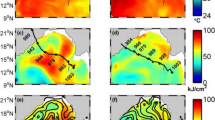
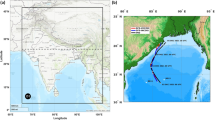
Abstract
In the present study an attempt has been made to investigate the impact of salinity stratification on the SST during the tropical cyclone (TC) passage. In this context, a severe post monsoon cyclone, Sidr, (Category 4) that developed over the south-eastern Bay of Bengal (BoB) during 11–16 November, 2007 was chosen as a case study. Pre-existence of a thick barrier layer (BL), temperature inversions and a higher effective oceanic layer for cyclogenesis (EOLC) were noticed along the path of the Sidr cyclone. The analysis of available Argo floats along the Sidr cyclone track also revealed less cooling during as well as after its passage as was reported from satellite derived SST. The role of BL on Sidr induced sea surface cooling was investigated using a diagnostic mixed layer model. Model results also depict the reduced sea surface cooling during the passage of Sidr. This is attributed to the presence of BL which results in the inhibition of the entrainment of cool thermocline water into the shallow mixed layer. Climatological as well as in situ observations of tropical cyclone heat potential (TCHP) and EOLC shows that the Sidr cyclone propagated towards the regions of higher EOLC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akter N, Tsuboki K (2012) Numerical Simulation of Cyclone Sidr Using a Cloud-Resolving Model: characteristics and formation process of an outer rainband. Mon Wea Rev 140:789–810. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1175/2011MWR3643.1
Balaguru K, Chang P, Saravanan R, Leunga LR, Xu Z, Li M, and Hsiehc JS (2012) Ocean barrier layers’ effect on tropical cyclone intensification. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(36):14343–14347. doi:10.1073/pnas.1201364109
Bender MA, Ginis I, Kurihara Y(1993) Numerical simulations of tropical cyclone-ocean interaction with a high resolution coupled model. J Geophys Res 98:23245–23263
Black PG (1983) Ocean temperature change induced by tropical cyclones. Ph.D. Thesis, The Pennsylvania State University, 278 p
Dare RA, McBride JL (2011) Sea Surface Temperature Response to Tropical Cyclones. Mon Wea Rev 139:3798–3808. doi: 10.1175/MWR-D-10-05019.1
Elsberry R, Fraim T, Trapnell Jr R(1976) A mixed layer model of the oceanic thermal response to hurricanes. J Geophys Res 81:1153–1162
Emanuel KA(1986) An air-sea interaction theory for tropical cyclone. Part I. Steady-state maintenance. J Atmos Sci 43:585–604
Jacob SD, Shay LK, Mariano AJ (2000) The 3D oceanic mixed layer response to Hurricane Gilbert. J Phys Oceanogr 14:59–78
Jacob SD, Shay LK (2003) The role of oceanic mesoscale features on the tropical cyclone-induced mixed layer response: a case study. J Phys Oceanogr 33:649–676
Kara AB, Rochford P, Hurlburt HE(2000) An optimal definition for ocean mixed layer depth. J Geophys Res 105(C7):16803–16821
Kumar A, Done J, Dudhia J, Dev N (2011) Simulations of Cyclone Sidr in the Bay of Bengal with a high-resolution model: sensitivity to large-scale boundary forcing. Meteorol Atmos Phys 114:123–137. doi:10.1007/s00703-011-0161-9
Leipper D, Volgenau D (1972) Upper ocean heat content of the Gulf of Mexico. J Phys Oceanogr 2:218–224
Lin II, Timothy LW, Wu CC, Pun IF, Ko DS (2008) Upper-ocean thermal structure and the western North Pacific category-5 typhoons. Part I: Ocean features and category-5 typhoon’s intensification. Mon Wea Rev 136:3288–3306
Mahapatra DK, Rao AD, Babu SV, Srinivas C (2007) Influence of coastline on upper oceans response to the tropical cyclone. Geophys Res Lett 34:L17603
Maneesha K, Sarma VVSS, Reddy NPC, Sadhuram Y, Ramana Murty TV, Sarma VV, Dileep KM (2011) Meso-scale atmospheric events promote phytoplankton blooms in the coastal Bay of Bengal. J Earth Syst Sci 120:773–782
McPhaden MJ, Foltz GR, Lee T, Murty VSN, Ravichandran M, Vecchi GA, Vialard J, Wiggert JD, Yu L (2009) Ocean-atmosphere interactions during cyclone Nargis. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 90:53–54
Murty VSN, Sarma MSS, Tilvi V (2000) Seasonal cyclogenesis and the role of near-surface stratified layer in the Bay of Bengal. In: Proceedings of PORSEC 2000 (A-092), NIO, Goa, India, 5–8 Dec, pp 453–457
Murty VSN, Subrahmanyam B, Sarma MSS, Tilvi V, Ramesh Babu V (2002) Estimation of sea surface salinity in the Bay of Bengal using Outgoing Longwave Radiation. Geophys Res Lett 29(16):22-1–22-4. doi:10.1029/2001GL014424
