Abstact
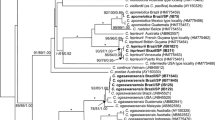
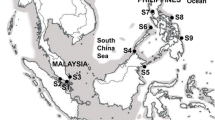
Although the marine red algal genus Neosiphonia is well characterized, many species of Neosiphonia are poorly understood. To correctly define the species delimitation of Neosiphonia yendoi using genetic variation, owing to the confusion over identification with “N. sphaerocarpa” from Korea, we investigated intensively the haplotype network of the mitochondrial COI and the plastid rbcL genes of specimens collected from Korea and Japan. The molecular analyses indicated that specimens collected in different sites of Korea and Japan belong to the same species, Neosiphonia yendoi and “Neosiphonia sphaerocarpa” from Korea, which is distinguished from N. sphaerocarpa from Florida and is allied with N. yendoi collected from the type locality, Muroran of Japan. A total of 29 COI and 13 rbcL haplotypes were found and the COI haplotype network shows evidence of a clear break between specimens from Jeju Island and all other locations of Korea, suggesting the possibility of cryptic diversity within N. yendoi.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott IA (1999) Marine red algae of the Hawaiian Islands. Bishop Museum Press, Honolulu, 477 p
Bárbara I, Choi H-G, Secilla A, Díaz-Tapia P, Gorostiaga JM, Seo TK, Jung MY, Berecibar E (2013) Lampisiphonia iberica gen. et sp. nov. (Ceramiales, Rhodophyta) based on morphology and molecular evidence. Phycologia 52:137–155
Boo GH, Mansilla A, Nelson W, Bellgrove A, Boo SM (2014) Genetic connectivity between trans-oceanic populations of Capreolia implexa (Gelidiales, Rhodophyta) in cool temperate waters of Australasia and Chile. Aquat Bot 119:73–79
Clement M, Posada D, Crandall KA (2000) TCS: a computer program to estimate gene genealogies. Mol Ecol 9:1657–1669
Guiry MD, Guiry GM (2015) AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org Accessed 7 Mar 2015
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids S 41:95–98
Hewitt CL, Campbell ML, Schaffelke B (2007) Introductions of seaweeds accidental transfer pathways and mechanisms. Bot Mar 50:326–337
Kang JC, Yang MY, Lin S-M, Kim MS (2015) Reappraisal of nine species of Martensia (Dlesseriaceae, Rhodophyta) reported from Korea based on morphology and molecular analyses. Bot Mar 58:151–166
Kang JW (1966) On the geographic distribution of marine algae in Korea. Bull Pusan Fish Coll 7:1–123
Kim B, Kim MS (2014) Three new species of Polysiphonia sensu lato (Rhodophyta) based on the morphology and molecular evidence. Algae 29:183–195
Kim KM, Hoarau G, Boo SM (2012) Genetic structure and distribution of Gelidium elegans (Gelidiales, Rhodophyta) in Korea based on mitochondrial cox1 sequence data. Aquat Bot 98:27–33
Kim MS, Abbott IA (2006) Taxonomic notes on Hawaiian Polysiphonia, with transfer to Neosiphonia (Rhodomelaceae, Ceramiales, Rhodophyta). Phycol Res 54:32–39
Kim MS, Lee IK (1997) Morphology and reproduction of Polysiphonia yendoi Segi (Rhodomelaceae, Rhodophyta) in Korea. Algae 12:73–81
Kim MS, Lee IK (1999) Neosiphonia flavimarina gen. et sp. nov. with a taxonomic reassessment of the genus Polysiphonia (Rhodomelaceae, Rhodophyta). Phycol Res 47:271–281
Kim MS, Yang EC (2006) Taxonomy and phylogeny of Neosiphonia japonica (Rhodomelaceae, Rhodophyta) based on rbcL and cpeA/B gene sequences. Algae 21:287–294
