Abstract
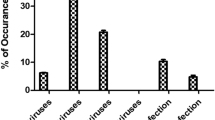
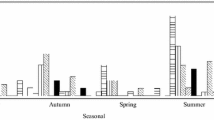
Waste water treatment plant (WWTP) is considered as an important source of surface water contamination by enteric pathogens. In this study, we describe the occurrence of enteric viruses (group A rotaviruses, noroviruses, astroviruses, sapoviruses, hepatitis A virus, and hepatitis E virus) and Clostridium difficile in the effluent of a wastewater treatment plant during a 1-year period. Enteric viruses were simultaneously and efficiently concentrated in a single step using methacrylate monolithic chromatographic support. Rotaviruses, noroviruses (genogroup I and II), and sapoviruses were detected in all 12 concentrated samples, whereas astroviruses were not detected in August and September and hepatitis A and E viruses were not detected at all. Clostridium difficile was detected in all samples and altogether 121 strains were isolated and grouped into 32 different ribotypes of which 014/020 and 010 were most prevalent. Pathogens detected in WWTP effluent partially reflect the epidemiological situation of enteric viruses and C. difficile in human population and open the discussion on implementation of possible techniques for virus and bacteria removal from WWTP effluent prior to release into the surface water system.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Saif, N., & Brazier, J. S. (1996). The distribution of Clostridium difficile in the environment of South Wales. Journal of Medical Microbiology, 45(2), 133–137.
Beller, M., Ellis, A., Lee, S. H., Drebot, M. A., Jenkerson, S. A., Funk, E., et al. (1997). Outbreak of viral gastroenteritis due to a contaminated well—International consequences. Jama-Journal of the American Medical Association, 278(7), 563–568. doi:10.1001/jama.278.7.563.
Bidet, P., Barbut, F., Lalande, V., Burghoffer, B., & Petit, J. C. (1999). Development of a new PCR-ribotyping method for Clostridium difficile based on ribosomal RNA gene sequencing. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 175(2), 261–266.
Bosch, A., Guix, S., Sano, D., & Pinto, R. M. (2008). New tools for the study and direct surveillance of viral pathogens in water. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 19(3), 295–301. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2008.04.006.
Bouzid, M., Steverding, D., & Tyler, K. M. (2008). Detection and surveillance of waterborne protozoan parasites. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 19(3), 302–306. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2008.05.002.
Carducci, A., Morici, P., Pizzi, F., Battistini, R., Rovini, E., & Verani, M. (2008). Study of the viral removal efficiency in a urban wastewater treatment plant. Water Science and Technology: A Journal of the International Association on Water Pollution Research, 58(4), 893–897. doi:10.2166/wst.2008.437.
Chan-it, W., Thongprachum, A., Okitsu, S., Mizuguchi, M., & Ushijima, H. (2010). Epidemiology and molecular characterization of sapovirus and astrovirus in Japan, 2008-2009. Japanese Journal of Infectious Diseases, 63(4), 302–303.
Chhabra, P., Payne, D. C., Szilagyi, P. G., Edwards, K. M., Staat, M. A., Shirley, S. H., et al. (2013). Etiology of viral gastroenteritis in children <5 years of age in the United States, 2008-2009. The Journal of Infectious Diseases, 208(5), 790–800. doi:10.1093/infdis/jit254.
Costafreda, M. I., Bosch, A., & Pinto, R. M. (2006). Development, evaluation, and standardization of a real-time TaqMan reverse transcription-PCR assay for quantification of hepatitis A virus in clinical and shellfish samples. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72(6), 3846–3855. doi:10.1128/AEM.02660-05.
Ellison, S. L., English, C. A., Burns, M. J., & Keer, J. T. (2006). Routes to improving the reliability of low level DNA analysis using real-time PCR. BMC Biotechnology, 6, 33. doi:10.1186/1472-6750-6-33.
Gonzalez, G. G., Liprandi, F., & Ludert, J. E. (2011). Molecular epidemiology of enteric viruses in children with sporadic gastroenteritis in Valencia, Venezuela. Journal of Medical Virology, 83(11), 1972–1982. doi:10.1002/jmv.22185.
Gutierrez-Aguirre, I., Banjac, M., Steyer, A., Poljsak-Prijatelj, M., Peterka, M., Strancar, A., et al. (2009). Concentrating rotaviruses from water samples using monolithic chromatographic supports. Journal of Chromatography A, 1216(13), 2700–2704. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2008.10.106.
