Abstract
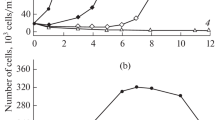
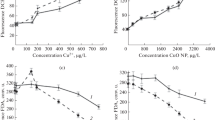
The effect of three Group IV metals (titanium, zirconium and tin) on the growth, morphology and chemical composition of the freshwater diatom Synedra acus subsp. radians (Kützing) Skabichevsky was studied and compared with germanium. The elements in their highest oxidation states were introduced into the culture medium in the form of hydroxides. Germanium was found to be toxic at ≥5 mol. % of the total Ge-Si content in the culture medium. In the presence of other elements, a slight decrease in the cell division rate was observed independent of the element within 1–15% content interval. The analysis of the obtained biomass and silica valves revealed the presence of all the added elements within the cells. However, only germanium was incorporated into the valves in considerable amounts. S. acus cultivation with the addition of 5% Group IV elements resulted in cells having the following aberrations in the structure of the silica valves: changes in valve shape, thickening of valves, alterations of the areolae rows, irregularity or absence of the areolae and a decrease in the mechanical strength of valves. Moreover, the effect of Group IV elements on silica formation was simulated in vitro using a synthetic polymer bearing polyamine and phosphate groups found in silaffines (proteins from diatom frustules). The studied elements were observed to provoke the formation of unstable silica particles in solution. We propose that the observed effects of germanium, titanium, zirconium and tin on diatom growth and structure are due to uncontrollable silica condensation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tréguer P, Nelson DM, Van Bennekom AJ et al (1995) The balance of silica in the world ocean: a reestimate. Science 268:375–379
Round FE, Chapman DJ (eds) (1990) Progress in phycological research. Biopress, Bristol
Round F, Crawford R, Mann D (1990) The diatoms. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Grachev MA, Annenkov VV, Likhoshway YeV (2008) Silicon nanotechnologies of pigmented heterokonts. BioEssays 30(4):328–337
Bao Z, Weatherspoon MR, Shian S et al (2007) Chemical reduction of three-dimensional silica micro-assemblies into microporous silicon replicas. Nature 446:172–175
Umernura K, Gao Y, Nishikawa T (2010) Preparation of photocatalyst using diatom frustules by liquid phase deposition method. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 10:4883–4888
Nassif N, Livage J (2011) From diatoms to silica-based biohybrids. Chem Soc Rev 40:849–859
Lewin J (1966) Silicon Metabolism in Diatoms. V. Germanium Dioxide, a Specific Inhibitor of Diatom Growth. Phycologia 6:1–12
Mehard CW, Sullivan CW, Azam F (1974) Role of silicon in diatom metabolism IV. Subcellular localization of silicon and germanium in Nitzschia alba and Cylindrotheca fusiformis. Physiol Plant 30:265–272
Rorrer GL, Chang C-H, Jiao J et al (2005) Biosynthesis of silicon-germanium oxide nanocomposites by the marine diatom Nitzschia frustulum. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 5:41–49
Jeffryes C, Gutu T, Jiao J et al (2008) Two-stage photobioreactor process for the metabolic insertion of nanostructured germanium into the silica microstructure of the diatom Pinnularia sp. Mater Sci Eng C 28(1):107–118
Jeffryes C, Solanki R, Rangineni Y et al (2008) Electroluminescence and photoluminescence from nanostructured diatom frustules containing metabolically inserted germanium. Adv Mater 20(13):2633–2637
Qin T, Gutu T, Jiao J et al (2008) Biological fabrication of photoluminescent nanocomb structures by metabolic incorporation of germanium into the biosilica of the diatom Nitzschia frustulum. ACS Nano 2:1296–1304
Gutu T, Dong L, Jiao J et al (2005) Characterization of silicon-germanium oxide nanocomposites fabricated by the marine diatom Nitzschia frustulum. Microsc Microanal 11:1958–1959
Li C-W, Chu S, Lee M (1989) Characterizing the silica deposition vesicle of diatoms. Protoplasma 151(2–3):158–163
Desclés J, Vartanian M, Harrak Ael et al (2008) New tools for labeling silica in living diatoms. New Phytol 177(3):822–829
Annenkov VV, Danilovtseva EN, Zelinskiy SN et al (2010) Novel fluorescent dyes based on oligopropylamines for the in vivo staining of eukaryotic unicellular algae. Anal Biochem 407(1):44–51
Dixit SS, Smol JP, Kingston JC et al (1992) Diatoms: powerful indicators of environmental change. Environ Sci Technol 26(1):23–33
