Abstract
Objectives
The aim of this study was to explore the frequency of malnutrition risk and associated risk of falling, social and mental factors among elderly without home-help service. The aim was also to explore factors associated with risk of falling.
Design
A cross-sectional design was used.
Setting
Elderly persons own homes.
Participants
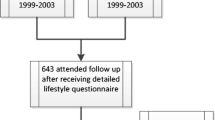
Data were collected during preventive home visits to 565 elderly (age range 73–90 years) without home-help service. Those with complete SCREEN II forms were included in the study (n=465).
Measurements
Measurements included rating scales regarding malnutrition risk (SCREEN II) and risk of falling (Downton). In addition, single-items: general health, satisfaction with life, tiredness, low-spiritedness, worries/anxiety and sleeping were used.
Results
According to the SCREEN II, 35% of the sample had no malnutrition risk, 35% had moderate risk and 30% had high malnutrition risk. In an ordinal regression analysis, increased malnutrition risk was associated with being a woman living alone (OR 4.63), male living alone (OR 6.23), lower age (OR 0.86), poorer general health (OR 2.03–5.01), often/always feeling tired (OR 2.38), and an increased risk of falling (OR 1.21). In a linear regression analysis, risk of falling was associated with higher age (B 0.020), not shopping independently (B 0.162), and low meat consumption (B 0.138).
Conclusion
There are complex associations between malnutrition risk and the gender-cohabitation interaction, age, general health, tiredness, and risk of falling. In clinical practice comprehensive assessments to identify those at risk of malnutrition including associated factors are needed. These have to be followed by individual nutritional interventions using a holistic perspective which may also contribute to reducing the risk of falling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edfors, E., and Westergren, A. Home-Living Elderly People’s Views on Food and Meals. Journal of aging research 2012, 761291.
Keller, H.H. The SCREEN I (Seniors in the Community: Risk Evaluation for Eating and Nutrition) index adequately represents nutritional risk. J Clin Epidemiol 2006;59, 836–841.
Keller, H.H. Meal programs improve nutritional risk: a longitudinal analysis of community-living seniors. J Am Diet Assoc 2006;106, 1042–1048.
Pajalic, Z., Skovdahl, K., Westergren, A., and Persson, L. How the professionals can identify needs for improvement and improve Food Distribution service fort he homeliving elderly people in Sweden — an action research project. Journal of Nursing Education and Practice 2013;3, 29–40.
Roy, M.A., and Payette, H. Meals-on-wheels improves energy and nutrient intake in a frail free-living elderly population. J Nutr Health Aging 2006;10, 554–560.
Johansson, Y., Bachrach-Lindstrom, M., Carstensen, J., and Ek, A.C. Malnutrition in a home-living older population: prevalence, incidence and risk factors. A prospective study. J Clin Nurs 2009;18, 1354–1364.
Keller, H.H., Goy, R., and Kane, S.L. Validity and reliability of SCREEN II (Seniors in the community: risk evaluation for eating and nutrition, Version II). Eur J Clin Nutr 2005;59, 1149–1157.
Keller, H.H., and Hedley, M.R. Nutritional risk needs assessment of communityliving seniors: prevalence of nutrition problems and priorities for action. Journal of community health 2002;27, 121–132.
Bartali, B., Frongillo, E.A., Bandinelli, S., Lauretani, F., Semba, R.D., Fried, L.P., and Ferrucci, L. Low nutrient intake is an essential component of frailty in older persons. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2006;61, 589–593.
Locher, J.L., Roth, D.L., Ritchie, C.S., Cox, K., Sawyer, P., Bodner, E.V., and Allman, R.M. Body mass index, weight loss, and mortality in community-dwelling older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2007;62, 1389–1392.
Ritchie, C.S., Locher, J.L., Roth, D.L., McVie, T., Sawyer, P., and Allman, R. Unintentional weight loss predicts decline in activities of daily living function and life-space mobility over 4 years among community-dwelling older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2008;63, 67–75.
Vailas, L.I., Nitzke, S.A., Becker, M., and Gast, J. Risk indicators for malnutrition are associated inversely with quality of life for participants in meal programs for older adults. J Am Diet Assoc 1998;98, 548–553.
Janssen, I., Shepard, D.S., Katzmarzyk, P.T., and Roubenoff, R. The healthcare costs of sarcopenia in the United States. J Am Geriatr Soc 2004;52, 80–85.
