Abstract
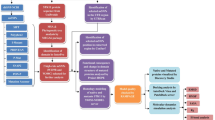
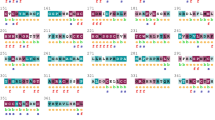
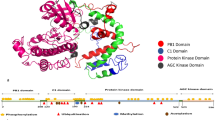
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR), a member of the receptor tyrosine kinase family has shown to be implicated in the development and progression of various cancers due to mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain (TKD). It is important to understand the functional significance of amino acid variation occurring within TKD due to non-synonymous Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (nsSNPs). Therefore, we have evaluated the influence of nsSNPs on the structure of EGFR-TKD using computational methods. Out of 2,493 SNPs in the EGFR gene, only 41 were found to be non-synonymous. In silico evaluation of these nsSNPs using a sequence based SIFT tool and structure based PolyPhen algorithm revealed that 13 nsSNPs disrupted the conformation of EGFR-TKD. Protein stability analysis using CUPSAT, I-mutant2.0 and iPTree-STAB identified 6 mutants that are less stable than the wild structure. Thereafter, to evaluate the structural impact of 5 mutants (G719A, P733L, V742A, S768I and H773R) the molecular dynamics (MD) simulation for 2 ns was performed. The MD trajectories showed that the native EGFR was stabilized after 0.9 ns while the stability of mutants was achieved after longer simulation. The RMSF profile of P-loop and A-loop shows an increased flexibility for all the mutants. We also observed that the 3 mutants (V742A, P733L and H773R) showed large root mean square deviation (2.075, 2.59 and 2.752 Å respectively) compared to the native EGFR. Further docking studies indicate that gefitinib can be administered for combating cancer occurring due to presence of these mutations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adzhubei, I.A., Schmidt, S., Peshkin, L., Ramensky, V.E., Gerasimova, A., Bork, P., Kondrashov, A.S., Sunyaev, S.R. 2010. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods 7, 248–249.
Avizienyte, E., Ward, R.A., Garner, A.P. 2008. Comparison of the EGFR resistance mutation profiles generated by EGFR-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors and the impact of drug combinations. Biochem J 415, 197–206.
Balak, M.N., Gong, Y., Riely, G.J., Somwar, R., Li, A.R., Zakowski, M.F., Chiang, A., Yang, G., Ouerfelli, O., Kris, M.G., Ladanyi, M., Miller, V.A., Pao, W. 2006. Novel D761Y and common secondary T790M mutations in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung adenocarcinomas with acquired resistance to kinase inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res 12, 6494–6501.
Capriotti, E., Fariselli, P., Casadio, R. 2005. IMutant2.0: Predicting stability changes upon mutation from the protein sequence or structure. Nucl Acid Res 33, W306–310.
De Alencar, S.A., Lopes, J.C. 2010. A comprehensive in silico analysis of the functional and structural impact of SNPs in the IGF1R gene. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010, Article ID: 715139.
Guex, N., Diemand, A., Pettsch, M.C. 1999. Protein modelling for all. Trends Biochem Sci 24, 364–367.
Hall, T.A. 1999. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser 41, 95–98.
Hess, B., Kutzner, C., van der Spoel, D., Lindahl, E. 2008. GROMACS 4: Algorithms for highly efficient, load-balanced, and scalable molecular simulation. J Chem Theory Comput 4, 435–447.
Huang, L.T., Gromiha, M.M., Ho, S.Y. 2007. iPTREESTAB: Interpretable decision tree based method for predicting protein stability changes upon mutations. Bioinformatics 23, 1292–1293.
Humphrey, W., Dalke, A., Schulten, K. 1996. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J Mol Graphics 14, 33–38.
Jones, G., Willett, P., Glen, R.C., Leach, A.R., Taylor, R. 1997. Development and validation of a genetic algorithm for flexible docking. J Mol Biol 267, 727–748.
Jorissen, R.N., Walker, F., Pouliot, N., Garrett, T.P., Ward, C.W., Burgess, A.W. 2003. Epidermal growth factor receptor: Mechanisms of activation and signalling. Exp Cell Res 284, 31–53.
Kumar, A., Petri, E.T., Halmos, B., Boggon, T.J. 2008. Structure and clinical relevance of the epidermal growth factor receptor in human cancer. J Clin Oncol 26, 1742–1751.
Linardou, H., Dahabreh, I.J., Bafaloukos, D., Kosmidis, P., Murray, S. 2009. Somatic EGFR mutations and efficacy of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in NSCLC. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 6, 352–366.
Matthews, D.J., Gerritsen, M.E. 2010. Targeting Protein Kinases for Cancer Therapy, 1st Ed. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., USA.
Murray, S., Dahabreh, I.J., Linardou, H., Manoloukos, M., Bafaloukos, D., Kosmidis, P. 2008. Somatic mutations of the tyrosine kinase domain of epidermal growth factor receptor and tyrosine kinase inhibitor response to TKIs in non-small cell lung cancer: An analytical database. J Thorac Oncol 3, 832–839.
Ng, P.C., Henikoff, S. 2003. SIFT: Predicting amino acid changes that affect protein function. Nucl Acid Res 31, 3812–3814.
Parthiban, V., Gromiha, M.M., Schomburg D. 2006. CUPSAT: Prediction of protein stability upon point mutations. Nucl Acid Res 34, W239–242.
Rajasekaran, R., Sethumadhavan, R. 2010. In silico identification of significant detrimental missense mutations of EGFR and their effect with 4-anilinoquinazoline-based drugs. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160, 1723–1733.
Sherry, S.T., Ward, M.H., Kholodov, M., Baker, J., Phan, L., Smigielski, E.M., Sirotkin, K. 2001. dbSNP: The NCBI database of genetic variation. Nucl Acid Res 29, 308–311.
Snow, J.B., Wackym, A.P. 2009. Ballenger’s Otorhinolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery, 17th Ed. Peoples Medical Publishing House, Shelton, USA.
Stein, R.A., Staros V.J. 2006. Insights into the evolution of the ErbB receptor family and their ligands from sequence analysis. BMC Evol Bio 6, 79.
Wallace, A.C., Laskowski, R.A., Thornton, J.M. 1995. LIGPLOT: A program to generate schematic diagrams of protein-ligand interactions. Protein Eng 8, 127–134.
West, C.M., Joseph, L., Bhana, S. 2008. Epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted therapy. Br J Radiol 81, S36–44.
Yuan, H.Y., Chiou, J.J., Tseng, W.H., Liu, C.H., Liu, C.K., Lin, Y.J., Wang, H.H., Yao, A., Chen, Y.T., Hsu, C.N. 2006. FASTSNP: An always up-to-date and extendable service for SNP function analysis and prioritization. Nucl Acid Res 34, 635–641.
Zhang, X., Gureasko, J., Shen, K., Cole, P.A., Kuriyan, J. 2006. An allosteric mechanism for activation of the kinase domain of epidermal growth factor receptor. Cell 125, 1137–1149.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raghav, D., Sharma, V. & Agarwal, S.M. Structural investigation of deleterious non-synonymous SNPs of EGFR gene. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 5, 60–68 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-013-0149-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-013-0149-x