Gutierrez-Aguirre, I., Steyer, A., Banjac, M., Kramberger, P., Poljsak-Prijatelj, M., & Ravnikar, M. (2011). On-site reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction detection of rotaviruses concentrated from environmental water samples using methacrylate monolithic supports. Journal of Chromatography A, 1218(17), 2368–2373. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2010.10.048.
Gutierrez-Aguirre, I., Steyer, A., Boben, J., Gruden, K., Poljsak-Prijatelj, M., & Ravnikar, M. (2008). Sensitive detection of multiple rotavirus genotypes with a single reverse transcription-real-time quantitative PCR assay. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 46(8), 2547–2554. doi:10.1128/Jcm.02428-07.
Hata, A., Kitajima, M., & Katayama, H. (2013). Occurrence and reduction of human viruses, F-specific RNA coliphage genogroups and microbial indicators at a full-scale wastewater treatment plant in Japan. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 114(2), 545–554. doi:10.1111/jam.12051.
Janezic, S., Ocepek, M., Zidaric, V., & Rupnik, M. (2012). Clostridium difficile genotypes other than ribotype 078 that are prevalent among human, animal and environmental isolates. BMC Microbiology, 12, 48. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-12-48.
Jothikumar, N., Cromeans, T. L., Robertson, B. H., Meng, X. J., & Hill, V. R. (2006). A broadly reactive one-step real-time RT-PCR assay for rapid and sensitive detection of hepatitis E virus. Journal of Virological Methods, 131(1), 65–71. doi:10.1016/j.jviromet.2005.07.004.
Kageyama, T., Kojima, S., Shinohara, M., Uchida, K., Fukushi, S., Hoshino, F. B., et al. (2003). Broadly reactive and highly sensitive assay for Norwalk-like viruses based on real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 41(4), 1548–1557.
Kolling, G., Wu, M., & Guerrant, R. L. (2012). Enteric pathogens through life stages. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 2, 114. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2012.00114.
Koopmans, M., & Duizer, E. (2004). Foodborne viruses: An emerging problem. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 90(1), 23–41. doi:10.1016/S0168-1605(03)00169-7.
Kovac, K., Gutierrez-Aguirre, I., Banjac, M., Peterka, M., Poljsak-Prijatelj, M., Ravnikar, M., et al. (2009). A novel method for concentrating hepatitis A virus and caliciviruses from bottled water. Journal of Virological Methods, 162(1–2), 272–275. doi:10.1016/j.jviromet.2009.07.013.
La Rosa, G., Pourshaban, M., Iaconelli, M., & Muscillo, M. (2010). Quantitative real-time PCR of enteric viruses in influent and effluent samples from wastewater treatment plants in Italy. Annali dell’Istituto superiore di sanita, 46(3), 266–273. doi:10.4415/ANN_10_03_07.
Laine, J., Huovinen, E., Virtanen, M. J., Snellman, M., Lumio, J., Ruutu, P., et al. (2011). An extensive gastroenteritis outbreak after drinking-water contamination by sewage effluent, Finland. Epidemiology and Infection, 139(7), 1105–1113. doi:10.1017/S0950268810002141.
Lodder, W. J., & de Roda Husman, A. M. (2005). Presence of noroviruses and other enteric viruses in sewage and surface waters in The Netherlands. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71(3), 1453–1461. doi:10.1128/AEM.71.3.1453-1461.2005.
Magill, S. S., Edwards, J. R., Bamberg, W., Beldavs, Z. G., Dumyati, G., Kainer, M. A., et al. (2014). Multistate point-prevalence survey of health care-associated infections. The New England Journal of Medicine, 370(13), 1198–1208. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1306801.
Masclaux, F. G., Hotz, P., Friedli, D., Savova-Bianchi, D., & Oppliger, A. (2013). High occurrence of hepatitis E virus in samples from wastewater treatment plants in Switzerland and comparison with other enteric viruses. Water Research, 47(14), 5101–5109. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2013.05.050.
Medici, M. C., Tummolo, F., Albonetti, V., Abelli, L. A., Chezzi, C., & Calderaro, A. (2012). Molecular detection and epidemiology of astrovirus, bocavirus, and sapovirus in Italian children admitted to hospital with acute gastroenteritis, 2008-2009. Journal of Medical Virology, 84(4), 643–650. doi:10.1002/jmv.23231.
