Abstract
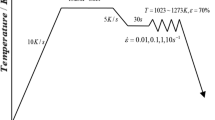
The hot deformation behavior of powder metallurgical (PM) TiAl alloys was investigated on Gleeble-3500 thermomechanical simulator, at a temperature range of 1050–1200 °C with an interval of 50 °C and a strain rate range of 0.001–1.000 s−1. The results show that the flow stress of PM TiAl alloy is sensitive to deformation temperature and strain rate, the peak stress decreases with the increase in deformation temperature and decrease in strain rate, and dynamic recrystallization occurs during the hot compression. The deformation active energy was calculated and the flow stress model during high-temperature deformation was established based on the Arrhenius equations and Zener–Hollomon parameter. The deformed microstructure consists of refined homogeneous γ and α2/γ grains.
Graphical Abstract
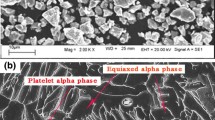
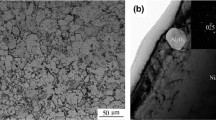
The fully dynamic recrystallization microstructure can be obtained when deformed at temperature 1150 °C and strain rate 0.001 s−1. Dynamic recrystallization plays an important role in hot working of PM TiAl alloy, and deformation temperature and strain rate have a strong effect on the recrystallization microstructure. The degree of dynamic recrystallization obviously improves with the increase in temperature. And refinement of recrystallization grains takes place as strain rate increases at a given temperature.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim YW. Ordered inter-metallic alloys, part III: gamma titanium aluminides. JOM. 1995;47(7):39.
Dimiduk DM. Gamma titanium aluminide alloys—an assessment within the competition of aerospace structural materials. Mater Sci Eng A. 1999;263(2):281.
Edward AL. Gamma titanium aluminides as prospective structural materials. Intermetallics. 2000;8(9–11):1239.
Appel F, Brossmann U, Christoph U, Eggert S, Janschek P, Lorenz U, Müllauer J, Oehring M, Paul JDH. Recent progress in the development of gamma titanium aluminide alloys. Adv Eng Mater. 2000;2(11):699.
Clemens H, Kestler H. Processing and application of engineering γ-TiAl based alloys. Adv Eng Mater. 2000;2(9):551.
Toshimitsu T. Development of a TiAl turbocharger for passenger vehicles. Mater Sci Eng A. 2002;329–331:582.
Wu XH. Review of alloy and process development of TiAl alloys. Intermetallics. 2006;14(10–11):1114.
Xu XJ, Xu LH, Lin JP, Wang YL, Lin Z, Chen GL. Pilot processing an microstructure control of high Nb containing TiAl alloy. Intermetallics. 2005;13(3–4):337.
Gerling R, Clemens H, Schimansky FP. Powder metallurgical processing of intermetallic gamma titanium aluminide. Adv Eng Mater. 2004;6(1–2):23.
Clemens H, Keatler H, Ebergardt N, Knabl W. Microstructural Evolution in Gamma Titanium Aluminides during Severe Hot-Working. In: Kim YW, Dimiduk DM, Loretto MH, editors. Gamma Titanium Aluminides. Warrendale: TMS; 1999. 209.
Moll JH, Yolton CF, Mctiernan BJ. PM processing of titanium aluminides. Int J Powder Metall. 1990;26(2):149.
Gerling R, Schimansky FP, Wagner R. Specification of the Novel Plasma Melting Inert Gas Atomization Facility PIGA 1/300. In: Capus JM, editor. Advances in Powder Metallurgical and Particulate Materials, vol. 1. Princeton: MPIF; 1992. 215.
Yolton CF, Kim YW, Habel U. Powder Metallurgy Processing of Gamma Titanium Aluminide. In: Kim Y-W, Clemens H, Rosenberger AH, editors. Gamma Titanium Aluminide. Warrendale: TMS; 2003. 233.
Hohmann M, Diemar W, Ludwig N. Modem systems for ceramic-free powder production. Adv Powder Metall Part Mater. 1992;1:27.
Prauchat B, Popoff F, Thomas M. Characterization of HIPed and extruded powder metallurgy titanium aluminide. Adv Eng Mater. 2002;4(3):133.
Liu B, Liu Y, Zhang W, Huang JS. Hot deformation behavior of TiAl alloys prepared by blended elemental powders. Intermetallics. 2011;19(2):154.
Huang Zh. Workability and microstructure evolution of Ti-47Al-2Cr-1Nb alloy during isothermal deformation. Intermetallic. 2005;13(3–4):245.
Liu ZC, Lin JP, Wang YL, Lin Z, Chen GL, Chang KM. High temperature deformation behavior of as-cast Ti-46Al-8.5Nb-0.2W alloy. Mater Lett. 2004;58(6):948.
Zhang J, Su X, Strom E, Zhong ZY, Li CH. Effect of minor addition of Ni on hot-deformation behavior of gamma TiAl alloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2002;329–331:499.
Wang H, Liu Y, Zhang W, Li Z, Li HZ, Wang L, Yang GY. Hot deformation behavior and processing maps of PM TiAl alloy. Chin J Rare Met. 2010;34(2):159.
Berbenni S, Favier V, Berveiller M. Micro–macro modelling of the effects of the grain size distribution on the plastic flow stress of heterogeneous materials. Comput Mater Sci. 2007;39(1):96.
Liu B. Study on the preparation and high temperature deformation behavior of TiAl based alloy. Changsha: Central South University; 2008. 72.
Seetharaman V, Lombard CM. Plastic Flow Behavior of a Ti–Al–Nb–Mn Alloy at High Temperatures. In: Kim Y-W, Boyer RR, editors. Microstructure Property Relationships in Titanium Aluminides and Alloys. Warrendale: TMS; 1991. 237.
Wang G, Xu L, Cui YY, Yang R. High temperature deformation behavior of powder metallurgy TiAl alloy and its constitutive model. Chin J Nonferr Met. 2010;20(1):269.
Shih DS, Scarr GK. High Temperature Deformation Behaviour of the γ Alloy Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb. In: Johnson LA, Pope DP, Stiegler JO, editors. High Temperature Intermetallic Alloys. Pittsburgh: Materials Research Society; 1991. 727.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51301157 and 51105102) and the National High Technology Research and Development Program (No. 2013AA031103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, N., Li, Z., Xu, WY. et al. Hot deformation behavior and microstructural evolution of powder metallurgical TiAl alloy. Rare Met. 36, 236–241 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-016-0746-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-016-0746-z