Abstract
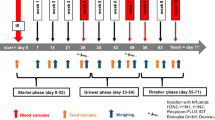
The present study examined the short-term effects of deoxynivalenol (DON), administered at two different concentrations via a feed preparation using naturally contaminated wheat, on feed intake, liver and kidney metabolism and immunomodulatory properties in horses. Twelve geldings were randomly assigned to one of three dietary treatments for 21 days. DON was provided via naturally contaminated wheat (14.6 ± 6.5 mg DON/kg dry matter). The daily feed intake was adjusted to 4 kg of wheat and 1.7 kg of silage per 100 kg of body weight (BW). Horses were fed one of the following diets: control wheat with 0 % contaminated wheat (CON), wheat mixture containing 53 ± 2 % of DON-contaminated wheat [low DON intake (LDI)] or wheat mixture containing 78 ± 4 % of DON-contaminated wheat [high DON intake (HDI)]. CON, LDI and HDI corresponded to a targeted daily DON intake via the complete ration of <5, 50 and 75 μg/kg BW, respectively. None of the horses demonstrated any clinical signs commonly associated with the intake of DON such as colic or depression. HDI was associated with lower daily wheat intake on day 21. Serum DON concentrations increased with higher DON intake. The non-toxic DON metabolite, deepoxy-deoxynivalenol (DOM-1) was only detected on day 21 of the DON feeding period. No changes in haematological and serum parameters or serum globulins or in the ex vivo proliferation response of peripheral blood mononuclear cells were observed. These results suggest that horses are less sensitive to DON exposure than other domestic species, for example, swine. Therefore, the European Commission guidance value for critical DON concentrations in swine feed (complete diet) of 0.9 mg/kg could be safely applied for rations intended for feeding adult horses as well.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergsjø B, Langseth W, Nafstad I, Jansen JH, Larsen HJS (1993) The effects of naturally deoxynivalenol-contaminated oats on the clinical condition, blood parameters, performance and carcass composition of growing pigs. Vet Res Comm 17:283–294
Binder EM, Tan LM, Chin LJ, Handl J, Richard J (2007) Worldwide occurrence of mycotoxins in commodities, feeds and feed ingredients. Anim Feed Sci Technology 137:265–282
Cote LM, Beasley VR, Bratich PM, Swanson SP, Shivaprasad HL, Buck WB (1985) Sex-related reduced weight gains in growing swine fed diets containing deoxynivalenol. J Anim Sci 61:942–950
Dänicke S, Goyarts T, Valenta H, Razzazi E, Böhm J (2004a) On the effects of deoxynivalenol (DON) in pigs feed on growth performance, nutrients utilization and DON metabolism. J Anim Feed Sci 13:539–556
Dänicke S, Keese C, Goyarts T, Döll S (2011) Effects of deoxynivalenol (DON) and related compounds on bovine peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) in vitro and in vivo. Mycotoxin Res 27:49–55
Dänicke S, Valenta H, Klobasa F, Döll S, Ganter M, Flachowsky G (2004b) Effects of graded levels of Fusarium toxin contaminated wheat in diets for fattening pigs on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, deoxynivalenol balance and clinical serum characteristics. Arch Anim Nutr 58:1–17
EFSA (2004) Opinion of the scientific panel on contaminants in the food chain on a request from the commission related to deoxynivalenol (DON) as undesirable substance in animal feed., 1-42, http://www.efsa.europa.eu
Forsell JH, Witt MF, Tai JH, Jensen R, Pestka JJ (1986) Effects of 8-week exposure of the B6C3F1 mouse to dietary deoxynivalenol (vomitoxin) and zearalenone. Food Chem Toxic 24:213–219
Goyarts T, Dänicke S (2006) Bioavailability of the Fusarium toxin deoxynivalenol (DON) from naturally contaminated wheat for the pig. Toxicol Lett 163:171–182
