Abstract
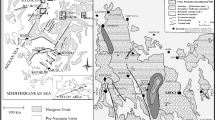
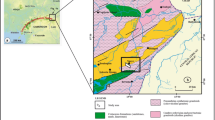
The Kestelek borate deposit has been the subject of geological and mineralogical research over the last decades, but major and trace element geochemistry of this deposit was first investigated in the present study. A total of 22 samples collected from surface exposures and different depths of deposit in boreholes (e.g., lower, middle and upper) comprise the material of this study. Major, trace and REE element analyses of samples were conducted with ICP-MS and ICP-ES methods. The Kestelek borate deposit of Miocene age was formed in playa lakes in an intermountain closed basin which was developed in volcanically and seismically active areas associated with growth faults and grabens affected the whole Anatolia at the beginning of Paleogene. Only colemanite was found as the borate mineral accompanied in lesser amount by calcite, aragonite, smectite, illite, chlorite, corrensite, heulandite and quartz. In colemanite samples, all major elements, except for Ca, show depletion trends with respect to average of earth crust and andesite. For the trace elements, Li, Cs, Sb, As, Sr and Se are characterized by significantly high concentrations. Evaluation of element concentrations and geochemical characteristics reveal that As, Cs, Sb and Li are of detrital origin, Se together with B and Ca are of non-detrital and Sr is indicative of both detrital and non-detrital origin. REE distributions indicate that at least two different depositional regimes prevail in the environment. Corrensite, a clay mineral forming in lake waters, is derived from volcanism. Negative Ce and positive Eu anomalies are indicative of contribution from hydrothermal solutions and fluids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Abollino, O., Aceto, M., Buoso, S., et al., 2004. Distribution of Major, Minor and Trace Elements in Lake Environments of Antarctica. Antarctic Science, 16(3): 277–291. doi: 10.1017/s0954102004002111
Akçay, M., 2002. Jeokimya Trabzon. Karadeniz Technical University Publications, Trabzon. 506 (in Turkish)
Akyol, E., Akgün, F., 1990. Palynology of Bigadiç, Kestelek, Emet and Kirka Borate-Bearing Neogene Deposits. MTA Bulletin, 111: 165–173 (in Turkish)
Atan, O., 1981. Geology of the Devecikonagi (Bursa) Region and Sedimentologic Characteristics of Some Formations. Can Press, Ankara (in Turkish)
Bau, M., 1991. Rare-Earth Element Mobility during Hydrothermal and Metamorphic Fluid-Rock Interaction and the Significance of the Oxidation State of Europium. Chemical Geology, 93(3/4): 219–230. doi:10.1016/0009- 2541(91)90115-8
Baysal, O., Ataman, G., 1975. A New Borate Mineral in Turkey: Discussion on Kernite Occurrence. Turkish Geological Survey Bull., 18: 3–10 (in Turkish)
Bhatia, M. R., 1985. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry of Australian Paleozoic Graywackes and Mudrocks: Provenance and Tectonic Control. Sedimentary Geology, 45(1/2): 97–113. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(85)90025-9
Boggs, S., 2009. Petrology of Sedimentary Rocks. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 600
Bonatti, E., Kraemer, T., Rydell, H., 1972. Classification and Genesis of Submarine Iron-Mangenese Deposits. In: Horn, D. R., ed., Ferromanganese Deposits on the Ocean Floor. Natt. SCI Found, Washington, D.C.. 149–166
Bowser, C. J., 1964. Geochemistry and Petrology of the Sodium Borates in the Non-marine Evaporite Environment: [Dissertation]. University of California, Los Angeles. l10
Bürküt, Y., 1977. Distribution of Li, Rb, Cs and Sr in Orthoand Para-gneiss and Some Petrologic Results: [Dissertation]. Istanbul Technical University, Faculty of Mining, Istanbul. 68 (in Turkish)