Horvatic J, Peršić V (2007) The Effect of Ni2 + , Co2 + , Zn2 + , Cd2 + and Hg2 + on the growth rate of marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum Bohlin: microplate growth inhibition test. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79(5):494–498
Mason RP, Reinfelder JR, Morel FMM (1996) Uptake, toxicity, and trophic transfer of mercury in a coastal diatom. Environ Sci Technol 30:1835–1845
Zhong H, Wang W-X (2009) Controls of dissolved organic matter and chloride on mercury uptake by a marine diatom. Environ Sci Technol 43:8998–9003
Duong TT, Morin S, Coste M et al (2010) Experimental toxicity and bioaccumulation of cadmium in freshwater periphytic diatoms in relation with biofilm maturity. Sci Total Environ 408(3):552–562
Brembu T, Jørstad M, Winge P (2011) Genome-wide profiling of responses to cadmium in the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Environ Sci Technol 45:7640–7647
Miao A-J, Wang W-X (2007) Predicting copper toxicity with its intracellular or subcellular concentration and the thiol synthesis in a marine diatom. Environ Sci Technol 41:1777–1782
Guiry MD, Guiry GM (2012) AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched on 24 Feb 2012
Safonova TA, Annenkov VV, Chebykin EP et al (2007) Aberration of morphogenesis of siliceous frustule elements of the diatom Synedra acus in the presence of germanic acid. Biochemistry-Moscow 72(11):1261–1270
Thompson AS, Rhodes JC, Pettman I (1988) Culture collections of algae and protozoa: catalogue of strains. Titus Wilson and Son, Kendal
Safonova TA, Aslamov IA, Basharina TN et al (2007) Cultivation and automatic counting of diatom algae cells in multi-well plastic plates. Diatom Res 22:189–195
Iler R (1979) The chemistry of silica. Wiley, New York, NY
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 17:208–212
Belton D, Paine G, Patwardhan SV, Perry CC (2004) Towards an understanding of (bio)silicification: the role of amino acids and lysine oligomers in silicification. J Mater Chem 14:2231–2241
Box MJ (1965) A new method of constrained optimisation and a comparison with other methods. Computer J 8:42–52
Pittrian FK (1940) Detection and elimination of phosphate in qualitative analysis by means of zirconium salts. Ind Eng Chem 12:514–515
Chiappino ML, Azam F, Volcani BE (1977) Effect of germanic acid on developing cell walls of diatoms. Protoplasma 93:191–204
Jeffryes C, Gutu T, Jiao J et al (2008) Metabolic insertion of nanostructured TiO2 into the patterned biosilica of the diatom Pinnularia sp. by a two-stage bioreactor cultivation process. ACS Nano 2:2103–2112
Sumper M (2004) Biomimetic patterning of silica by long-chain polyamines. Angew Chem Int Ed 116:2301–2304
Annenkov VV, Danilovtseva EN, Pal’shin VA et al (2011) Poly (vinyl amine) – silica composite nanoparticles: models of the silicic acid cytoplasmic pool and as a silica precursor for composite materials formation. Biomacromolecules 12:1772–1780
Kröger N, Deutzmann R, Sumper M (1999) Polycationic peptides from diatom biosilica that direct silica nanosphere formation. Science 286:1129–1132
Sumper M, Kröger N (2004) Silica formation in diatoms: the function of long-chain polyamines and silaffins. J Mater Chem 14:2059–2065
Annenkov VV, Danilovtseva EN, Likhoshway YV et al (2008) Controlled stabilisation of silicic acid below pH 9 using poly(1-vinylimidazole). J Mater Chem 18:553–559
Klüfers P, Vogler C (2007) Polyol metal complexes. Part 55. Germanes with alkylenedioxy substituents. Z Anorg Allg Chem 633:908–912
Erxleben A, Claffey J, Tacke M (2010) Binding and hydrolysis studies of antitumoural titanocene dichloride and Titanocene Y with phosphate diesters. J Inorg Biochem 104:390–396
Kohli P, Blanchard GJ (2000) Probing interfaces and surface reactions of zirconium phosphate/phosphonate multilayers using 31P NMR spectrometry. Langmuir 16:695–701
Arjmand F, Jamsheera A (2011) Synthesis, characterization and in vitro DNA binding studies of tin(IV) complexes of tert-butyl 1-(2-hydroxy-1-phenylethylamino)-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl carbamate. J Organomet Chem 696:3572–3579
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basharina, T.N., Danilovtseva, E.N., Zelinskiy, S.N. et al. The Effect of Titanium, Zirconium and Tin on the Growth of Diatom Synedra Acus and Morphology of Its Silica Valves. Silicon 4, 239–249 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-012-9119-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-012-9119-x