Abstract
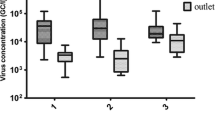
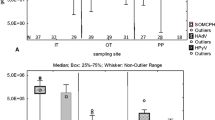
A study of enteric viruses in raw and treated sewage from two secondary treatment plants, which received sewage from Oslo city (plant A) and small municipalities in Hedmark county in Norway (plant B), showed high levels of noro-, adeno-, and bocavirus throughout the year. A seasonal variation was observed for adeno- and GII norovirus with higher levels during winter and bocavirus that had more positive samples during winter. The virus concentrations in raw sewage were comparable in the two plants, with medians (log10 genome copies per liter) of 6.1, 6.3, 6.0, and 4.5 for noro GI, noro GII, adeno-, and bocavirus, respectively. The level of hepatitis E virus was not determined as it was below the limit of quantification. The mean log10 virus reduction was 0.55 (plant A) and 1.44 (plant B) with the highest reduction found in the plant with longer hydraulic retention time. The adenoviruses were dominantly serotype 41, while serotype 12 appeared sporadically. Of the 102 raw and treated sewage samples that were tested, eight were positive for hepatitis E virus of which four were from treated sewage. Two of the four obtained gene sequences from hepatitis E virus originated from the rural sewage samples and showed high similarity with a genotype 3 strain of hepatitis E virus detected in local piglets. Two other hepatitis E virus sequences obtained from urban sewage samples showed high similarities with genotype 3 strains isolated from urban sewage in Spain and a human genotype 1 isolate from India. The study gives information on the levels of noroviruses in raw and treated sewage, which is valuable to risk assessment, information indicating that some infections with hepatitis E viruses in Norway have a regional origin and that human bocavirus 2 and 3 are prevalent in the Norwegian population.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellou, M., Kokkinos, P., & Vantarakis, A. (2013). Shellfish-borne viral outbreaks: a systematic review. Food and Environmental Virology, 5(1), 13–23. doi:10.1007/s12560-012-9097-6.
Blinkova, O., Rosario, K., Li, L., Kapoor, A., Slikas, B., Bernardin, F., et al. (2009). Frequent detection of highly diverse variants of cardiovirus, cosavirus, bocavirus, and circovirus in sewage samples collected in the United States. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 47(11), 3507–3513. doi:10.1128/jcm.01062-09.
Bosch, A., Guix, S., Sano, D., & Pinto, R. M. (2008). New tools for the study and direct surveillance of viral pathogens in water. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 19(3), 295–301. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2008.04.006.
Calgua, B., Barardi, C. R., Bofill-Mas, S., Rodriguez-Manzano, J., & Girones, R. (2011). Detection and quantitation of infectious human adenoviruses and JC polyomaviruses in water by immunofluorescence assay. Journal of Virological Methods, 171(1), 1–7. doi:10.1016/j.jviromet.2010.09.013.
da Silva, A. K., Le Saux, J. C., Parnaudeau, S., Pommepuy, M., Elimelech, M., & Le Guyader, F. S. (2007). Evaluation of removal of noroviruses during wastewater treatment, using real-time reverse transcription-PCR: different behaviors of genogroups I and II. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 73(24), 7891–7897. doi:10.1128/aem.01428-07.
Erker, J. C., Desai, S. M., & Mushahwar, I. K. (1999). Rapid detection of Hepatitis E virus RNA by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction using universal oligonucleotide primers. Journal of Virological Methods, 81(1–2), 109–113.
Flannery, J., Keaveney, S., Rajko-Nenow, P., O’Flaherty, V., & Dore, W. (2012). Concentration of norovirus during wastewater treatment and its impact on oyster contamination. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 78(9), 3400–3406. doi:10.1128/aem.07569-11.
Fong, T. T., Phanikumar, M. S., Xagoraraki, I., & Rose, J. B. (2010). Quantitative detection of human adenoviruses in wastewater and combined sewer overflows influencing a Michigan river. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 76(3), 715–723. doi:10.1128/aem.01316-09.
Gibson, K. E. (2014). Viral pathogens in water: occurrence, public health impact, and available control strategies. Current Opinion in Virology, 4, 50–57. doi:10.1016/j.coviro.2013.12.005.
Grondahl-Rosado, R. C., Yarovitsyna, E., Trettenes, E., Myrmel, M., & Robertson, L. J. (2014). A one year study on the concentrations of norovirus and enteric adenoviruses in wastewater and a surface drinking water source in Norway. Food and Environmental Virology,. doi:10.1007/s12560-014-9161-5.
Hall, B. G. (2013). Building phylogenetic trees from molecular data with MEGA. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30(5), 1229–1235. doi:10.1093/molbev/mst012.
Hata, A., Kitajima, M., & Katayama, H. (2013). Occurrence and reduction of human viruses, F-specific RNA coliphage genogroups and microbial indicators at a full-scale wastewater treatment plant in Japan. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 114(2), 545–554. doi:10.1111/jam.12051.
Jothikumar, N., Cromeans, T. L., Hill, V. R., Lu, X., Sobsey, M. D., & Erdman, D. D. (2005). Quantitative real-time PCR assays for detection of human adenoviruses and identification of serotypes 40 and 41. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 71(6), 3131–3136. doi:10.1128/aem.71.6.3131-3136.2005.
Jothikumar, N., Cromeans, T. L., Robertson, B. H., Meng, X. J., & Hill, V. R. (2006). A broadly reactive one-step real-time RT-PCR assay for rapid and sensitive detection of hepatitis E virus. Journal of Virological Methods, 131(1), 65–71. doi:10.1016/j.jviromet.2005.07.004.
