Abstract
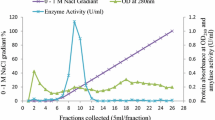
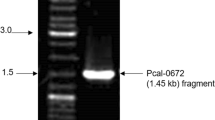
Indian rock oyster Saccostrea forskali is an important commercial species in Thailand. In this study, its full-length α-amylase (SfAmy) cDNA nucleotide sequence was investigated. The SfAmy cDNA was 1,689 bp long and contained a 1,563-bp open reading frame encoding 520 amino acid residues, including a 17-amino acid signal peptide. The molecular mass and the estimated isoelectric point (pI) of the deduced mature S. forskali α-amylase (SfAMY) were 55.948 kDa and 6.45, respectively. The deduced protein sequence showed 45–88 % identity to other mollusk AMYs. The molecular weight was confirmed by the weight of the purified native enzyme. The specific activities of crude and purified native enzymes toward 1 % starch were 29.53 and 187.42 U/mg. In addition, the obtained recombinant SfAMY also showed activity in digesting 1 % starch. The specific activities of the crude and purified recombinant proteins were 11.8 and 46 U/mg. Both enzymes showed optimal activity temperature at 40 °C but their optimum pH values were different, 6.0 for the native and 5.0 for the recombinant. The expression of SfAmy examined by RT-PCR showed the highest levels in the digestive gland but none was observed in the adductor muscle.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vihinen M, Mäntsälä P (1989) Microbial amylolytic enzymes. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 24:329–418
Pandey A, Nigam P, Soccol CR, Soccol VT, Singh D, Mohan R (2000) Advances in microbial amylases. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 31:135–152
Boer PH, Hickey DA (1986) The alpha-amylase gene in Drosophila melanogaster: nucleotide sequence, gene structure and expression motifs. Nucleic Acids Res 14:8399–8411
Grossman GL, Campos Y, Severson DW, James AA (1997) Evidence for two distinct members of the amylase gene family in the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 27:769–781
Benkel BF, Nguyen T, Ahluwalia N, Benkel K, Hickey DA (1997) Cloning and expression of a chicken alpha-amylase gene. Gene 192:261–270
Van Wormhoudt A, Sellos D (1996) Cloning and sequencing analysis of three amylase cDNAs in the shrimp Penaeus vannamei (Crustacea: Decapoda): evolutionary aspects. J Mol Evol 42:543–551
Frøystad MK, Lilleeng E, Sundby A, Krogdahl A (2006) Cloning and characterization of alpha-amylase from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 145(4):479–492
Pasero L, Mazzéi-Pierron Y, Abadie B, Chicheportiche Y, Marchis-Mouren G (1986) Complete amino acid sequence and location of the five disulfide bridges in porcine pancreatic alpha-amylase. Biochim Biophys Acta 869:147–157
Horii A, Emi M, Tomita N, Nishide T, Ogawa M, Mori T, Matsubara K (1987) Primary structure of human pancreatic alpha-amylase gene: its comparison with human salivary alpha-amylase gene. Gene 60:57–64
Le Moine S, Sellos D, Moal J, San Juan Serrano F, Samain JF, Van Wormhoudt A (1997) Amylase on Pecten maximus (Mollusca, bivalves): protein and cDNA characterization; quantification of the expression in the digestive gland. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol 6:228–237
Sellos D, Moal J, Degremont L, Huvet A, Daniel JY, Nicoulaud S, Boudry P, Samain JF, Wormhoudt AV (2003) Structure of amylase genes in populations of Pacific cupped oyster (Crassostrea gigas): tissue expression and allelic polymorphism. Mar Biotechnol 5:360–372
Da Lage J, Van Wormhoudt A, Cariou M (2002) Diversity and evolution of the α-amylase genes in animals. Biologia (Bratisl) 57:181–189
Nikapitiya C, Oh C, Whang I, Kim CG, Lee YH, Kim SJ, Lee J (2009) Molecular characterization, gene expression analysis and biochemical properties of α-amylase from the disk abalone, Haliotis discus discus. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 152:271–281
Kumagai Y, Satoh T, Inoue A, Ojima T (2013) Enzymatic properties and primary structures of two α-amylase isozymes from the Pacific abalone Haliotis discus hannai. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 164:80–88
Janecek S (1997) Alpha-amylase family: molecular biology and evolution. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 67:67–97
Janecek S (1993) Sequence similarities in (alpha/beta)8-barrel enzymes revealed by conserved regions of alpha-amylase. FEBS Lett 316:23–26
Qian M, Ajandouz EH, Payan F, Nahoum V (2005) Molecular basis of the effects of chloride ion on the acid-base catalyst in the mechanism of pancreatic alpha-amylase. Biochemistry 44:3194–3201
Da Lage J-L, Feller G, Janecek S (2004) Horizontal gene transfer from Eukarya to bacteria and domain shuffling: the alpha-amylase model. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:97–109
Nakajima R, Imanaka T, Aiba S (1986) Comparison of amino acid sequences of eleven different alpha-amylases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 23:355–360
Janeček Š (2002) How many conserved sequence regions are there in the α-amylase family? Biologia (Bratisl) 57:29–41
D’Amico S, Gerday C, Feller G (2000) Structural similarities and evolutionary relationships in chloride-dependent alpha-amylases. Gene 253:95–105
Yoosukh W, Duangdee T (1999) Living oysters in Thailand. Phuket Mar Biol Cent Spec Publ 19:363–370
Yan T, Teo LH, Sin YM (1996) Effects of metals on α-amylase activity in the digestive gland of the green mussel, Perna viridis L. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 56:677–682
