Abstract
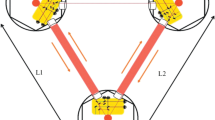
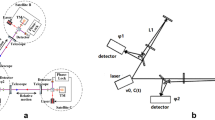
In Japan, not only the ground-based gravitational wave (GW) detector mission KAGRA but also the space GW detector mission DECIGO (DECi-hertz Interferometer Gravitational wave Observatory) and its milestone mission B-DECIGO have been promoted. The designed strain sensitivity of DECIGO and B-DECIGO are δL/L < 10−23. Since the GW detector requires high power and highly-stable light source, we have developed the light source with high frequency and intensity stability for DECIGO and B-DECIGO. The frequency of the Yb-doped fiber DFB lasers are stabilized to the iodine saturated absorption at 515 nm, and the intensity of the laser at 1 Hz (observation band) is stabilized by controlling the pump source of an Yb-doped fiber amplifier. The intensity of the laser at 200 kHz (modulation band) is also stabilized using an acousto-optic modulator to improve the frequency stability of the laser. In the consequences, we obtain the frequency stability of δf = 0.4 Hz/√Hz (in-loop) at 1 Hz, and the intensity stability of δI/I = 1.2 × 10−7/√Hz (out-of-loop) and δI/I = 1.5 × 10−7/√Hz (in-loop) at 1 Hz and 200 kHz, respectively.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, B.P., et al.: Observation of gravitational waves from a binary black hole merger. Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, 061102 (2016)
Kuroda, K., et al.: The status of LCGT. Class. Quantum Gravity 23, S215–S221 (2006)
Seto, N., Kawamura, S., Nakamura, T.: Possibility of direct measurement of the acceleration of the universe using laser interferometer gravitational wave antenna in space. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 221103 (2001)
Cheng, W., Chen, L., Yoon, T.H., Hall, J.L., Ye, J.: Sub-Doppler molecular-iodine transitions near the dissociation limit (523–498 nm). Opt. Lett. 27, 571 (2002)
Shirley, J.H.: Modulation transfer processes in optical heterodyne saturation spectroscopy. Opt. Lett. 7, 537 (1982)
Demtröder, W.: Laser Spectroscopy, vol. 1, 4th edn, section 3. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), and by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS), Grand-in-Aid for Scientific Research (KAKENHI)15H02082, Grand-in-Aid for Research Fellowship for Young Scientists 16J09106.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is based on a presentation at the International Conference on Space Optics (ICSO), 18–21 October, 2016, Biarritz, France.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suemasa, A., Shimo-oku, A., Nakagawa, K. et al. Developments of high frequency and intensity stabilized lasers for space gravitational wave detector DECIGO/B-DECIGO. CEAS Space J 9, 485–491 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12567-017-0151-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12567-017-0151-y