Abstract
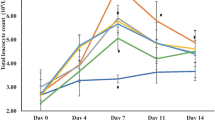
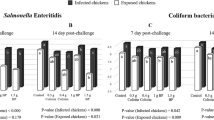
This study was conducted to investigate the effect of feeding a probiotic, Bacillus subtilis, on antibody titers against Newcastle and infectious bursal viruses in broiler chickens challenged with Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis. One hundred and sixty 1-day-old broiler chicks were randomly assigned to four treatments in a completely randomized design. The treatments were negative control, probiotic-treated group, challenged group, and challenged probiotic treated group. Salmonella challenging decreased (P < 0.05) the relative weights of spleen and bursa. Inclusion of probiotic to diet of challenged chickens increased the relative weight of spleen, but had no effect on the relative weight of bursa. There were no differences for the antibody titers of chickens between negative control and probiotic-treated group. Salmonella challenging decreased (P < 0.05) antibody titers against Newcastle and infectious bursal viruses. Improvements in the antibody titers were observed by the addition of probiotic to diet of these chickens. The results showed that dietary inclusion of probiotic had no significant effect on immune parameters of chickens at non-contaminated environment, display a greater efficacy at environment contaminated with pathogen and can improve immune responses of infected chickens.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sorum H, Sunde M (2001) Resistance to antibiotics in the normal flora of animals. Vet Res 32:227–241
Koenen ME, Kramer J, Van Der Hulst R et al (2004) Immunomodulation by probiotic lactobacilli in layer- and meat-type chickens. Brit Poult Sci 45:355–366
Allan WH, Gough LE (1974) A standard haemaglutination inhibition test for Newcastle disease: a comparison of macro and micro-methods. Vet Rec 95:120–123
Schierack P, Wieler LH, Taras D et al (2007) Bacillus cereus var. toyoi enhanced systemic immune response in piglets. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 118:1–11
Panigrahi A, Kiron V, Kobayashi T et al (2004) Immune responses in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss induced by a potential probiotic bacteria Lactobacillus rhamnosus JCM 1136. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 102:379–388
Haghighi HR, Gong J, Gyles CL et al (2005) Modulation of antibody-mediated immune response by probiotics in chickens. Clin Diag Lab Immunol 12:1387–1392
Kim DH, Austin B (2006) Cytokine expression in leucocytes and gut cells of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum, induced by probiotics. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 114:297–304
Panda AK, Ramarao SV, Reddy MR et al (1999) Effect of dietary inclusion of probiotic on growth, carcass traits and immune response in broilers. Indian J Poult Sci 34:343–346
Seifert S, Fritz C, Carlini N et al (2011) Modulation of innate and adaptive immunity by the probiotic Bifidobacterium longum PCB133 in turkeys. Poult Sci 90:2275–2280
Khaksefidi A, Ghoorchi T (2006) Effect of probiotic on performance and immunocompetence in broiler chicks. J Poult Sci 43:296–300
Li SP, Zhao XJ, Wang JY (2009) Synergy of Astragalus polysaccharides and probiotics (Lactobacillus and Bacillus cereus) on immunity and intestinal microbiota in chicks. Poult Sci 88:519–525
Elangovan AV, Mandal AB, Shrivastav AK, Yadhav AS (2011) Supplementing probiotics (GalliPro) to broiler chicken on growth performance, immunity and gut microbial population. Anim Nut Feed Technol 11:169–176
Rahimi S, Khaksefidi A (2010) A comparison between the effects of a probiotic (Bioplus 2B) and an antibiotic (virginiamycin) on the performance of broiler chickens under heat stress condition. Iran J Vet Res 7:23–28
Okamura M, Lillehoj HS, Raybourne RB et al (2004) Cell-mediated immune responses to a killed Salmonella enteritidis vaccine: lymphocyte proliferation, T-cell changes and interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-1, IL-2, and IFN-γ production. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 27:255–272
Maassen CB, Van Holten-Neelen C, Balk F et al (2000) Strain-dependent induction of cytokine profiles in the gut by orally administered Lactobacillus strains. Vaccine 18:2613–2623
Post J, Rebel JMJ, Huurne AAHM (2003) Physiological effects of elevated plasma corticosterone concentrations in broiler chickens. An alternative means by which to assess the physiological effects of stress. Poult Sci 82:1313–1318
Gross WB (1992) Effect of short-term exposure of chickens to corticosterone on resistance to challenge exposure with Escherichia coli and antibody response to sheep erythrocytes. Am J Vet Res 27:972–979
Vleck CM, Vertalino N, Vleck D et al (2000) Stress, corticosterone, and heterophil to lymphocyte ratios in free-living adélie penguins. The Condor 102:392–400
Khansari DN, Murgo AJ, Faith RE (1990) Effects of stress on the immune system. Immunol Today 11:170–175
Maxwell MH, Robertson GW (1998) The avian heterophil leukocyte: a review. World’s Poult Sci J 54:155–178
Higgins SE, Torres-Rodriguez A, Vicente JL et al (2005) Evaluation of intervention strategies for idiopathic diarrhea in commercial turkey brooding houses. J Appl Poult Res 14:345–348
Gaggia F, Mattarelli P, Biavati B (2010) Probiotics and prebiotics in animal feeding for safe food production. Int J Food Microbiol 141:S15–S28
Selvam R, Maheswari P, Kavitha P et al (2009) Effect of Bacillus subtilis PB6, a natural probiotic on colon mucosal inflammation and plasma cytokines levels in inflammatory bowel disease. Indian J Biochem Biophys 46:79–85
Swaggerty CL, Kaiser P, Rothwell L et al (2006) Heterophil cytokine mRNA profiles from genetically distinct lines of chickens with differential heterophil-mediated innate immune responses. Avian Pathol 35:102–108
Riddell C (1987) Page 10 in: avian histopathology. American Association of Avian Pathologists, Kennett Square
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Islamic Azad University for research funding support, to the Agricultural, Medical and Industrial Research School, NSTRI, for supplying the basal diet and allowing the use of their poultry unit, and to the Biochem Company (Zusatzstoffe GmbH, Germany) for providing a sample of the probiotic Gallipro®. We also thank all of the staff members at the poultry unit for the assistance in the care and feeding of the chickens used in this research.
Conflict of interest
Ali Asghar Sadeghi, Parvin Shawrang and Shirin Shakorzadeh declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadeghi, A.A., Shawrang, P. & Shakorzadeh, S. Immune Response of Salmonella Challenged Broiler Chickens Fed Diets Containing Gallipro®, a Bacillus subtilis Probiotic. Probiotics & Antimicro. Prot. 7, 24–30 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-014-9175-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-014-9175-1