Abstract
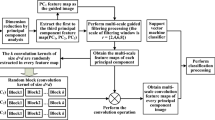
High spatial resolution hyperspectral images not only contain abundant radiant and spectral information, but also display rich spatial information. In this paper, we propose a multi-feature high spatial resolution hyperspectral image classification approach based on the combination of spectral information and spatial information. Three features are derived from the original high spatial resolution hyperspectral image: the spectral features that are acquired from the auto subspace partition technique and the band index technique; the texture features that are obtained from GLCM analysis of the first principal component after principal component analysis is performed on the original image; and the spatial autocorrelation features that contain spatial band X and spatial band Y, with the grey level of spatial band X changing along columns and the grey level of spatial band Y changing along rows. The three features are subsequently combined together in Support Vector Machine to classify the high spatial resolution hyperspectral image. The experiments with a high spatial resolution hyperspectral image prove that the proposed multi-feature classification approach significantly increases classification accuracies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appice, A., Guccione, P., & Malerba, D. (2017). A novel spectral-spatial co-training algorithm for the transductive classification of hyperspectralimagery data. Pattern Recognition, 63(3), 229–245.
Camps-Valls, G., Gómez-Chova, L., Calpe-Maravilla, J., Martin-Guerrero, J. D., Soria-Olivas, E., Alonso-Chorda, L., et al. (2004). Robust support vector method for hyper-spectral data classification and knowledge discovery. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 42(7), 1530–1542.
Camps-Valls, G., Gómez-Chova, L., Muñoz-Marí, J., Vila-Francés, J., & Calpe-Maravilla, J. (2006). Composite kernels for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 3(1), 93–97.
Camps-Valls, G., Shervashidze, N., & Borgwardt, K. M. (2010). Spatio-spectral remote sensing image classification with graph kernels. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 7(4), 741–745.
Chen, C., Li, W., Su, H., & Liu, K. (2014). Spectral-spatial classification of hyperspentral images based on kernel extreme learning machine. Remote Sensing, 6(6), 5795–5814. doi:10.3390/rs6065795.
Cooley, T., Anderson, G. P., Felde, G. W., et al. (2002). FLAASH, a MODTRAN4-based atmospheric correction algorithm, its application and validation. Geoscience and remote Sensing Symposium, 2002, IGRASS 2002, 3, 1414–1418.
Crammer, K., & Singer, Y. (2001). On the algorithmic implementation of multiclass kernel-based vector machines. Journal of machine Learning Research, 2, 265–292.
Damodaran, B. B., & Nidamanuri, R. R. (2014). Assessment of the impact of dimensionality reduction methods on information classes and classifiers for hyperspectral image classification by multiple classifier system. Advances in Space Research, 53(12), 1720–1734.
Galloway, M. (1975). Texture analysis using gray level run lengths. Computer Graphics and Image Processing, 4(2), 172–179.
Gao Y., Chua TS. (2013) Hyperspectral Image Classification by Using Pixel Spatial Correlation. In: S. Li et al. (Eds.), Advances in multimedia modeling. MMM 2013. Lecture notes in computer science, (vol 7732). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer.
Gorretta, N., Rabatel, G., Fiorio, C., Lelong, C., & Roger, J. M. (2012). An iterative hyperspectral image segmentation method using a cross analysis of spectral and spatial information. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 117(1), 213–223.
Gu, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2003). Feature extraction based on automatic subspace partition for hyperspectral images. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 18(6), 384–387. (in Chinese).
Haralick, R. M., Shanmuga, K., & Dinstein, I. (1973). Textural features for image classification. IEEE Transactions of Systems, Man and Cybernetics, SMS-3(6), 610–621.
Hou, Q., Wang, F., & Yan, L. (2013). Extraction of color image texture feature based on gray-level co-occurrence matrix. Remote Sensing for Land and Resources, 25(4), 26–32.
Hughes, G. (1968). On the mean accuracy of statistical pattern recognizers. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 14(1), 55–63.
Khodadadzadeh, M., Li, J., Plaza, A., Ghassemian, H., Bioucas-dias, J. M., & Li, X. (2014). Spectral-spatial classification of hyperspectral data using local and global probabilities for mixed pixel characterization. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 52(10), 6298–6314.
Kumar, B., Dikshit, O. (2014). Texture Based Hyperspectral Image Classification. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2014 ISPRS Technical Commission VIII Symposium, Vol XL-809, 793–798.
Kuo, B., Huang, C., Hung, C., Liu, Y., & Chen, I. (2010). Spatial information based support vector machine for hyperspectral image classification. IGRASS, 2010, 832–835.
Li, S., Wu, H., Wan, D., & Zhu, J. (2011). An effective feature selection method for hyperspectral image classification based on genetic algorithm and support vector machine. Knowledge-Based Systems, 24(1), 40–48.