Kapoor, A., Simmonds, P., Slikas, E., Li, L., Bodhidatta, L., Sethabutr, O., et al. (2010). Human bocaviruses are highly diverse, dispersed, recombination prone, and prevalent in enteric infections. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 201(11), 1633–1643. doi:10.1086/652416.
Katayama, H., Haramoto, E., Oguma, K., Yamashita, H., Tajima, A., Nakajima, H., et al. (2008). One-year monthly quantitative survey of noroviruses, enteroviruses, and adenoviruses in wastewater collected from six plants in Japan. Water Research, 42(6–7), 1441–1448. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2007.10.029.
La Rosa, G., Fontana, S., Di Grazia, A., Iaconelli, M., Pourshaban, M., & Muscillo, M. (2007). Molecular identification and genetic analysis of Norovirus genogroups I and II in water environments: comparative analysis of different reverse transcription-PCR assays. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 73(13), 4152–4161. doi:10.1128/aem.00222-07.
Logan, C., O’Leary, J. J., & O’Sullivan, N. (2006). Real-time reverse transcription-PCR for detection of rotavirus and adenovirus as causative agents of acute viral gastroenteritis in children. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 44(9), 3189–3195. doi:10.1128/jcm.00915-06.
Loisy, F., Atmar, R. L., Guillon, P., Le Cann, P., Pommepuy, M., & Le Guyader, F. S. (2005). Real-time RT-PCR for norovirus screening in shellfish. Journal of Virological Methods, 123(1), 1–7. doi:10.1016/j.jviromet.2004.08.023.
Lu, X., & Erdman, D. D. (2006). Molecular typing of human adenoviruses by PCR and sequencing of a partial region of the hexon gene. Archives of Virology, 151(8), 1587–1602. doi:10.1007/s00705-005-0722-7.
Lysen, M., Thorhagen, M., Brytting, M., Hjertqvist, M., Andersson, Y., & Hedlund, K. O. (2009). Genetic diversity among food-borne and waterborne norovirus strains causing outbreaks in Sweden. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 47(8), 2411–2418. doi:10.1128/jcm.02168-08.
Maunula, L., Kaupke, A., Vasickova, P., Soderberg, K., Kozyra, I., Lazic, S., et al. (2013). Tracing enteric viruses in the European berry fruit supply chain. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 167(2), 177–185. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.09.003.
Mena, K. D., & Gerba, C. P. (2009). Waterborne adenovirus. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 198, 133–167. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-09647-6_4.
Myrmel, M., Berg, E. M., Grinde, B., & Rimstad, E. (2006). Enteric viruses in inlet and outlet samples from sewage treatment plants. Journal of Water and Health, 4(2), 197–209.
Neske, F., Blessing, K., Tollmann, F., Schubert, J., Rethwilm, A., Kreth, H. W., et al. (2007). Real-time PCR for diagnosis of human bocavirus infections and phylogenetic analysis. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 45(7), 2116–2122. doi:10.1128/jcm.00027-07.
Nordgren, J., Matussek, A., Mattsson, A., Svensson, L., & Lindgren, P. E. (2009). Prevalence of norovirus and factors influencing virus concentrations during one year in a full-scale wastewater treatment plant. Water Research, 43(4), 1117–1125. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2008.11.053.
Phillips, G., Tam, C. C., Rodrigues, L. C., & Lopman, B. (2010). Prevalence and characteristics of asymptomatic norovirus infection in the community in England. Epidemiology and Infection, 138(10), 1454–1458. doi:10.1017/s0950268810000439.
Rodriguez-Manzano, J., Alonso, J. L., Ferrus, M. A., Moreno, Y., Amoros, I., Calgua, B., et al. (2012). Standard and new faecal indicators and pathogens in sewage treatment plants, microbiological parameters for improving the control of reclaimed water. Water Science and Technology, 66(12), 2517–2523. doi:10.2166/wst.2012.233.
Rohayem, J. (2009). Norovirus seasonality and the potential impact of climate change. Clinical Microbiology & Infection, 15(6), 524–527. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02846.x.
Schildgen, O. (2013). Human bocavirus: lessons learned to date. Pathogens, 2(1), 1–12. doi:10.3390/pathogens2010001.
Svraka, S., Duizer, E., Vennema, H., de Bruin, E., van der Veer, B., Dorresteijn, B., et al. (2007). Etiological role of viruses in outbreaks of acute gastroenteritis in The Netherlands from 1994 through 2005. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 45(5), 1389–1394. doi:10.1128/jcm.02305-06.
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Peterson, D., Filipski, A., & Kumar, S. (2013). MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30(12), 2725–2729. doi:10.1093/molbev/mst197.
WHO. (2011). Guidelines for drinking water quality (Vol. 4). Geneva: World Health Organization.
Widen, F., Sundqvist, L., Matyi-Toth, A., Metreveli, G., Belak, S., Hallgren, G., et al. (2011). Molecular epidemiology of hepatitis E virus in humans, pigs and wild boars in Sweden. Epidemiology and Infection, 139(3), 361–371. doi:10.1017/s0950268810001342.
Acknowledgments
The study was funded by the Norwegian Research Council, Grant number 173021/I10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Myrmel, M., Lange, H. & Rimstad, E. A 1-Year Quantitative Survey of Noro-, Adeno-, Human Boca-, and Hepatitis E Viruses in Raw and Secondarily Treated Sewage from Two Plants in Norway. Food Environ Virol 7, 213–223 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-015-9200-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-015-9200-x