Abstract
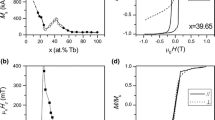
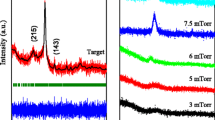
Anisotropic Pr–Fe–B films with soft-magnetic layer (Fe) and/or antiferromagnetic layer (Mn, FeMn or MnO) were prepared by direct-current (DC) magnetron sputtering on Si (100) substrates heated at 650 °C. The influence of four types’ different structures on the magnetic properties of Pr–Fe–B films was investigated. The phase and magnetic properties were characterized by means of X-ray diffraction (XRD) and superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID). Addition of antiferromagnetic layer enhances both the coercivity and the remanence ratios of Pr–Fe–B films with suitable structures. The interface number increases and the antiferromagnetic–ferromagnetic exchange interaction is likely to become stronger, which affect the improvement of magnetic properties. To further understand the influence of structures with soft-magnetic Fe layer and/or antiferromagnetic FeMn layer on the magnetic properties of Pr–Fe–B hard-magnetic films, the thickness of Pr–Fe–B layer was designed to decrease from 600 to 50 nm. The improvement of magnetic properties becomes obvious in Mo(50 nm)/Pr–Fe–B(25 nm)Mo(2 nm)FeMn(20 nm)Mo(2 nm)Pr–Fe–B(25 nm)/Mo(50 nm) film.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dempsey NM, Walther A, May F, Givord D, Khlopkov K, Gutfleisch O. High performance hard magnetic NdFeB thick films for integration into micro-electro-mechanical systems. Appl Phys Lett. 2007;90(9):092509.
Jiang CB, An SZ. Recent progress in high temperature permanent magnetic materials. Rare Met. 2013;32(5):431.
Neu V, Melcher S, Hannemann U, Fähler S, Schultz L. Growth, microstructure, and magnetic properties of highly textured and highly coercive Nd–Fe–B films. Phys Rev B. 2004;70:144418.
Al-Omari IA, Sellmyer DJ. Magnetic properties of nanostructured CoSm/FeCo films. Phys Rev B. 1995;52(5):3441.
Zhang J, Takahashi YK, Gopalan R, Hono K. SmCo, Cu5/Fe exchange spring multilayer films with high energy product. Appl Phys Lett. 2005;86(12):122509.
Yang C, Hou YL. Advance in the chemical synthesis and magnetic properties of nanostructured rare-earth-based permanent magnets. Rare Met. 2013;32(2):105.
Liu W, Li XZ, Liu JP, Sun X, Chen CL, Skomski R, Zhang ZD, Sellmyer DJ. Enhanced coercivity in thermally processed (Nd, Dy)(Fe, Co, Nb, B)5.5/a-Fe nanoscale multilayer magnets. J Appl Phys. 2005;97(10):104308.
Yang CJ, Kim SW. Exchange coupling in Nd2Fe14B/Fe/Nd2Fe14B sandwich films and their magnetic properties. J Appl Phys. 2000;87(9):6134.
Ao Q, Zhang WL, Wu JS. Exchange coupling and remanence enhancement in nanocomposite Nd–Fe–B/FeCo multilayer films. J Magn Magn Mater. 2006;299(2):440.
Cui WB, Zheng SJ, Liu W, Ma XL, Yang F, Yao Q, Zhao XG, Zhang ZD. Structure, magnetic properties and coercivity mechanism of the Mo-spacered Nd2Fe14B/a-Fe textured multilayer films. J Appl Phys. 2008;104(5):053903.
Cui WB, Liu W, Li J, Yang F, Zhang Q, Liu XG, Zhang ZD. Anisotropic behavior of exchange coupling in textured Nd2Fe14B/a-Fe multilayer films. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2008;41:245007.
Kato H, Kubota H, Koyama K, Miyazaki T. Fabrication of SmFe12/a-Fe thin films as anisotropic nanocomposite magnet. J Alloys Compd. 2006;408–412:1368.
Yang F, Wang X, Liu W, Liu XH, Liu XG, Zhao XG, Zhang ZD. Coercivity enhancement in sputtered Pr–Fe–B/FeMn thin films. J Alloys Compd. 2009;485(1–2):33.
Yang F, Liu W, Lv XK, Liu XH, Guo S, Gong WJ, Zhang ZD. Magnetic properties of Nd–Fe–B/FeMn multilayer films. Mater Lett. 2009;63(30):2652.
Yang F, Liu W, Zhang ZD. Magnetic properties of R–Fe–B/Mn films with different structures. Mater Lett. 2012;69:52.
Yang F, Liu W, Cui WB, Yao Q, Zhao XG, Zhang ZD. Structure and magnetic properties of high coercive [Pr–Fe–B x /Cu] n films with out-of-plane orientation. Mater Lett. 2009;63(21):1866.
Jeong SK, Ohkubo T, Roy AG, Laughlin DE, McHenry ME. In situ ordered polycrystalline FePt L10(001) nanostructured films and the effect of CrMn and Zn top layer diffusion. J Appl Phys. 2002;91(10):6863.
Chen SK, Yuan FT, Chin TS. Effect of interfacial diffusion on microstructure and magnetic properties of Cu/FePt bilayer thin films. J Appl Phys. 2005;97(7):073902.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Key Basic Research Program of China (No. 2010CB934603), and the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Nos. 50931006 and 50971123).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, F., Liu, W. & Zhang, ZD. Magnetic properties of sputtered anisotropic Pr–Fe–B thin films with different structures and antiferromagnetic materials. Rare Met. 35, 926–929 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0420-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0420-2