Abstract
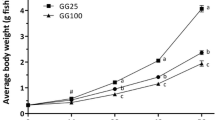
In finfish aquaculture, fish meal is heated during the manufacturing process, which affects the digestibility and protein absorption by fish. However, manufactured fishmeal that is not heated does not undergo thermal denaturation. Few studies have investigated the effects of non-heated animal protein sources on the growth performance of fish. We investigated the effects of heated and non-heated squid and krill meal as diets for red sea bream. Five test diets were formulated to contain heated squid meal, non-heated squid meal, heated krill meal, non-heated krill meal, and fish meal as a control. Fifty fish (initial mean weight = 3.5 g) were distributed in ten 100-l experimental tanks. Fish were fed one of the five diets 3 times daily until satiation for 5 weeks. Regarding growth performance, fish fed the krill meal diet exhibited better growth than those fed squid meal during the first week of the rearing period. However, the squid meal diet group showed better performance than the krill meal diet group during the third week. Moreover, differences in body weight among treatments were greater during the fifth week. Better weight gain and thermal growth coefficient were recorded in the non-heated diet groups than in the heated diet groups. Higher feed intake was observed in the non-heated diet groups than in the heated diet groups. These results suggest higher performance of non-heated squid and krill meal as the protein source of the red sea bream diet. Further, the suitability of the diet type (e.g., squid and krill) might depend on the feeding period and/or developmental stage of fish.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajandouz EH, Puigserver A (1999) Nonenzymatic browning reaction of essential amino acids: effect of pH on caramelization and Maillard reaction kinetics. J Agric Food Chem 47:1786–1793
Amaya EA, Davis DA, Rouse DB (2007) Replacement of fish meal in practical diets for the Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) reared under pond conditions. Aquaculture 262:393–401
AOAC (1995) Official methods of analysis. Association of the Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington
Bell JG, McEvoy LA, Estevez A, Shields RJ, Sargent JR (2003) Optimising lipid nutrition in first-feeding flatfish larvae. Aquaculture 227:211–220
Bessonart M, Izquierdo MS, Salhi M, Hernández CCM, González MM, Fernández PH (1999) Effect of dietary arachidonic acid levels on growth and survival of gilthead sea bream Sparus aurata larvae. Aquaculture 179:265–275
Biswas AK, Kaku H, Ji SC, Seoka M, Takii K (2007) Use of soybean meal and phytase for partial replacement of fish meal in the diet of red sea bream, Pagrus major. Aquaculture 267:284–291
Boonyoung S, Haga Y, Satoh S (2012) Preliminary study on effects of methionine hydroxyl analog and taurine supplementation in a soy protein concentrate-based diet on the biological performance and amino acid composition of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Wallbaum). Aquac Res 44:1339–1347
Boyd CE, Tucker C, McNevin A, Bostick K, Clay J (2007) Indicators of resource use efficiency and environmental performance in fish and crustacean aquaculture: a review. Fish Sci 15:327–360
Cho SH, Lee SM, Lee SM, Park BH, Park IS, Choi CY, Min BH, Hur SB, Jo JY (2005) Effect of partial replacement of fish meal with squid liver meal™ in the diet on growth and body composition of juvenile olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) during winter season. Fish Aquat Sci 8:65–69
Cho JH, Haga Y, Kamimura Y, Akazawa A, Itoh A, Satoh S (2016) Production performance of Pacific bluefin tuna Thunnus orientalis larvae and juveniles fed commercial diets and effects of switching diets. Aquac Sci 64:359–370
De Schrijver R, Ollevier F (2000) Protein digestion in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) and effects of dietary administration of Vibrio proteolyticus. Aquaculture 186:107–116
Everson I (2000) Krill: biology, ecology, and fisheries. Blackwell Science, Oxford
FAO (2015) The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 2014. http://www.fao.org/3/a-i3720e/index.html. Accessed 11 May 2015
Floreto EA, Bayer RC, Brown PB (2000) The effects of soybean-based diets, with and without amino acid supplementation, on growth and biochemical composition of juvenile American lobster, Homarus americanus. Aquaculture 189:211–235
Folch J, Lees M, Stanley GHS (1957) A simple method for isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–507
Forster I, Ogata HY (1998) Lysine requirement of juvenile Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus and juvenile red sea bream Pagrus major. Aquaculture 161:131–142
Francis G, Makkar HPS, Becker K (2001) Antinutritional factors present in plant-derived alternate fish feed ingredients and their effects in fish. Aquaculture 199:197–227