Payette, H., Coulombe, C., Boutier, V., and Gray-Donald, K. Nutrition risk factors for institutionalization in a free-living functionally dependent elderly population. J Clin Epidemiol 2000;53, 579–587.
MacIntosh, C., Morley, J.E., and Chapman, I.M. The anorexia of aging. Nutrition 2000;16, 983–995.
Payette, H., Coulombe, C., Boutier, V., and Gray-Donald, K. Weight loss and mortality among free-living frail elders: a prospective study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 1999;54, M440–445.
Beck, A.M., Ovesen, L., and Osler, M. The’ Mini Nutritional Assessment’ (MNA) and the ‘Determine Your Nutritional Health’ Checklist (NSI Checklist) as predictors of morbidity and mortality in an elderly Danish population. Br J Nutr 1999;81, 31–36.
Payette, H. Nutrition as a determinant of functional autonomy and quality of life in aging: a research program. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2005;83, 1061–1070.
Alberda, C., Graf, A., and McCargar, L. Malnutrition: etiology, consequences, and assessment of a patient at risk. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2006;20, 419–439.
Chen, C.C.-H., Bai, Y.-Y., Huang, G.-H., and Tang, S.T. Revisiting the concept of malnutrition in older people. Journal of clinical nursing 2007;16, 2015–2026.
Callen, B.L., and Wells, T.J. Screening for nutritional risk in community-dwelling old-old. Public Health Nurs 2005;22, 138–146.
Locher, J.L., Robinson, C.O., Roth, D.L., Ritchie, C.S., and Burgio, K.L. The effect of the presence of others on caloric intake in homebound older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2005;60, 1475–1478.
Locher, J.L., Ritchie, C.S., Robinson, C.O., Roth, D.L., Smith West, D., and Burgio, K.L. A multidimensional approach to understanding under-eating in homebound older adults: the importance of social factors. Gerontologist 2008;48, 223–234.
White, J.V. Risk factors for poor nutritional status. Prim Care 1994;21, 19–31.
de Groot, C.P., van Staveren, W.A., and de Graaf, C. Determinants of macronutrient intake in elderly people. Eur J Clin Nutr 2000;54Suppl 3, S70–76.
Hughes, G., Bennett, K.M., and Hetherington, M.M. Old and alone: barriers to healthy eating in older men living on their own. Appetite 2004;43, 269–276.
Gustafsson, K., and Sidenvall, B. Food-related health perceptions and food habits among older women. Journal of Advanced Nursing 20002;39, 164–173.
Neyens, J., Halfens, R., Spreeuwenberg, M., Meijers, J., Luiking, Y., Verlaan, G., and Schols, J. Malnutrition is associated with an increased risk of falls and impaired activity in elderly patients in Dutch residential long-term care (LTC): a crosssectional study. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 2013;56, 265–269.
Downton, J.H., and Andrews, K. Prevalence, characteristics and factors associated with falls among the elderly living at home. Aging (Milano) 1991;3, 219–228.
Isenring, E., Baker, J., and Kerr, G. Malnutrition and falls risk in communitydwelling older adults. J Nutr Health Aging 2013;17, 277–279.
Meijers, J.M., Halfens, R.J., Neyens, J.C., Luiking, Y.C., Verlaan, G., and Schols, J.M. Predicting falls in elderly receiving home care: the role of malnutrition and impaired mobility. J Nutr Health Aging 2012;16, 654–658.
Cameron, I.D., Murray, G.R., Gillespie, L.D., Robertson, M.C., Hill, K.D., Cumming, R.G., and Kerse, N. Interventions for preventing falls in older people in nursing care facilities and hospitals. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2010;CD005465.
Cederholm, T., Cruz-Jentoft, A.J., and Maggi, S. Sarcopenia and fragility fractures. European journal of physical and rehabilitation medicine 2013;49, 111–117.
Gillespie, L.D., Robertson, M.C., Gillespie, W.J., Sherrington, C., Gates, S., Clemson, L.M., and Lamb, S.E. Interventions for preventing falls in older people living in the community. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012;9, CD007146.
Landi, F., Liperoti, R., Russo, A., Giovannini, S., Tosato, M., Capoluongo, E., Bernabei, R., and Onder, G. Sarcopenia as a risk factor for falls in elderly individuals: results from the ilSIRENTE study. Clin Nutr 2012;31, 652–658.
