoobi-Ershadi MR, Javadian E, Tahvildare-Bidruni GH (1994) The isolation of Leishmania major from Phlebotomus (Paraphlebotomus) caucasicus in Isfahan province, Islamic Republic of Iran. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 88:518–519
Yaghoobi-Ershadi MR, Javadian E, Tahvildare-Bidruni GH (1995) Leishmania major MON-26 isolated from naturally infected Phlebotomus papatasi (Diptera: Psychodidae) in Isfahan province, Iran. Acta Trop 59:279–282
Yaghoobi-Ershadi MR, Akhavan A, Mohebali M (1996) Meriones libycus and Rhombomys opimus (Rodentia: Gerbellidae) are the main reservoir hosts in a new focus of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 90:503–504
Yaghoobi-Ershadi MR, Hanafi-Bojd AA, Akhavan AA, Zahrai-Ramazani AR, Mohebali M (2001a) Epidemiological study in a new focus of cutaneous leishmaniosis due to Leishmania major in Ardestan town, central Iran. Acta Trop 79(2):115–121
Yaghoobi-Ershadi MR, Akhavan AA, Mohebali M (2001b) Monthly variation of Leishmania major MON-26 infection rates in Phlebotomus papatasi (Diptera: Psychodidae) from rodent burrows in Badrood area of Iran. Med J Islam Repub Iran 15(3):175–178
Yaghoobi-Ershadi MR, Akhavan AA, Zahraei-Ramazani AV, Abai MR, Ebrahimi B, Vafaei-Nezhad R, Hanafi-Bojd AA, Jafari R (2003) Epidemiological study in a new focus of cutaneous leishmaniasis in the Islamic Republic of Iran. East Mediterr Health J 9(4):816–826
Yaghoobi-Ershadi MR, Jafari R, Hanafi-Bojd AA (2004) A new epidemic focus of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in central Iran. Ann Saudi Med 24(2):98–101
Yaghoobi-Ershadi MR, Akhavan AA, Zahraei- Ramazani AR, Jalali-Zand AR, Piazak N (2005) Bionomics of Phlebotomus papatasi (Diptera: Psychodidae) in an endemic focus of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in central Iran. J Vect Ecol 30(1):115–118
Yaghoobi-Ershadi M, Hakimiparizi M, Zahraei-Ramazani A, Abdoli H, Akhavan A, Aghasi M, Arandian M, Ranjbar A (2010) Sand fly surveillance within an emerging epidemic focus of cutaneous leishmaniasis in southeastern Iran. J Arthropod Borne Dis 4(1):17–23
Yaghoobi-Ershadi MR, Shahbazi F, Darvishi M, Akhavan AA, Jafari R, Khajeian M, Rassi Y, Soleimani H, Shirzadi MR, Hanafi-Bojd AA, Darabi H, Arandian MH, Sanei-Dehkordi A, Heidari M (2013) Molecular epidemiological study of cutaneous leishmaniasis in the focus of Bushehr city, southwestern Iran. J Arthropod Borne Dis 7(2):113–121
Yaghoobi-Ershadi MR, Marvi-Moghadam N, Jafari R, Akhavan AA, Solimani H, Zahrai-Ramazani AR, Arandian MH, Dehghan-Dehnavi AR (2015) Some epidemiological aspects of cutaneous leishmaniasis in a new focus, central Iran. Dermatol Res Pract 2015:286408. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/286408
Yazdanpanah H, Rostamianpur M (2013) Analysis of spatial distribution of leishmaniasis and its relationship with climatic parameters (case study: Ilam province). Bull Environ Pharmacol Life Sci 2(12):80–86
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely acknowledge their gratitude to the efforts of CDC staff of the Mehran Health Center. Authors are highly thankful to Mr. Hossein Davoodi, technician of Museum of Medical Entomology (TUME), School of Public Health (SPH), Tehran University of Medical Sciences (TUMS) for assistance in archiving the sand flies slides. Thanks also to Mr. Yassin Ghasemi, technician of SPH Animal House, TUMS, for his assist in maintenance of the field caught rodents. This study was supported by Tehran University of Medical Sciences; Project No. 28137.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moradi, M., Rassi, Y., Abai, M.R. et al. Some epidemiological aspects of cutaneous leishmaniasis with emphasis on vectors and reservoirs of disease in the borderline of Iran and Iraq. J Parasit Dis 42, 243–251 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-018-0991-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-018-0991-1