Canet, C., Prol-Ledesma, R. M., Proenza, J. A., et al., 2005. Mn-Ba-Hg Mineralization at Shallow Submarine Hydrothermal Vents in Bahía Concepción, Baja California Sur, Mexico. Chemical Geology, 224(1–3): 96–112. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.07.023
Cantrell, K. J., Byrne, R. H., 1987. Rare Earth Element Complexation by Carbonate and Oxalate Ions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 51(3): 597–605. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(87)90072-x
Choi, J. H., Hariya, Y., 1992. Geochemistry and Depositional Environment of Mn Oxide Deposits in the Tokoro Belt, Northeastern Hokkaido, Japan. Economic Geology, 87(5): 1265–1274. doi:10.2113/gsecongeo.87.5.1265
Christ, C. L., Truesdell, A. H., Erd, R. C., 1967. Borate Mineral Assemblages in the System Na2O-CaO-MgO-B2O3-H2O. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 31(3): 313–337. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(67)90045-2
Constantopoulos, J., 1988. Fluid Inclusions and Rare Earth Element Geochemistry of Fluorite from South-Central Idaho. Economic Geology, 83(3): 626–636. doi:10.2113/gsecongeo.83.3.626
Crerar, D. A., Namson, J., Chyi, M. S., et al., 1982. Manganiferous Cherts of the Franciscan Assemblage: I, General Geology, Ancient and Modern Analogues, and Implications for Hydrothermal Convection at Oceanic Spreading Centers. Economic Geology, 77(3): 519–540. doi:10.2113/gsecongeo.77.3.519
Elkin, E. M., Margrave, J. L., 1968. Selenium and Selenium Compounds. Kirk Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, 17: 809–833
Erkül, F., Helvaci, C., Sözbilir, H., 2005. Stratigraphy an Geochronology of the Early Miocene Volcanic Units in the Bigadiç Borate Basin Western Turkey Turkish. Journal of Earth Sciences, 14: 227–253
Fee, J. A., Gaudette, H. E., Lyons, W. B., et al., 1992. Rare- Earth Element Distribution in Lake Tyrrell Groundwaters, Victoria, Australia. Chemical Geology, 96(1/2): 67–93. doi:10.1016/0009-2541(92)90122-l
Floyd, P. A., Helvaci, C., Mittwede, S. K., 1998. Geochemical Discrimination of Volcanic Rocks Associated with Borate Deposits: An Exploration Tool? Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 60(3): 185–205
Fu, X. G., Wang, J., Zeng Y. L., et al., 2011. Geochemistry and Origin of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) in the Shengli River Oil Shale, Northern Tibet, China. Chemie Der Erde–Geochemistry, 71(1): 21–30. doi: 10.1016/j.chemer.2010.07.003
Gale, G. H., Dabek, L. B., Fedikov, M. A. F., 1997. The Application of Rare Earth Element Analyses in the Exploration for Volcanogenic Massive Sulphide Deposits: Mining Geology, 6(3): 233–252
Graf, J. L., 1977. Rare Earth Elements as Hydrothermal Tracers during the Formation of Massive Sulfide Deposits in Volcanic Rocks. Economic Geology, 72(4): 527–548. doi:10.2113/gsecongeo.72.4.527
Halilova, H., 2004. Biogeochemistry of Microelements (I, Zn, Co, Mn, Cu, Se). Ilke-Eker Press, Ankara. 110 (in Turkish)
Helke, A., 1955. Examination of Turkish Mineral Deposits II. N. Jb. Min. Abh., 88: 178–180 (in German)
Helvaci, C., 1983. Mineralogy of the Turkish Borate Deposits. Geol. Eng. Bull., 17: 37–54 (in Turkish)
Helvaci, C., Dora, Ö., 1985. New Opinions on the Formation of Bigadiç Borate Deposits. Proceedings of the 39th Turkish Geological Congress, February, 1985, Ankara. 75–76 (in Turkish with English Abstract)
Helvaci, C., Alaca, O., 1991. Geology and Mineralogy of Bigadiç Borate Deposits. MTA Bulletin, 113: 61–92 (in Turkish)
