Abstract
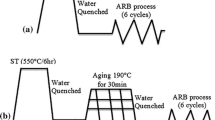
This work is focused on the effect of pre-aging time on the properties of Al-2wt%Cu alloy processed by accumulative roll bonding (ARB) process. Following aged at 190 °C for 10 or 30 min, the samples were deformed up to a strain of 4.8 by the ARB process. The microstructure evolution was investigated by transmission electron microscope and electron backscattering diffraction analyzes. The results showed that the Al2Cu precipitates were formed with different sizes due to the different pre-aging times and the finer precipitates were more effective on the formation of high angle grain boundaries during the ARB process. The grain size of Aged-10 min and Aged-30 min specimens decreased to 400 nm and 420 nm, respectively, after 6 cycles of the ARB process. Also, the final texture after 6 cycles of the ARB process, shown in the {111} pole figure, were different depending on the starting microstructures. The mechanical properties of specimens were investigated by the Vickers microhardness measurements and the tensile tests. The results showed that the mechanical properties are affected by the starting microstructure. The mechanical properties of Aged-10 min specimen were different compared to Aged-30 min specimen due to the different size of the pre-existing precipitates. Although by continuing process, the precipitates were probably dissolved due to the heavy deformation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Azad and E. Borhani, J. Min. Metall. Sect. B (In press).
E. Borhani, H. Jafarian, H. Adachi, D. Terada, and N. Tsuji, J. Mater. Sci. Forum 667-669, 211 (2010).
R. Z. Valiev and T. G. Langdon, Prog. Mater. 51, 881, (2006).
R. Z. Valiev, R. K. Islamgaliev, and I. V. Alexandrov, Prog. Mater. Sci. 45, 103 (2000).
M. Richert, Q. Liu, and N. Hansen, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 260, 27 (1999).
Y. Saito, H. Utsunomiya, N. Tsuji, and T. Sakai, Acta Mater. 47, 579 (1999).
E. Borhani, H. Jafarain, A. Shibata, and N. Tsuji, J. Mater. Trans. 53, 1863 (2012).
S. H. Lee, Y. Saito, T. Sakai, and H. Utsunomiya, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 325, 228 (2002).
V. D. Cojocaru, D. Raducanu, D. M. Gordin, and I. Cinca, J. Alloy Compd. 546, 260 (2013).
E. Borhani, H. Jafarian, D. Terada, H. Adachi, and N. Tsuji, Mater. Trans. 53, 72 (2011).
E. Borhani, H. Jafarian, T. Sato, D. Terada, Y. Miyajima, and N. Tsuji, Proc. 12th Intern. Conf. on Al. Alloy, p.2168, Japan (2010).
B. K. Min, H. W. Kim, and S. B. Kang, J. Mater. Proc. Tech. 162-163, 355 (2005).
N. Tsuji, T. Toyoda, Y. Minamino, Y. Koizumi, T. Yamane, M. Komatsu, and M. Kiritani, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 350, 108 (2003).
J. M. Silcock, T. J. Heal, and H. K. Hardy, J. Inst. Met. 82, 239 (1953-1954).
A. Biswas, D. J. Siegel, C. Wolverton, and D. N. Seidman, Acta Mater. 59, 6187 (2011).
X. Huang, N. Tsuji, N. Hansen, and Y. Minamino, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 340, 265 (2003).
B. G. Clark, I. M. Robertson, and L. M. Dougherty, Mater. Res. 20, 1792 (2005).
F. Salimyanfard, M. Reza Toroghinejad, F. Ashrafizadeh, and M. Jafari, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 5348 (2011).
C. Xu, M. Furukawa, Z. Horita, and T. G. Langdon, Acta Mater. 51, 6139 (2003).
Y. Iwahashi, Z. Horita, M. Nemoto, and T. G. Langdon, Acta Mater. 46, 3317 (1998).
K.-T. Park, H.-J. Kwon, W.-J. Kim, and Y.-S. Kim, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 316, 145 (2001).
X. Huang, N. Tsuji, N. Hansen, and Y. Minamino, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 340, 265 (2003).
L. S. Toropova, D. G. Eskin, M. L. Kharakterova, and T. V. Dobatkina, Advanced Aluminum Alloys Containing Scandium: Structure and Properties, Gordon and Breach Science, The Netherlands (1998).
F. J. Humphreys and M. Hatherly, Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena, pp.73–87, Pergamon Press, Oxford (1995).
Z. Horita, K. Oh-ishi, and K. Kaneko, Sci. Tech. Adv. Mater. 7, 649 (2006).
G. F. Carter and D. E. Paul, Materials Science and Engineering, p.81, Materials Park, ASM International, Ohio (1991).
B. Azad and E. Borhani, J. Mat. Eng. Per. 24, 4789 (2015).
K. T. Park, H. J. Kwon, W. J. Kim, and Y. S. Kim, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 316, 145 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azad, B., Borhani, E. Pre-aging time dependence of microstructure and mechanical properties in nanostructured Al-2wt%Cu alloy. Met. Mater. Int. 22, 243–251 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-016-5510-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-016-5510-2