Furuita H, Takeuchi T, Watanabe T, Fujimoto H, Sekiya S, Imaizumi K (1996) Requirement of larval yellowtail for eicosapentaenoic acid, docosahexaenoic acid, and n-3 highly unsaturated fatty acid. Fish Sci 62:372–379
Fyhn HJ (1989) First feeding of marine fish larvae: are free amino acids the source of energy? Aquaculture 80:111–120
Fyhn HJ, Serigstad B (1987) Free amino acids as energy substrate in developing eggs and larvae of the cod Gudas morhua. Mar Biol 96:335–341
Gatlin DM, Barrows FT, Brown P, Dabrowski K, Gaylord TG, Hardy RW, Herman E, Hu G, Krogdahl A, Nelson R, Overturf K, Rust M, Sealey W, Skonberg D, Souza EJ, Stone D, Wilson R, Wurtele E (2007) Expanding the utilization of sustainable plant products in aquafeeds: a review. Aquac Res 38:551–579
Glencross BD, Booth M, Allan GL (2007) A feed is only as good as its ingredients—a review of ingredient evaluation strategies for aquaculture feeds. Aquac Nutr 13:17–34
Hansen JØ, Shearer KD, Øverland M, Penn MH, Krogdahl Å, Mydland LT, Storebakken T (2011) Replacement of LT fish meal with a mixture of partially deshelled krill meal and pea protein concentrates in diets for Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 315:275–282
Huang SSY, Oo AN, Higgs DA, Brauner CJ, Satoh S (2007) Effect of dietary canola oil level on the growth performance and fatty acid composition of juvenile red sea bream, Pagrus major. Aquaculture 271:420–431
Ishihara K, Saito H (1996) The docosahexaenoic acid content of the lipid of juvenile bluefin tuna Thunnus orientalis caught in the sea off Japanese coast. Fish Sci 62:840–841
Kader MA, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S, Bulbul M, Honda Y, Mamauag RE, Laining A (2011) Growth, nutrient utilization, oxidative condition, and element composition of juvenile red sea bream Pagrus major fed with fermented soybean meal and scallop by-product blend as fish meal replacement. Fish Sci 77:119–128
Koshio S (2002) Red sea bream, Pagrus major. In: Webster CD, Lim CE (eds) Nutrient requirements and feeding of finfish for aquaculture. CABI Publishing, New York, pp 51–63
Lim SJ, Lee KJ (2009) Partial replacement of fish meal by cottonseed meal and soybean meal with iron and phytase supplementation for parrot fish Oplegnathus fasciatus. Aquaculture 290:283–289
Lu HFS, Bruheim I, Jacobsen C (2014) Oxidative stability and non-enzymatic browning reactions in Antarctic krill oil (Euphausia superba). Lipid Tech 26:111–114
MAFF (2017) Statistics Division from Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Japan: Fisheries and aquaculture production statistics report (inclusive of fisheries economics, October 2015)
Matsukura K, Iino S, Haga Y, Kitagima R, Satoh S (2017) Effect of supplementation with enzyme complex to non-fish meal diet in adult red sea bream Pagrus major. Aquac Sci 65:19–27
McCallum IM, Higgs DA (1989) An assessment of processing effects on the nutritive value of marine protein sources for juvenile chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). Aquaculture 77:181–200
MMAF (2013) Aquaculture Statistic from Ministry of Maritime Affairs and Fisheries of Korea (2013)
Morrison WR, Smith LM (1964) Preparation of fatty acid methylesters and dimethyl acetals from lipids with boron trifluoridemethanol. J Lipid Res 5:600–608
Nordgreen A, Tonheim S, Hamre K (2009) Protein quality of larval feed with increased concentration of hydrolysed protein: effects of heat treatment and leaching. Aquac Nutr 15:525–536
Olsen RE, Suontama J, Langmyhr E, Mundheim H, Ringø E, Melle W, Malde MK, Hemre GI (2006) The replacement of fish meal with Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba in diets for Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar. Aquac Nutr 12:280–290
Ostaszewska T, Dabrowski K, Palacios ME, Olejniczak M, Wieczorek M (2005) Growth and morphological changes in the digestive tract of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and pacu (Piaractus mesopotamicus) due to casein replacement with soybean proteins. Aquaculture 245:273–286
Pérez-Jiménez A, Guedes MJ, Morales AE, Olivia-Teles A (2007) Metabolic responses to short starvation and refeeding in Dicentrarchus labrax. Effect of dietary composition. Aquaculture 265:325–335
Rehbein H (1981) Amino acid composition and pepsin digestibility of krill meal. J Agric Food Chem 29:682–684
Sáez MI, Navarro G, García MS, Martínez TF, García GM, Suárez MD (2013) Influence of pre-slaughtering feed restriction on muscle characteristics of farmed sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) during cold storage. J Sci Food Agric 93:2323–2330
Saito H, Ishihara K, Murase T (1996) Effect of prey fish lipids on the docosahexaenoic acid content of total fatty acids in the lipid of Thunnus albacores yellowfin tuna. Biosci Biotech Biochem 60:962–965
Sargent J, McEvoy L, Estevez A, Bell G, Bell M, Henderson J, Tocher D (1999) Lipid nutrition of marine fish during early development: current status and future directions. Aquaculture 179:217–229