Villareal, D.T., Apovian, C.M., Kushner, R.F., and Klein, S. Obesity in older adults: technical review and position statement of the American Society for Nutrition and NAASO, The Obesity Society. Am J Clin Nutr 2005;82, 923–934.
Eiben, G., Dey, D.K., Rothenberg, E., Steen, B., Bjorkelund, C., Bengtsson, C., and Lissner, L. Obesity in 70-year-old Swedes: secular changes over 30 years. Int J Obes (Lond) 2005;29, 810–817.
Fange, A., and Ivanoff, S.D. The home is the hub of health in very old age: Findings from the ENABLE-AGE Project. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 2009;48, 340–345.
Dahlin-Ivanoff, S., Gosman-Hedstrom, G., Edberg, A.K., Wilhelmson, K., Eklund, K., Duner, A., Ziden, L., Welmer, A.K., and Landahl, S. Elderly persons in the risk zone. Design of a multidimensional, health-promoting, randomised three-armed controlled trial for “prefrail” people of 80+ years living at home. BMC Geriatr 2010;10, 27.
Elkan, R., Kendrick, D., Dewey, M., Hewitt, M., Robinson, J., Blair, M., Williams, D., and Brummell, K. Effectiveness of home based support for older people: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2001;323, 719–725.
Westergren, A., Nilsson, M., Edfors, E., Lindskov, S., and Hagell, P. Adaption of “seniors in the community: risk evaluation for eating and nutrition, version II” (SCREEN II) for use in Sweden: Report on the translation process and field test. Clinical nutrition, supplements 2010;5, 9–10.
Downton, J.H. Falls in the elderly, (London: Edward Arnold, 1993).
Nyberg, L., and Gustafson, Y. Using the Downton index to predict those prone to falls in stroke rehabilitation. Stroke 1996;27, 1821–1824.
Rosendahl, E., Lundin-Olsson, L., Kallin, K., Jensen, J., Gustafson, Y., and Nyberg, L. Prediction of falls among older people in residential care facilities by the Downton index. Aging Clin Exp Res 2003;15, 142–147.
Vassallo, M., Stockdale, R., Sharma, J.C., Briggs, R., and Allen, S. A comparative study of the use of four fall risk assessment tools on acute medical wards. J Am Geriatr Soc 2005;53, 1034–1038.
Altman, D.G. Practical statistics for medical research, 2 Edition, 1991, (Taylor & Francis).
Chan, Y. Biostatistics 305. Multinominal logistic regression. Singapore medical journal 2005;46, 259–269.
Ernsth Bravell, M., Westerlind, B., Midlov, P., Ostgren, C.J., Borgquist, L., Lannering, C., and Molstad, S. How to assess frailty and the need for care? Report from the Study of Health and Drugs in the Elderly (SHADES) in community dwellings in Sweden. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 2011;53, 40–45.
Gollub, E.A., and Weddle, D.O. Improvements in nutritional intake and quality of life among frail homebound older adults receiving home-delivered breakfast and lunch. J Am Diet Assoc 2004;104, 1227–1235.
Locher, J.L., Burgio, K.L., Yoels, W.C., and Ritchie, C.S. The Social Significance of Food and Eating in the Lives of Older Recipients of Meals on Wheels. Journal of Nutrition For the Elderly 1998;17, 15–33.
Nilsson, M.H., Hariz, G.M., Iwarsson, S., and Hagell, P. Walking ability is a major contributor to fear of falling in people with Parkinson’s disease: implications for rehabilitation. Parkinsons Dis 2012;2012, 713236.
English, K.L., and Paddon-Jones, D. Protecting muscle mass and function in older adults during bed rest. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2010;13, 34–39.
Evans, W.J. Skeletal muscle loss: cachexia, sarcopenia, and inactivity. Am J Clin Nutr 2010;91, 1123S–1127S.
Cruz-Jentoft, A.J., Baeyens, J.P., Bauer, J.M., Boirie, Y., Cederholm, T., Landi, F., Martin, F.C., Michel, J.P., Rolland, Y., Schneider, S.M., et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing 2010;39, 412–423.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Westergren, A., Hagell, P. & Sjödahl Hammarlund, C. Malnutrition and risk of falling among elderly without home-help service — A cross sectional study. J Nutr Health Aging 18, 905–911 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-014-0469-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-014-0469-5