Abstract
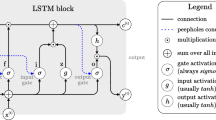
Gesture recognition has been suffering from long-term dependencies and complex variations in both spatial and temporal dimensions. Many traditional methods use hand cropping and sliding window scheme in the spatial and temporal space, respectively. In this paper, we propose a sequentially supervised long short-term memory architecture, which allows using pose information to guide the learning process of gesture recognition using variable length inputs. Technically, we add supervision at each frame using human joint positions. Our proposed methods can solve gesture recognition and pose estimation problems simultaneously using only RGB videos without hand cropping. Experimental results on two benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework compared with the state-of-the-art methods.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rautaray SS, Agrawal A. Adaptive hand gesture recognition system for multiple applications. In: Agrawal A, Tripathi RC, Yi-Luen Do E, Tiwari MD, editors. Intelligent interactive technologies and multimedia. Berlin: Springer; 2013. p. 53–65.
Squartini S, Schuller B, Hussain A. Cognitive and emotional information processing for human–machine interaction. Cogn Comput. 2012;4(4):383–5.
Xu D, Wu X, Chen YL, Xu Y. Online dynamic gesture recognition for human–robot interaction. J Intell Robot Syst. 2014;77(3–4):583–96.
Kröger BJ, Birkholz P, Kannampuzha J, Kaufmann E, Mittelberg I. Movements and holds in fluent sentence production of American sign language: the action-based approach. Cogn Comput. 2011;3(3):449–65.
Rautaray SS, Agrawal A. Vision based hand gesture recognition for human–computer interaction: a survey. Artif Intell Rev. 2015;43(1):1–54.
Shi MY, Zhan DC. Multi gesture recognition: a tracking learning detection approach. In: Sun C, Fang F, Zhou Z-H, Yang W, Liu Z-Y, editors. Intelligence science and big data engineering. Berlin: Springer; 2013. p. 714–21.
Fang Y, Wang K, Cheng J, Lu H. A real-time hand gesture recognition method. In: 2007 IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo. USA: IEEE; 2007. p. 995–98
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems (NIPS). 2012. p. 1106–14
Girshick RB, Donahue J, Darrell T, Malik J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). 2014. p. 580–7
Girshick RB. Fast R-CNN. CoRR abs/1504.08083 (2015)
Ren S, He K, Girshick RB, Sun J. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. CoRR abs/1506.01497 (2015)
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. CoRR abs/1411.4038 (2014)
Graves A, Mohamed Ar, Hinton G. Speech recognition with deep recurrent neural networks. In: 2013 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP). USA: IEEE; 2013. p. 6645–9.
LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. In: Haykin S, Kosko B, editors. Intelligent signal processing. USA: IEEE; 2001. p. 306–51.
Neverova N, Wolf C, Taylor GW, Nebout F. Multi-scale deep learning for gesture detection and localization. In: Computer vision-ECCV 2014 workshops. Berlin: Springer; 2014. p. 474–90.
Pigou L, Dieleman S, Kindermans PJ, Schrauwen B. Sign language recognition using convolutional neural networks. In: Computer vision-ECCV 2014 workshops. Berlin: Springer; 2014. p. 572–8.
Sutskever I, Martens J, Dahl G, Hinton G. On the importance of initialization and momentum in deep learning. In: Proceedings of the 30th international conference on machine learning (ICML-13); 2013. p. 1139–47.
Sipiran I, Bustos B. Harris 3D: a robust extension of the harris operator for interest point detection on 3d meshes. Vis Comput. 2011;27(11):963–76.
Klaser A, Marszałek M, Schmid C. A spatio-temporal descriptor based on 3d-gradients. In: BMVC 2008—19th British Machine Vision Conference. British Machine Vision Association; 2008. p. 275–1.
Dollár P, Rabaud V, Cottrell G, Belongie S. Behavior recognition via sparse spatio-temporal features. In: 2nd joint IEEE international workshop on visual surveillance and performance evaluation of tracking and surveillance, 2005. USA: IEEE; 2005. p. 65–72.