Liang, S., Fang, H., & Chen, M. (2001). Atmospheric correction of Landsat ETM + land surface imagery—Part 1: Methods. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 39(11), 2490–2498.
Liang, L., Yang, M., & Li, Y. (2010). Hyperspectral remote sensing image classification based on ICA and SVM algorithm. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 30(10), 2724–2728.
Lmani, M., & Ghassemian, H. (2017). Local histogram and discriminative learning-basedhyperspectraldataclassification. Remote Sensing Letters, 8(1), 86–95.
Melgani, F., & Bruzzone, L. (2004). Classification of hyperspectral remote sensing images with support vector machines. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 42(8), 1778–1790.
Mhangara, P., & Odindi, J. (2013). Potential of texture-based classification in urban landscapes using multispectral aerial photos. South African Journal of Science, 109(3/4), 8. doi:10.1590/sajs.2013/1273.
Mohanaiah, P., Sathyanarayana, P., & GuruKumar, L. (2013). Image texture feature extraction using GLCM approach. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, 3(5), 1–5.
Rojas, M., Dopido, I., Plaza, A., & P. Gamba. (2010). Comparison of support vector machine-based processing chains for hyperspectral image classification. In B. Huang, A.J. Plaza, J. Serra-Sagrista, C. Lee, Y. Li, & S. Qian (Eds.), Satellite data compression, communications, and processing VI Proceedings of SPIE 7810, (vol 78100B). doi: 10.1117/12.860413.
Santiago, V., & Vidya, M. (2009). Improving hyperspectral image classification using spatial preprocessing. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 6(2), 297–301.
Selvarajah, S., & Kodituwakku, S. R. (2011). Analysis and comparison of texture features for content based image retrieval. International Journal of Latest Trends in Computing, 2(1), 108–113.
Su, H., Shen, Y., & Du, P. (2007). Application of Auto subspace partition in band selection of hyperspectral images. Geo-Information Science, 9(4), 124–128. (in Chinese).
Sun, H., Ju, H., Zhang, H., Lin, H., Liu, H., Ling, C., et al. (2013). Comparison of band selection methods for hyperion image data. Infrared, 34(2), 27–34. (in Chinese).
Tan, K., Li, E., Du, Q., & Du, P. (2014). An efficient semi-supervised classification approach for hyperspectral imagery. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 97, 36–45.
Tang, X. (1998). Texture information in run-length matrices. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 7(11), 1602–1609.
Tarabalka, Y., Fauvel, M., Chanussot, J., & Benediktsson, J. A. (2012). SVM- and MRF-based method for accurate classification of hyperspectral images. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 7(4), 736–740.
Tian, Y., Guo, P., & Lu, H. (2004). Texture feature extraction of multiband remote sensing image based on gray level co-occurrence matrix. Computer Science, 31(12), 162–195. (in Chinese).
Wang, L., Gu, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2005). Band selection method based on combination of support vector machines and subspatial partition. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 27(6), 974–977. (in Chinese).
Wang, L., Shi, C., Diao, C. Y., Ji, W. J., & Yin, D. M. (2016). A survey of methods incorporating spatial information in image classification and spectral unmixing. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 37(16), 3870–3910.
Wang, L., Sousa, W. P., Gong, P., & Biging, G. S. (2004). Comparison of IKONOS and QuickBird images for mapping mangrove species on the Caribbean coast of Panama. Remote Sensing of Environment, 91(3–4), 432–440.
Wang, L., Sun, J., & Xiao, Q. (2010). Combination of spatial information and spectral information for hyperspectral imagery classification. Journal of Natural Science of Heilongjiang University, 27(6), 788–791. (in Chinese).
Wei, Z., Zhang, X., Zhang, B., & Li, X. (2005). General and special methods studying on bands selection of hyperspectral remote sensing data. IGRASS, 2005(5), 3223–3226.
Wu, H. (2012). Classification methodology combined with texture feature for hyperspectral remote sensing image. Computer Engineering and Design, 33(5), 1993–1997. (in Chinese).
Zhang, Q., Zhu, M., & Liu, B. (2010). Atmospheric correction for Hyperon image. Computer Measurement and Control, 18(1), 220–221.
Zhao, H., Yan, G., Deng, X., Wang, J., Yang, H., & Li, X. (2003). A classification method based on spatial information. Journal of Remote Sensing, 7(5), 358–363. (in Chinese).
Acknowledgements
This work is cofunded by State Grid Scientific Project 2016 (No. GCB17201600036) “Research on data processing theory and methods of the auxiliary lines selection based on satellite remote sensing image” and Key Science &Technology Project 2016 on phase II scientific control for Three Gorges Reservoir. We acknowledge two anonymous reviewers for their detailed and very constructive remarks.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, Y., Xia, W., Xu, B. et al. Multi-Feature Classification Approach for High Spatial Resolution Hyperspectral Images. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 46, 9–17 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-017-0663-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-017-0663-0