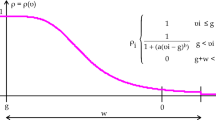
Abstract
Information on highways is an essential input for various geospatial applications, including car navigation, forensic analysis on highway geometries, and intelligent transportation systems. Semi-automatic and automatic extractions of highways are critical for the regular updating of municipal databases and for highway maintenance. This study presents a semi-automatic data processing approach for extracting highways from high-resolution airborne LiDAR height information and aerial orthophotos. The method was developed based on two data sets. Experimental results for the first testing site showed that the accuracy of the proposed method for highway extraction was 74.50 % for completeness and 73.13 % for correctness. Meanwhile, the completeness and correctness for the second testing site were 71.20 and 70.72 %, respectively. The proposed method was compared with an object-based approach on a different data set. The accuracy for highway extraction of the object-based approach was 64.29 % for completeness and 63.11 % for correctness, whereas that of the proposed method was 67.14 % for completeness and 65.08 % for correctness. This research aims to promote semi-automatic highway extraction from LiDAR data and orthophotos by proposing a new approach and a multistep post-processing technique. The proposed method provides an accurate final output that is valuable for a wide range of geospatial applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyko, A., & Funkhouser, T. (2011). Extracting roads from dense point clouds in large scale urban environment. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 66(6), S2–S12.
Brennan, R., & Webster, T. L. (2006). Object-oriented land cover classification of lidar-derived surfaces. Canadian Journal of Remote Sensing, 32(2), 162–172.
Cao, C., & Sun, Y. (2014). Automatic road centerline extraction from imagery using road GPS data. Remote Sensing, 6(9), 9014–9033.
Chauhan, I., Brenner, C., Garg, R. D., & Parida, M. (2014). A new approach to 3D dense LiDAR data classification in urban environment. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 42(3), 673–678.
Chen, L.-C., & Lo, C.-Y. (2009). 3D road modeling via the integration of large-scale topomaps and airborne LIDAR data. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, 32(6), 811–823. doi:10.1080/02533839.2009.9671565.
Choi, Y.-W., Jang, Y.-W., Lee, H.-J., & Cho, G.-S. (2008). Three-dimensional LiDAR data classifying to extract road point in urban area. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 5(4), 725–729.
Clode, S., Kootsookos, P. J., & Rottensteiner, F. (2004). The automatic extraction of roads from LIDAR data. In ISPRS 2004.
Craven, M., & Wing, M. G. (2014). Applying airborne LiDAR for forested road geomatics. Scandinavian Journal of Forest Research, 29(2), 174–182. doi:10.1080/02827581.2014.881546.
Evans, J. S., & Hudak, A. T. (2007). A multiscale curvature algorithm for classifying discrete return lidar in forested environments. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 45(4), 1029–1038.
Ghasemloo, N., Mobasheri, M. R., Zare, A. M., & Eftekhari, M. M. (2013). Road and tunnel extraction from SPOT satellite images using neural networks. Journal of Geographic Information System, 05(01), 69–74. doi:10.4236/jgis.2013.51007.
Gong, L., Zhang, Y., Li, Z., & Bao, Q. (2010). Automated road extraction from LiDAR data based on intensity and aerial photo. In 2010 3rd international congress on image and signal processing (CISP), (Vol. 5, pp. 2130–2133). IEEE.
Han, J., Kim, D., Lee, M., & Sunwoo, M. (2014). Road boundary detection and tracking for structured and unstructured roads using a 2D lidar sensor. International Journal of Automotive Technology, 15(4), 611–623.
Hatger, C., & Brenner, C. (2003). Extraction of road geometry parameters from laser scanning and existing databases. International Archives of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 34(part 3), W13.
Heipke, C., Mayer, H., Wiedemann, C., & Jamet, O. (1997). Evaluation of automatic road extraction. International Archives of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 32(3 SECT 4W2), 151–160.