Okoh, A. I., Sibanda, T., & Gusha, S. S. (2010). Inadequately treated wastewater as a source of human enteric viruses in the environment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 7(6), 2620–2637. doi:10.3390/ijerph7062620.
Paul, J. H., Rose, J. B., Jiang, S. C., Zhou, X. T., Cochran, P., Kellogg, C., et al. (1997). Evidence for groundwater and surface marine water contamination by waste disposal wells in the Florida Keys. Water Research, 31(6), 1448–1454. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(96)00374-0.
Romano, V., Pasquale, V., Krovacek, K., Mauri, F., Demarta, A., & Dumontet, S. (2012). Toxigenic Clostridium difficile PCR ribotypes from wastewater treatment plants in southern Switzerland. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 78(18), 6643–6646. doi:10.1128/AEM.01379-12.
Rupnik, M. (2010). Clostridium difficile toxinotyping. Methods in Molecular Biology, 646, 67–76. doi:10.1007/978-1-60327-365-7_5.
Rupnik, M., & Songer, J. G. (2010). Clostridium difficile: Its potential as a source of foodborne disease. Advances in Food and Nutrition Research, 60, 53–66. doi:10.1016/S1043-4526(10)60003-4.
Simmons, F. J., & Xagoraraki, I. (2011). Release of infectious human enteric viruses by full-scale wastewater utilities. Water Research, 45(12), 3590–3598. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2011.04.001.
Smit, J., & Nasr, J. (1992). Urban agriculture for sustainable cities: Using wastes and idle land and water bodies as resources. Environment and Urbanization, 4(2), 141–152. doi:10.1177/095624789200400214.
Steyer, A., Bajzelj, M., Znuderl, K., Berce, I., Drinovec, B., Harlander, T., et al. (2009). Molecular epidemiology of rotaviruses during rotavirus vaccine introduction in Slovenia. Zdravniski Vestnik-Slovenian Medical Journal, 78(8), 381–386.
Steyer, A., Naglic, T., Mocilnik, T., Poljsak-Prijatelj, M., & Poljak, M. (2011a). Hepatitis E virus in domestic pigs and surface waters in Slovenia: Prevalence and molecular characterization of a novel genotype 3 lineage. Infection Genetics and Evolution, 11(7), 1732–1737. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2011.07.007.
Steyer, A., Torkar, K. G., Gutierrez-Aguirre, I., & Poljsak-Prijatelj, M. (2011b). High prevalence of enteric viruses in untreated individual drinking water sources and surface water in Slovenia. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 214(5), 392–398. doi:10.1016/j.ijheh.2011.05.006.
Svraka, S., van der Veer, B., Duizer, E., Dekkers, J., Koopmans, M., & Vennema, H. (2009). Novel approach for detection of enteric viruses to enable syndrome surveillance of acute viral gastroenteritis. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 47(6), 1674–1679. doi:10.1128/JCM.00307-09.
Toplak, N., Okršlar, V., Stani-Racman, D., Gruden, K., & Žel, J. (2004). A high-throughput method for quantifying transgene expression in transformed plants with real-time PCR analysis. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 22, 237–250.
Weese, J. S. (2010). Clostridium difficile in food–innocent bystander or serious threat? Clinical microbiology and infection : the official publication of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 16(1), 3–10. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.03108.x.
Williamson, W. M., Ball, A., Wolf, S., Hewitt, J., Lin, S., Scholes, P., et al. (2011). Enteric viruses in New Zealand drinking-water sources. Water Science and Technology: A Journal of the International Association on Water Pollution Research, 63(8), 1744–1751.
Zidaric, V., Beigot, S., Lapajne, S., & Rupnik, M. (2010). The occurrence and high diversity of Clostridium difficile genotypes in rivers. Anaerobe, 16(4), 371–375. doi:10.1016/j.anaerobe.2010.06.001.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Slovenian National research Agency (ARRS) Grant L2-4314.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steyer, A., Gutiérrez-Aguirre, I., Rački, N. et al. The Detection Rate of Enteric Viruses and Clostridium difficile in a Waste Water Treatment Plant Effluent. Food Environ Virol 7, 164–172 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-015-9183-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-015-9183-7