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Zółtowska K (2001) Purification and characterization of alpha-amylases from the intestine and muscle of Ascaris suum (Nematoda). Acta Biochim Pol 48:763–774
Zeng F, Cohen AC (2000) Partial characterization of alpha-amylase in the salivary glands of Lygus hesperus and L. lineolaris. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 126:9–16
Strobl S, Gomis-Rüth FX, Maskos K, Frank G, Huber R, Glockshuber R (1997) The alpha-amylase from the yellow meal worm: complete primary structure, crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis. FEBS Lett 409:109–114
Sharma P, Shankar PR, Subramaniam G, Kumar A, Tandon A, Suresh CG, Rele MV, Kumar LS (2009) Cloning and sequence analysis of the amylase gene from the rice pest Scirpophaga incertulas Walker and its inhibitor from wheat (Variety Mp Sehore). Int J Insect Sci 1:29–44
Ngernyuang N, Kobayashi I, Promboon A, Ratanapo S, Tamura T, Ngernsiri L (2011) Cloning and expression analysis of the Bombyx mori α-amylase gene (Amy) from the indigenous Thai silkworm strain, Nanglai. J Insect Sci 11:38
Grossman GL, James AA (1993) The salivary glands of the vector mosquito, Aedes aegypti, express a novel member of the amylase gene family. Insect Mol Biol 1:223–232
Qian M, Spinelli S, Driguez H, Payan F (1997) Structure of a pancreatic alpha-amylase bound to a substrate analogue at 2.03 A resolution. Protein Sci 6:2285–2296
Strobl S, Maskos K, Betz M, Wiegand G, Huber R, Gomis-Ryth F, Glockshuber R (1998) Crystal structure of yellow meal worm alpha-amylase at 1.64 A resolution. J Mol Biol 278:617–628
Lombraña M, Suárez P, San Juan F (2005) Two forms of alpha-amylase in mantle tissue of Mytilus galloprovincialis: purification and molecular properties of form II. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 142:56–66
Hsieh M-S, Yin L-J, Jiang S-T (2008) Purification and characterization of the amylase from a small abalone Haliotis sieboldii. Fish Sci 74:425–432
Tsao C-Y, Hsu Y-H, Chao L-M, Jiang S-T (2004) Purification and characterization of three amylases from viscera of hard clam Meretrix lusoria. Fish Sci 70:174–182
Lemos FJA, Campos FAP, Silva CP, Xavier-Filho J (1990) Proteinases and amylases of larval midgut of Zabrotes subfasciatus reared on cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) seeds. Entomol Exp Appl 56:219–227
Dojnov B, Bozić N, Nenadović V, Ivanovic J, Vujcic J (2008) Purification and properties of midgut alpha-amylase isolated from Morimus funereus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) larvae. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 149:153–160
Dojnov B, Lončar N, Božić N, Nenadovic V, Ivanovic J, Vujčić Z (2010) Comparison of alpha-amylase isoforms from the midgut of Cerambyx cerdo L. (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) larvae developed in the wild and on an artificial diet. Arch Biol Sci Belgrad 62:575–583
Hagenbüchle O, Bovey R, Young RA (1980) Tissue-specific expression of mouse-alpha-amylase genes: nucleotide sequence of isoenzyme mRNAs from pancreas and salivary gland. Cell 21:179–187
Ferey-Roux G, Perrier J, Forest E, Marchis-Mouren G, Puigserver A, Santimone M (1998) The human pancreatic alpha-amylase isoforms: isolation, structural studies and kinetics of inhibition by acarbose. Biochim Biophys Acta 1388:10–20
Wagner W, Möhrlen F, Schnetter W (2002) Characterization of the proteolytic enzymes in the midgut of the European cockchafer, Melolontha melolontha (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Insect Biochem Mol Biol 32:803–814
Huvet A, Jeffroy F, Daniel JY, Quéré C, Souchu PL, Van Wormhoudt A, Boudry P, Moal J, Samain JF (2012) Starch supplementation modulates amylase enzymatic properties and amylase B mRNA level in the digestive gland of the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 163:96–100
Klaus U (1990) Comparative animal biochemistry. Springer, Berlin
Promboon A, Engkakul A, Ngernsiri L, Saksoong P (1993) Amylases of the polyvoltine silkworm (Bombyx mori): variation of activity in the Thai local race. Sericologia 33:603–609
Asadi A, Ghadamyari M, Gajedi RH, Sendi JJ, Tabari M (2010) Biochemical characterization of midgut, salivary glands and haemolymph α-amylases of Naranga aenescens. Bull Insectol 63:175–181
Castro P, Freitas ACV, Santana WM, Costa HMS, Carvalho LB, Bezerra RS (2012) Comparative study of amylases from the midgut gland of three species of penaeid shrimp. J Crustac Biol 32:607–613
Baker JE (1983) Properties of amylase from midgets of larvae of Sitophilus zeamais and Sitophilus granaries. Insect Biochem 13:421–428
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Nora Fascestti for critical reading of manuscript. We thank the Higher Education Commission of Thailand and the Center of Agricultural Biotechnology, Kasetsart University, Kampaengsaen Campus, Nakon Pathom, for the grant to TT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
T. Thongsaiklaing and W. Sehawong contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thongsaiklaing, T., Sehawong, W., Kubera, A. et al. Analysis of the α-amylase gene sequence and the enzyme activity of Indian rock oyster Saccostrea forskali . Fish Sci 80, 589–601 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-014-0708-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-014-0708-z