Murty VSN, Sarma MSS, Jenson GV, Vidya PJ (2008) Impact of freshwater influx on the cyclogenesis, tracks of cyclones and air-sea coupling over the Bay of Bengal. In: Proceedings volume of Workshop on Natural Hazards and Coastal Processes of Indian Coast (NHACPIC-2008), 30 April, pp 54–63
Park JJ, Kwon YO, and Price JF (2011) Argo array observation of ocean heat content changes induced by tropical cyclones in the north Pacific. J Geophys Res 116:C12025. doi:10.1029/2011JC007165
Powell MD, Vichery PJ, Reinhold T (2003) Reduced drag coefficient for high wind speeds in tropical cyclones. Nature 422:279–283
Prasad KB, Barman R, Dube SK, Pandey PC, Ravichandran M, Nayak S (2009) Development of a new comprehensive ocean atlas for Indian Ocean utilizing Argo data. Int J Climatol 30:185–196
Price JF (1981) Upper ocean response to a hurricane. J Phys Oceanogr 11:153–175
Price JF (1983) Internal wave wake of a moving storm. Part I. Scales, energy budget, and observations. J Phys Oceanogr 13:949–965
Price JF (2009) Metrics of hurricane-ocean interaction: verticallyintegrated or vertically-averaged ocean temperature? Ocean Sci 5:351–368
Rao AD, Dash S, Babu SV, Jain I (2007) Numerical modeling of cyclone impact on the ocean-a case study of the Orissa Supper Cyclone. J Coastal Res 23(5):1245–1250
Rao AD, Madhu J, Jain I, Ravichandran M (2010) Response of subsurface waters in the eastern Arabian Sea to tropical cyclones. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 89:267–276
Sadhuram Y, Rao BP, Rao DP, Shastri PNM, Subrahmanyam MV (2004) Seasonal variability of cyclone heat potential in the Bay of Bengal. Nat Hazards 32:191–209
Sengupta D, Bharath RJ, Anitha DS (2008) Cyclone-induced mixing does not cool SST in the post-monsoon north Bay of Bengal. Atmos Sci Lett 9:1–6
Shay LK, Uhlhorn EW (2008) Loop current response to Hurricanes Isidore and Lili. Mon Wea Rev 136:3248–3274
Subrahmanyam B, Murty VSN, Sharp RJ, O’Brien JJ (2005) Air-sea coupling during the Tropical Cyclones in the Indian Ocean: a case study using satellite observations. Pure Appl Geophys 162:1643–1672
Thadathil P, Gopalakrishna VV, Muraleedharan PM, Reddy GV, Nilesh A, Shenoy S (2002) Surface layer temperature inversion in the Bay of Bengal. Deep-Sea Res I 49:1801–1818
Thadathil P, Muraleedharan PM, Rao RR, Somayajulu YK, Reddy GV, Revichandran C (2007) Observed seasonal variability of barrier layer in the Bay of Bengal. J Geophys Res 112:C02009. doi:10.1029/2006JC003651
Tummala SK, Mupparthy RS, Kumar MN, Nayak SR (2009) Phytoplankton bloom due to cyclone Sidr in the central Bay of Bengal. J Appl Remote Sens 3(1):033547
Vinayachandran PN, Mathew S (2003) Phytoplankton bloom in the Bay of Bengal during the northeast monsoon and its intensification by cyclones. Geophys Res Lett 30(11):1572. doi:10.1029/2002GL016717
Vinayachandran PN, Kagimoto T, Masumoto Y, Chauhan P, Nayak SR, Yamagata T (2005) Bifurcation of the East India Coastal Current east of Sri Lanka. Geophys Res Lett 32:L15606. doi:10.1029/2005GL022864
Vincent EM, Lengaigne M, Madec G, Vialard J, Samson G, Jourdain NC, Menkes CE, Jullien S (2012) Processes setting the characteristics of sea surface cooling induced by tropical cyclones. J Geophys Res 117:C02020. doi:10.1029/2011JC007396
Vissa NK, Satyanarayana ANV, Prasad KB (2012a) Response of Upper Ocean during passage of MALA cyclone utilizing Argo data. Int J Appl Earth Observ Geo Infor 14:149–159
Vissa NK, Satyanarayana ANV, Prasad KB (2012b) Comparison of Mixed Layer Depth and Barrier Layer Thickness for the Indian Ocean using two different Climatologies. Int J Climatol. doi:10.1002/joc.3635
Vissa NK, Satyanarayana ANV, Prasad KB (2013a) Response of Oceanic Cyclogenesis Metrics for NARGIS Cyclone: a case study. Atmos Sci Lett 14(1):7–13
Vissa NK, Satyanarayana ANV, Prasad KB (2013b) Intensity of Tropical cyclones during pre and post monsoon seasons in relation to Accumulated Tropical Heat Potential over Bay of Bengal. Nat Hazards 68:351–371. doi:10.1007/s11069-013-0625-y
Vissa NK, Satyanarayana ANV, Prasad KB (2013c) Impact of South China Sea cold surges and PEIPAH typhoon in initiating Sidr cyclone in the Bay of Bengal. Pure Appl Geophys. doi:10.1007/s00024-013-0671-0
Wang X, Han G, Qi Y, and Li W (2011) Impact of barrier layer on typhoon-induced sea surface cooling. Dynam Atmos Oceans 52:367–385
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vissa, N.K., Satyanarayana, A.N.V. & Kumar, B.P. Response of upper ocean and impact of barrier layer on Sidr cyclone induced sea surface cooling. Ocean Sci. J. 48, 279–288 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-013-0026-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-013-0026-x