Hu, X., Li, Y., Shan, J., Zhang, J., & Zhang, Y. (2014). Road centerline extraction in complex urban scenes from LiDAR data based on multiple features. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 52(11), 7448–7456.
Im, J., Jensen, J. R., & Hodgson, M. E. (2008). Object-based land cover classification using high-posting-density LiDAR data. GIScience and Remote Sensing, 45(2), 209–228.
Jabari, S., & Zhang, Y. (2013). Very high resolution satellite image classification using fuzzy rule-based systems. Algorithms, 6(4), 762–781.
Lim, J., & Yang, M. H. (2005). A direct method for modeling non-rigid motion with thin plate spline. In IEEE computer society conference on Computer vision and pattern recognition, 2005. (CVPR’2005). (Vol. 1, pp. 1196–1202). IEEE.
Lin, X., Zhang, J., Liu, Z., Shen, J., & Duan, M. (2011). Semi-automatic extraction of road networks by least squares interlaced template matching in urban areas. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 32(17), 4943–4959. doi:10.1080/01431161.2010.493565.
Mastin, T., & Strohman, R. (2010). Forest roads mapped using LiDAR in steep forested terrain. Remote Sensing, 2(4), 1120–1141.
Matkan, A. A., Hajeb, M., & Sadeghian, S. (2014). Road extraction from lidar data using support vector machine classification. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 80(5), 409–422. doi:10.14358/pers.80.5.409.
Pereira, L. G., & Janssen, L. L. F. (1999). Suitability of laser data for DTM generation: A case study in the context of road planning and design. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 54(4), 244–253.
Samadzadegana, F., Bigdelia, B., & Hahnb, M. (2009). Automatic road extraction from lidar data based on classifier fusion in urban area. Laser Scanning, 38, pp. 1–2.
Sirmacek, B., & Unsalan, C. (2010). Road network extraction using edge detection and spatial voting. pp. 3113–3116. doi: 10.1109/icpr.2010.762.
Song, M., & Civco, D. (2004). Road extraction using SVM and image segmentation. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 70(12), 1365–1371.
Tiwari, P. S., Pande, H., & Pandey, A. K. (2009). Automatic urban road extraction using airborne laser scanning/altimetry and high resolution satellite data. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 37(2), 223–231.
Wang, J., González-Jorge, H., Lindenbergh, R., Arias-Sánchez, P., & Menenti, M. (2013). Automatic estimation of excavation volume from laser mobile mapping data for mountain road widening. Remote Sensing, 5(9), 4629–4651.
Wang, G., Zhang, Y., Li, J., & Song, P. (2011). 3D road information extraction from LIDAR data fused with aerial-images. In 2011 IEEE international conference on spatial data mining and geographical knowledge services (ICSDM) (pp. 362–366). IEEE.
Zhang, Y., & Yan, L. (2007). Road surface modeling and representation from point cloud based on fuzzy clustering. Geo-spatial Information Science, 10(4), 276–281.
Zhao, J., & You, S. (2012). Road network extraction from airborne LiDAR data using scene context. In 2012 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops (CVPRW) (pp. 9–16). IEEE.
Zhao, J., You, S., & Huang, J. (2011). Rapid extraction and updating of road network from airborne LiDAR data. In 2011 IEEE applied imagery pattern recognition workshop (AIPR), (pp. 1–7). IEEE.
Zhou, W. (2013). An object-based approach for urban land cover classification: Integrating LiDAR height and intensity data. Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, IEEE, 10(4), 928–931.
Zhou, L., & Stein, A. (2013). Application of random sets to model uncertainty of road polygons extracted from airborne laser points. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 41, 289–298.
Zhu, P., Lu, Z., Chen, X., Honda, K., & Eiumnoh, A. (2004). Extraction of city roads through shadow path reconstruction using laser data. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 70(12), 1433–1440.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Sameen, M.I., Pradhan, B. A Simplified Semi-Automatic Technique for Highway Extraction from High-Resolution Airborne LiDAR Data and Orthophotos. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 45, 395–405 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-016-0610-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-016-0610-5