Kim MS, Kim SY, Nelson W (2010) Symphyocladia lithophila sp. nov. (Rhodomelaceae, Ceramiales), a new Korean red algal species based on morphology and rbcL sequences. Bot Mar 53:233–241
Lane CE, Lindstrom SC, Saunders GW (2007) A molecular assessment of northeast Pacific Alaria species (Laminariales, Phaeophyceae) with reference to the utility of DNA barcoding. Mol Phylogenet Evol 44:634–648
Le Gall L, Saunders GW (2010) DNA barcoding is a powerful tool to uncover algal diversity: a case study of the Phyllophoraceae (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta) in the Canadian flora. J Phycol 46:374–389
Lee JH, Cho CH, Lee JH, Lee S, Tang Y (2000) Seasonal variation in the Cheju warm current in the Northern East China Sea. J Oceanogr 56:197–211
Lee KM, Boo GH, Coyer JA, Nelson WA, Miller KA, Boo SM (2014) Distribution patterns and introduction pathways of the cosmopolitan brown alga Colpomenia peregrine using mt cox3 and atp6 sequences. J Appl Phycol 26:491–504
Lee KM, Yang EC, Coyer JA, Zucarrello GC, Wang WL, Choi CG, Boo SM (2012) Glacial refugia for the benthic seaweed, Ishige okamurae (Phaeophyceae), in the Northwest Pacific region. Mar Biol 159:1021–1028
Lee Y (2008) Marine algae of Jeju. Academy Publication, Seoul, 477 p
Leliaert F, Verbruggen H, Vanormelingen P, Steen F, Lopez-Bautista JM, Zuccarello GC, De Clerck O (2014) DNA-based species delimitation in algae. Eur J Phycol 49:179–196
Mamoozadeh NR, Freshwater DW (2011) Taxonomic notes on Caribbean Neosiphonia and Polysiphonia (Ceramiales, Florideophyceae): five species from Florida, USA and Mexico. Bot Mar 54:269–292
Muangmai N, West JA, Zuccarello GC (2014) Evolution of four Southern Hemisphere Bostrychia (Rhodomelaceae, Rhodophyta) species: phylogeny, species delimitation and divergence times. Phycologia 53:593–601
Saunders GW (2005) Applying DNA barcoding to red macroalgae: a preliminary appraisal holds promise for future applications. Philos T Roy Soc B 360:1879–1888
Segi T (1951) Systematic study of the genus Polysiphonia from Japan and its vicinity. J Fac Fish Prefect Univ Mie 1:169–272
Stamataski A (2006) RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 22:2688–2690
Verbruggen H (2014) Morphological complexity, plasticity, and species diagnosability in the application of old species names in DNA-based taxonomies (Algae Highlights). J Phycol 50:26–31
Wiens JJ (2007) Species delimitation: new approaches for discovering diversity. Syst Biol 56:875–878
Yang MY, Geraldino PJL, Kim MS (2013) DNA barcode assessment of Gracilaria salicornia (Gracilariaceae, Rhodophyta) from Southeast Asia. Bot Stud 54:27. doi:10.1186/1999-3110-54-27
Yang MY, Kim MS (2015) Taxonomy of Grateloupia (Halymeniales, Rhodophyta) by DNA barcode marker analysis and a description of Pachymeniopsis volvita sp. nov. J Appl Phycol 27:1373–1384
Yoon HY (1986) A taxonomic study of genus Polysiphonia (Rhodophyta) from Korea. Korean J Phycol 1:3–86
Yoshida T (1998) Marine algae of Japan. Uchida Rokakuho Publishing, Tokyo, 1222 p
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, B., Yang, M.Y. & Kim, M.S. Delimiting the species Neosiphonia yendoi (Rhodomelaceae, Rhodophyta) based on COI and rbcL genetic variation in Korea and Japan. Ocean Sci. J. 51, 507–516 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-016-0045-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-016-0045-5