Goyarts T, Dänicke S, Rothkötter HJ, Spilke J, Tiemann U, Schollenberger M (2005) On the effects of a chronic deoxynivalenol intoxication on performance, haematological and serum parameters of pigs when diets are offered either for ad libitum consumption or fed restrictively. J Vet Med 52:305–314
Johnson PJ, Casteel SW, Messer NT (1997) Effect of feeding deoxynivalenol (vomitoxin)-contaminated barley to horses. J Vet Diagn Invest 9:219–221
Keese C, Meyer U, Valenta H, Schollenberger M, Starke A, Weber IA, Rehage J, Breves G, Dänicke S (2008) No carry over of unmetabolised deoxynivalenol in milk of dairy cows fed high concentrate proportions. Mol Nutr Food Res 52:1514–529
Khol-Parisini HP, Razzazi-Fazeli E, Saalmüller A, Strasser A, Zentek J (2012) Highly deoxynivalenol contaminated oats and immune function in horses. Archiv Anim Nutr 66:149–161
Kraft W, Dürr UM (2013) Klinische Labordiagnostik in der Tiermedizin. Moritz A (Ed). Schattauer Verlag Stuttgart, Germany
Minervini F, Dell´Aquila ME (2008) Zearalenone and reproductive function in farm animals. Intern J Mol Sci 9:2570–2584
Pestka JJ (2007) Deoxynivalenol: toxicity, mechanisms and animal health risks. Anim Feed Sci Techn 137:283–298
Prelusky DB (1993) The effect of low-level deoxynivalenol on neurotransmitter levels measured in pig cerebral spinal fluid. J Environ Health Sci 28:731–761
Prelusky DB, Gerdes RG, Underhill KL, Rotter BA, Jui PY, Trenholm HL (1994) Effects of low-level dietary deoxynivalenol on haematological and clinical parameters of the pig. Natural Toxins 2:97–104
Raymond SL, Smith TK, Swamy HVLN (2003) Effects of feeding a blend of grains naturally contaminated with Fusarium mycotoxins on feed intake, serum chemistry, and hematology of horses, and the efficacy of a polymeric glucomannan mycotoxin absorbent. J Anim Sci 81:2123–2130
Raymond SL, Smith TK, Swamy HVLN (2005) Effects of feeding a blend of grains naturally contaminated with Fusarium mycotoxins on feed intake, metabolism, and indices of athletic performance of exercised horses. J Anim Sci 83:1267–1273
Rotter BA, Prelusky DB, Pestka JJ (1996) Toxicology of deoxynivalenol (vomitoxin). J Toxicol Environ Health 48:1–34
Rotter BA, Thompson BK, Lessard M, Trenholm HL, Tryphonas H (1994) Influence of low-level exposure to Fusarium mycotoxins on selected immunological and hematological parameters in young swine. Fund Applied Toxicol 23:117–124
Seeling K, Dänicke S, Valenta H, Van Egmond HP, Schothorst RC, Jekel AA, Lebzien P, Schollenberger M, Razzazi-Fazeli E, Flachowsky G (2006) Effects of Fusarium toxin-contaminated wheat and feed intake level on the biotransformation and carry-over of deoxynivalenol in dairy cows. Food Additives Contaminants 23:1008–1020
Smith TK, McMillan EG, Castillo JB (1997) Effect of feeding blends of Fusarium mycotoxin- contaminated grains containing deoxynivalenol and fusaric acid on growth and feed consumption of immature swine. J Anim Sci 75:2184–2191
Valenta H, Dänicke S, Blüthgen A (2002) Mycotoxins in soy bean feedstuffs used in Germany. Mycotoxin Res 18(Suppl 2):208–211
Wood GE (1992) Mycotoxins in foods and feeds in the United States. J Anim Sci 70:3941–3949
Acknowledgments
The study was funded by the Schaumann Stiftung. The authors want to thank Sabine Klemann for the great technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors of this paper has a financial or personal relationship with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence or bias the content of the paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schulz, AK., Kersten, S., Dänicke, S. et al. Effects of deoxynivalenol in naturally contaminated wheat on feed intake and health status of horses. Mycotoxin Res 31, 209–216 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12550-015-0234-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12550-015-0234-6