Helvaci, C., 1992. Mineral Assemblages and Formation of the Kestelek and Sultançayiri Borate Deposits. Proceedings of the 29th International Geological Congress, Part A, Kyoto. 245–264
Helvaci, C., Stamatakis, M., Zagouroglou, C., et al., 1993. Borate Minerals and Related Authigenic Silicates in Northeastern Mediterranean Late Miocene Continental Basins. Exploration and Mining Geology, 2(2): 171–178
Helvaci, C., 1995. Stratigraphy, Mineralogy, and Genesis of the Bigadic Borate Deposits, Western Turkey. Economic Geology, 90(5): 1237–1260. doi:10.2113/gsecongeo.90.5.1237
Helvaci, C., Orti, F., 1998. Sedimentology and Diagenesis of Miocene Colemanite-Ulexite Deposits (Western Anatolia, Turkey). Journal of Sedimentary Research, 68(5): 1021–1033. doi:10.2110/jsr.68.1021
Helvaci, C., Alonso, R. N., 2000. Borate Deposits of Turkey and Argentina: A Summary and Geological Comparison. Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 9: 1–27
Helvaci, C., 2001. Turkish Borate Deposits. Chambers of Geological Engineers Publications, 71: 34 (in Turkish)
Helvaci, C., Mordogan, H., Çolak, M., et al., 2004. Presence and Distribution of Lithium in Borate Deposits and some Recent Lake Waters of West-Central Turkey. International Geology Review, 46(2): 177–190. doi:10.2747/0020-6814.46.2.177
Helvaci, C., 2003. Turkish Borate Deposits: Their Geologic Setting, Economic Importance and Boron Policy. Balikesir University Bulletin, 5(1): 4–41 (in Turkish)
Helvaci, C., 2004. Turkish Borate Deposits: Their Geologic Setting, Economic Importance and Boron Policy. 5th Industrial Raw Materials Symposium, 13–14 May, Izmir. 11–27 (in Turkish)
Inan, K., 1975. A Model for Formation of Hydrous Borate Minerals. Turkish Geological Survey Bull., 18: 165–168 (in Turkish)
Istanbul Technical University (ITU), 1982. Exploration and Pre-Feasibility Project of the Etibank Kestelek Colemanite. ITÜ Faculty of Mine, Mineralogy-Mineral Deposits Section, Istanbul (in Turkish)
Istanbul Technical University, 1985. Investigation of Zeolitization around the Etibank Kestelek Colemanite Deposit. ITÜ Earth Sciences and Underground Sources UYG–AR Center, Istanbul (in Turkish)
Johannesson, K. H., Lyons, W. B., Yelken, M. A., et al., 1996. Geochemistry of the Rare-Earth Elements in Hypersaline and Dilute Acidic Natural Terrestrial Waters: Complexation Behavior and Middle Rare-Earth Element Enrichments. Chemical Geology, 133(1–4): 125–144. doi:10.1016/s0009-2541(96)00072-1
Kistler, R. B., Helvaci, C., 1994. Boron and Borates. In: Donald, D. C., ed., Industrial Minerals and Rocks. 6th Edition. Society of Mining, Metallurgy and Exploration, Inc., Littleton, Colarado. 171–186
Krauskopf, K. B., 1989. Introduction to Geochemistry. McGraw-Hill International Editions, London. 617
Koç, S., Birey, M., Kavrazli, Ö., et al., 2008a. Geochemical Properties of Kestelek Borate Deposits and Their Changes of Depending on Depth and High Technological Material Investigations on Borate Samples. TÜBITAK Project No: 105M356 (in Turkish)
Koç, S., Kavrazli, Ö., Koçak, I., 2008b. Geochemistry of Colemanite Deposit of Kestelek, Bursa, Turkey. 33rd. International Geological Congress, August 6–14, Oslo, Norway. Abstracts MRB-01
Koç, S., Kavrazli, Ö., Koçak, I., 2008c. Trace Elements Concentrations of Colemanite in Kestelek Borate Deposit. 16th International Symposium on Boron, Borides and Related Materials. September 7th–12th, Matsue, Shimane, Japan. 57–58
Koçak, N., 1989. Geologic Investigation of Kestelek Neogene Basin. Etibank Mineral Research Exploration Department Report, Ankara (in Turkish)
Koçak, I., Koç, S., 2009. Trace Element Enrichment of Bigadiç Borates Deposits, Balikesir, Turkiye. Goldschmidt Conference Abstracts 2009, Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 73(Suppl.): A671
