Abstract
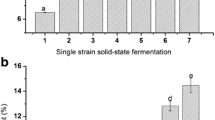
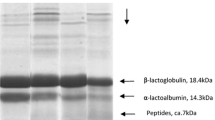
Hydrolysis of wheat proteins during sourdough fermentation was determined in the present study. Sourdoughs were characterized with respect to cell counts, pH, TTA, and proteolytic activity as well as the quantity of total proteins and water-soluble proteins. Moreover, composition analysis of total proteins and water-soluble proteins using SDS-PAGE was carried out. Sourdough fermentation using Lactobacillus plantarum showed a decrease in pH and increase in TTA during fermentation. Fermentation resulted in hydrolysis and solubilization of wheat proteins. It demonstrated that protein hydrolysis in sourdough was mainly caused by pH-dependent activation of cereal enzymes according to change in proteolytic activity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rupesh SC, Shraddha RC (2011) Sourdough technology—a traditional way for wholesome foods: a review. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 10:170–183
Gänzle MG, Vogel RF (2002) Contribution of reutericyclin production to the stable persistence of Lactobacillus reuteri in an industrial sourdough fermentation. Int J Food Microbiol 80:31–45
Lavermicocca P, Valerio F, Evidente A, Lazzaroni S, Corsetti A, Gobbetti M (2000) Purification and characterization of novel antifungal compounds from the sourdough Lactobacillus plantarum strain 21B. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:4084–4090
Thiele C, Gänzle MG, Vogel RF (2002) Contribution of sourdough lactobacilli, yeast, and cereal enzymes to the generation of amino acids in dough relevant for bread flavor. Cereal Chem 79:45–51
Armero E, Collar C (1998) Crumb firming kinetics of wheat breads with anti-staling additives. J Cereal Sci 28:165–174
Collar Esteve C, Benetido de Barber C, Martinez-Anaya M (1994) Microbial sour doughs influence acidification properties and breadmaking potential of wheat dough. J Food Sci 59(629–633):674
Liljeberg HGM, Björck IME (1996) Delayed gastric emptying rate as a potential mechanisms for lowered glycemia after eating sourdough bread: studies in humans and rats using test products with added organic acids or an organic salt. Am J Clin Nutr 64:886–893
Park YH, Jung LH, Jeon ER (2006) Quality characteristics of bread using sourdough. Food Sci Nutr 33:323–327
Vermeulen N, Gänzle MG, Vogel RF (2006) Influence of peptide supply and co-substrates on phenylalanine metabolism of Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis DSM20451T and Lactobacillus plantarum TMW1.468. Food Chem 54:3832–3839
De Vuyst L, Neysens P (2005) The sourdough microflora: biodiversity and metabolic interactions. Trends Food Sci Technol 16:43–56
Thieking M, Korakli M, Ehrmann MA, Gänzle MG, Vogel RF (2003) In situ production of exopolysaccharides during sourdough fermentation by cereal and intestinal isolates of lactic acid bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:945–952
Gänzlea MG, Loponena J, Gobbetti M (2008) Proteolysis in sourdough fermentations: mechanisms and potential for improved bread quality. Trends Food Sci Technol 19:513–521
Mugula JK, Sørhaug T, Stepaniak L (2003) Proteolytic activities in togwa, a Tanzanian fermented food. Int J Food Microbiol 84:1–12
Clarke CI, Schober TJ, Angst E, Arendt EK (2003) Use of response surface methodology to investigate the effects of processing conditions on sourdough wheat bread quality. Eur Food Res Technol 217(1):23–33
Loponen J (2006) Prolamin degradation in sourdoughs. (dissertation) EKT series 1372. University of Helsinki, Yliopistopaino, Helsinki, Finland, http://urn.fi/URN:ISBN:952-10-3582-X
Mikola L (1986) Acid carboxypeptidases in grains and leaves of wheat, Triticum aestivum L. Plant Physiol 81:823–829
Bleukx W, Brijs K, Torrekens S, van Leuven F, Delcour JA (1998) Specificity of a wheat gluten aspartic proteinase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1387:317–324
Bleukx W, Delcour JA (2000) A second aspartic proteinase associated with wheat gluten. J Cereal Sci 32:31–42
Kunji ER, Mierau I, Hagting A, Poolman B, Konings WN (1996) The proteolytic system of lactic acid bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 70:187–221
Guédon E, Renault P, Ehrlich SD, Delorme C (2001) Transcriptional pattern of genes coding for the proteolytic system of Lactococcus lactis and evidence for coordinated regulation of key enzymes by peptide supply. J Bacteriol 183:3614–3622
Juillard V, le Bars D, Kunji ERS, Konings WN, Gripon JC, Richard J (1995) Oligopeptides are the main source of nitrogen for Lactococcus lactis during growth in milk. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3024–3030
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the financial support of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31071496), Zhengzhou Science and Technology Innovation Team Program (No. 121PCXTD518) and the Education Department of Henan Province, the Natural Science Project (No. 15A180033). The authors are grateful to Dr. F. MacRitchie for editorial assistance with the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, Y., Wang, J., Yang, S. et al. Protein Degradation in Wheat Sourdough Fermentation with Lactobacillus plantarum M616. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 7, 205–210 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-015-0262-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-015-0262-0