Shiau SY (1997) Utilization of carbohydrates in warmwater fish—with particular reference to tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus × O. aureus. Aquaculture 151:79–96
Skalli A, Hidalgo MC, Abellán E, Arizcum M, Cardenete G (2004) Effects of the dietary protein/lipid ratio on growth and nutrient utilization in common dentex (Dentex dentex L.) at different growth stages. Aquaculture 235:1–11
Skipnes D, Plancken IV, Loey AV, Hendrickx ME (2008) Kinetics of heat denaturation of proteins from farmed Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). J Food Eng 85:51–58
Storebakken T, Refstie S, Ruyter B (2000) Soy products as fat and protein sources in fish feeds for intensive aquaculture. In: Drackly JK (ed) Soy in animal nutrition. Federation of Animal Science Societies, Champaign, pp 127–170
Takeuchi T, Arai S, Watanabe T, Shimma Y (1980) Requirement of eel Anguilla japonica for essential fatty acids. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 46:345–353 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Takeuchi T, Toyota M, Satoh S, Watanabe T (1990) Requirement of juvenile red sea bream Pagrus major for eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 58:1263–1269
Takii K, Seoka M, Izumi M, Hosokawa H, Shimeno S, Ukawa M, Kohbara J (2007) Apparent digestibility coefficient and energy partition of juvenile Pacific bluefin tuna, Thunnus orientalis and chub mackerel, Scomber japonicus. Aquac Sci 55:571–577
Taşbozan O, Emre Y, Gökçe MA, Erbaş C, Özcan F, Kıvrak E (2016) The effects of different cycles of starvation and re-feeding on growth and body composition in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum, 1792). J Appl Ichthyol 32:583–588
Tibbetts SM, Olsen RE, Lall SP (2011) Effects of partial or total replacement of fish meal with freeze-dried krill (Euphausia superba) on growth and nutrient utilization of juvenile Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) and Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus) fed the same practical diets. Aquac Nutr 17:287–303
Tonheim SK, Nordgreen A, Høgøy I, Hamre K, Rønnestad I (2007) In vitro digestibility of water-soluble and water-insoluble protein fractions of some common fish larvae feeds and feed ingredients. Aquaculture 262:426–435
van der Meeren T, Olsen R, Hamre K, Fyhn H (2008) Biochemical composition of copepods for evaluation of feed quality in production of juvenile marine fish. Aquaculture 274:375–397
Venou B, Alexis MN, Fountoulaki E, Haralabous J (2009) Performance factors, body composition and digestion characteristics of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) fed pelleted or extruded diets. Aquac Nutr 15:390–401
Watanabe T, Arakawa T, Kitajima C, Fujita S (1984a) Effect of nutritional quality of broodstock diets on reproduction of red sea bream. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 50:495–501
Watanabe T, Itoh A, Murakami A, Tsukashima Y, Kitajima C, Fujita S (1984b) Effect of nutritional quality of diets given to broodstock on the verge of spawning on reproduction of red sea bream. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 50:1023–1028
Wilson RP (1989) Amino acids and proteins. In: Halver JE (ed) Fish nutrition. Academic Press Inc., San Diego, pp 112–151
Wu G (1998) Intestinal mucosal amino acid catabolism. J Nutr 128:1249–1252
Xu HG, Zhao M, Zheng KK, Wei YL, Yan L, Liang MQ (2017) Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) meal in the diets improved the reproductive performance of tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis) broodstock. Aquac Nutr 23:1287–1295
Yamamoto S, Sakamoto S, Takeuchi M (2002) Estimation of protein sources and effects of water-soluble nitrogen components in artificial diets on larval ayu. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 68:327–333 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Yoshitomi B, Aoki M, Oshima S, Hata K (2006) Evaluation of krill (Euphausia superba) meal as a partial replacement for fish meal in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) diets. Aquaculture 261:440–446
Zhou QC, Tan BP, Mai KS, Liu YJ (2004) Apparent digestibility of selected feed ingredients for juvenile cobia Rachycentron canadum. Aquaculture 241:441–451
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (26252034) from the Japanese Society for Promotion of Science to S. S. and a scholarship from the Tokyu Foundation for Foreign Students to J-H.C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, JH., Haga, Y., Masuda, R. et al. Periodic changes in the growth performance and biochemical composition of juvenile red sea bream Pagrus major fed non-heated and heated squid and krill meal-based diets. Fish Sci 84, 699–713 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-018-1205-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-018-1205-6