Koçak, I., Koç, S., 2011. Trace Element Contents of Bigadiç and Kestelek Borate Deposits. 17th International Symposium on Boron, Borides and Related Materials, September 11–17, Istanbul. 232
Koçak, I., Koç, S., 2012. Major and Trace Element Geochemistry of the Bigadiç Borate Deposit, Balikesir, Turkiye. Geochemistry International, 50(11): 926–951. doi:10.1134/s0016702912090030
Meixner, H., 1956. New Borate Site in Iskeleköy, Bigadiç Town, Balikesir City Sonderabdruck aus Kali und Steinsalz, Essen, Verlag Glöckauf, Essen. Part 2. 43–47 (in German)
Nicholson, K., 1990. Stratiform Manganese Mineralisation near Inverness, Scotland: A Devonian Sublacustrine Hot- Spring Deposit? Mineralium Deposita, 25(2): 126–131. doi:10.1007/bf00208855
Nance, W. B., Taylor, S. R., 1977. Rare Earth Element Patterns and Crustal Evolution—II. Archean Sedimentary Rocks from Kalgoorlie, Australia. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 41(2): 225–231. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(77)90229-0
Özpeker, I., 1969. Comparative Genetic Survey on the Western Anatolian Borate Deposits: [Dissertation]. I. T. U. Press, Istanbul. 116 (in Turkish)
Özpeker, I., Inan, K., 1978. Mineral Assemblages in Western Anatolian Borate Deposits and Their Relations with Deposit Occurrence. Bulletin of the Geological Society of Turkey, 21: 1–10 (in Turkish)
Petrascheck, E. W., Pohl, W., 1982. Mineral Deposits. Schweizerbart’sche Verlagsbuchhandlung, Stuttgart, Germany. 441 (in German)
Roy, S., Dasgupta, S., Mukhopadhyay, S., et al., 1990. A Typical Ferromanganese Nodules from Pelagic Areas of the Indian Basins, Equatorial Indian Ocean. Marine Geology, 92: 269–283
Sant’Anna, L. G., Clauer, N., Cordani, U. G., et al., 2006. Origin and Migration Timing of Hydrothermal Fluids in Sedimentary Rocks of the Paraná Basin, South America. Chemical Geology, 230(1/2): 1–21. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.11.009
Schroll, E., 1975. Analytical Geochemistry. Ferdinand Enke Verlag, Stuttgart. 292 (in German)
Sunder, M., 1980. Geochemistry of Sarikaya (Kirka-Eskisehir) Borate Deposits. Turkish Geological Survey Bull., 2: 19–34 (in Turkish)
Sahinci, A., 1991. Geochemistry of Natural Waters. Reform Press, Izmir. 548 (in Turkish)
Taylor, S. R., McLennan, S. M., 1985. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution. Blackwell, Oxford. 312
Weaver, C. E., Pollard, L. D., 1973. The Chemistry of Clay Minerals. Elsevier Scientific, New York. 213
Yalçinkaya, S., Afsar, Ö., 1980. Geology of Mustafa Kemalpasa and Surrounding Region. MTA Report, Ankara (in Turkish)
Yılmaz, O., Gündoğdu, M., Gümüş, S., 1982. Geology of Neogene Bigadiç Volcano Sedimentary Basin. Etibank Project, Ankara. 89 (in Turkish)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Boron Research Institute (BOREN) and the Scientific and Technical Research Council of Turkey (No. 105M356). Scientific foundation unit of the Ankara University is also greatly acknowledged for the support. The final publication is available at Springer via http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12583-015-0616-x.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Şükrü Koç: http://orcid-org/0000-0003-2757-8286
İsmail Koçak: http://orcid-org/0000-0002-4519-4561
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koç, Ş., Kavrazlı, Ö. & Koçak, İ. Geochemistry of Kestelek colemanite deposit, Bursa, Turkey. J. Earth Sci. 28, 63–77 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-015-0616-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-015-0616-x