Wang H, Ullah MM, Klaser A, Laptev I, Schmid C. Evaluation of local spatio-temporal features for action recognition. In: BMVC 2009—British Machine Vision Conference. BMVA Press; 2009. p. 124–31.
Peng X, Wang L, Cai Z, Qiao Y. Action and gesture temporal spotting with super vector representation. In: Computer vision-ECCV 2014 workshops. Berlin: Springer; 2014. p. 518–27.
Zhang H, Bai X, Zhou J, Cheng J, Zhao H. Object detection via structural feature selection and shape model. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2013;22(12):4984–95.
Tu Z, Zheng A, Yang E, Luo B, Hussain A. A biologically inspired vision-based approach for detecting multiple moving objects in complex outdoor scenes. Cogn Comput. 2015;7(5):539–51.
Wu J, Cheng J, Zhao C, Lu H. Fusing multi-modal features for gesture recognition. In: Proceedings of the 15th ACM on international conference on multimodal interaction. New York: ACM; 2013. p. 453–60.
Wu J, Cheng J. Bayesian co-boosting for multi-modal gesture recognition. J Mach Learn Res. 2014;15(1):3013–36.
Wu D, Shao L. Leveraging hierarchical parametric networks for skeletal joints based action segmentation and recognition. In: 2014 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). USA: IEEE; 2014. p. 724–31.
Toshev A, Szegedy C. Deeppose: Human pose estimation via deep neural networks. In: 2014 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). USA: IEEE; 2014. p. 1653–60.
Tompson JJ, Jain A, LeCun Y, Bregler C. Joint training of a convolutional network and a graphical model for human pose estimation. In: Advances in neural information processing systems; 2014. p. 1799–807.
Neverova N, Wolf C, Paci G, Sommavilla G, Taylor GW, Nebout F. A multi-scale approach to gesture detection and recognition. In: 2013 IEEE international conference on computer vision workshops (ICCVW). USA: IEEE; 2013. p. 484–91.
Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997;9(8):1735–80.
Ruffieux S, Lalanne D, Mugellini E. Chairgest: a challenge for multimodal mid-air gesture recognition for close HCI. In: Proceedings of the 15th ACM on international conference on multimodal interaction. USA: ACM; 2013. p. 483–88.
Escalera S, Baró X, Gonzalez J, Bautista MA, Madadi M, Reyes M, Ponce-López V, Escalante HJ, Shotton J, Guyon I. Chalearn looking at people challenge 2014: dataset and results. In: Computer vision-ECCV 2014 workshops. Berlin: Springer; 2014. p. 459–73.
Bergstra J, Breuleux O, Bastien F, Lamblin P, Pascanu R, Desjardins G, Turian J, Warde-Farley D, Bengio Y. Theano: a CPU and GPU math expression compiler. In: Proceedings of the Python for scientific computing conference (SciPy), vol. 4. Austin, TX; 2010. p. 3.
Bastien F, Lamblin P, Pascanu R, Bergstra J, Goodfellow I, Bergeron A, Bouchard N, Warde-Farley D, Bengio Y. Theano: new features and speed improvements. arXiv preprint arXiv:1211.5590 (2012).
Cao C, Zhang Y, Lu H. Multi-modal learning for gesture recognition. In: 2015 IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo (ICME). USA: IEEE; 2015. p. 1–6.
Donahue J, Hendricks LA, Guadarrama S, Rohrbach M, Venugopalan S, Saenko K, Darrell T. Long-term recurrent convolutional networks for visual recognition and description. arXiv preprint arXiv:1411.4389 (2014).
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, Huang Z, Karpathy A, Khosla A, Bernstein M, et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int J Comput Vis. 2015;115(3):211–52.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61332016) and Project of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDB02060001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Peisong Wang, Qiang Song, Hua Han and Jian Cheng declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008 (5). Additional informed consent was obtained from all patients for which identifying information is included in this article.
Human and Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Song, Q., Han, H. et al. Sequentially Supervised Long Short-Term Memory for Gesture Recognition. Cogn Comput 8, 982–991 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-016-9388-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-016-9388-6