Abstract
Background
Medical therapy is rarely effective in patients with fulminant Wilson’s disease (FWD). Liver transplantation is limited by the lack of donor liver in most patients with FWD at the time of diagnosis. New Wilson’s index, model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) and Child-Pugh score are useful tools for decision-making of liver transplantation; however, none of them is an independent decisive tool. It is worthwhile to explore a more effective and practical therapeutic strategy and reevaluate the prediction systems for patients with FWD.
Methods
Nine patients with FWD associated with hemolytic crisis and fulminant hepatic failure (FHF) were investigated. The clinical presentation, prognostic score and medical therapies of the patients were analyzed.
Results
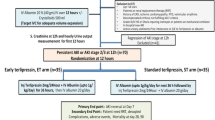
In 7 of the 9 patients with FWD who received the comprehensive therapy of corticosteroid, copper-chelating agent (dimercaptopropansulfonate sodium) and therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE), 6 patients recovered from FHF. The remaining one had been improved through the comprehensive therapy but died of septicemia 51 days later. Two patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) died from liver failure in three or five hospital days without plasma exchange or chelating therapy. All of the 9 patients with FWD presented with acute hepatic failure, severe jaundice and mild to severe hemolytic anemia. No marked difference in the incidence of severe hemolytic anemia was detected between the survival and deceased groups. However, the incidence and the degree of hepatic encephalopathy (HE) in the non-survival group were higher than those in the survival group. Unlike the deceased group, the survival group had no complications induced by bacterial infection. Compared to new Wilson’s index, Child-Pugh score and MELD score, the variation of prothrombin activity (PTA) between the survival and deceased groups was more evident.
Conclusion
For patients with FWD, the episode of severe hepatic encephalopathy or/and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis indicates worse prognosis, and PTA is a recommendable predictor. An emergent liver transplantation should be considered for patients whose PTA is below 20%, or for those with severe HE or/and SBP. The comprehensive therapy of corticosteroid, copper-chelating agent and TPE is effective for patients without SBP and whose PTA is higher than 20%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roberts EA, Schilsky ML, American Association for Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD). Diagnosis and treatment of Wilson disease: an update. Hepatology 2008;47:2089–2111.
Ala A, Walker AP, Ashkan K, Dooley JS, Schilsky ML. Wilson’s disease. Lancet 2007;369:397–408.
Schilsky ML. Wilson disease: genetic basis of copper toxicity and natural history. Semin Liver Dis 1996;16:83–95.
Markiewicz-Kijewska M, Szymczak M, Ismail H, Prokurat S, Teisseyre J, Socha P, et al. Liver transplantation for fulminant Wilson’s disease in children. Ann Transplant 2008;13:28–31.
Sutcliffe RP, Maguire DD, Muiesan P, Dhawan A, Mieli-Vergani G, O’Grady JG, et al. Liver transplantation for Wilson’s disease: long-term results and quality-of-life assessment. Transplantation 2003;75:1003–1006.
Medici V, Mirante VG, Fassati LR, Pompili M, Forti D, Del Gaudio M, et al. Liver transplantation for Wilson’s disease: the burden of neurological and psychiatric disorders. Liver Transpl 2005;11:1056–1063.
Sevmis S, Karakayali H, Aliosmanoglu I, Yilmaz U, Ozcay F, Torgay A, et al. Liver transplantation for Wilson’s disease. Transplant Proc 2008;40:228–230.
Ohya Y, Okajima H, Honda M, Hayashida S, Suda H, Matsumoto S, et al. Re-evaluation of the indications for liver transplantation in Wilson’s disease based on the outcomes of patients referred to a transplant center. Pediatr Transplant 2013;17:369–373.
Dhawan A, Taylor RM, Cheeseman P, De Silva P, Katsiyiannakis L, Mieli-Vergani G. Wilson’s disease in children: 37-year experience and revised King’s score for liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 2005;11:441–448.
European Association for Study of Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: Wilson’s disease. J Hepatol 2012;56:671–685.
Lucey MR, Brown KA, Everson GT, Fung JJ, Gish R, Keeffe EB, et al. Minimal criteria for placement of adults on the liver transplant waiting list: a report of a national conference organized by the American Society of Transplant Physicians and the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Liver Transpl Surg 1997;3:628–637.
Yamashiki N, Sugawara Y, Tamura S, Kaneko J, Nojiri K, Aoki T, et al. Model for end-stage liver disease and model for endstage liver disease-Na scores predict both before-listing and wait-list mortality. Transplant Proc 2012;44:389–392.
Sharpton SR, Feng S, Hameed B, Yao F, Lai JC. Combined effects of recipient age and model for end-stage liver disease score on livertransplantation outcomes. Transplantation 2014;98:557–562.
Boulard M, Blume KG, Beutler E. The effect of copper on red cell enzyme activities. J Clin Invest 1972;51:459–461.
Forman SJ, Kumar KS, Redeker AG, Hochstein P. Hemolytic anemia in Wilson disease: clinical findings and biochemical mechanisms. Am J Hematol 1980;9:269–275.
Hamlyn AN, Gollan JL, Douglas AP, Sherlock S. Fulminant Wilson’s disease with haemolysis and renal failure: copper studies and assessment of dialysis regimens. Br Med J 1977;2:660–663.
Shlomai A, Halfon P, Goldiner I, Zelber-Sagi S, Halpern Z, Oren R, et al. Serum bile acid levels as a predictor for the severity of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Viral Hepat 2013;20:95–102.
Cheng F, Li GQ, Zhang F, Li XC, Sun BC, Kong LB, et al. Outcomes of living-related liver transplantation for Wilson’s disease: a single-center experience in China. Transplantation 2009;87:751–757.
Narumi S, Umehara M, Toyoki Y, Ishido K, Kudo D, Kimura N, et al. Liver transplantation for Wilson’s disease in pediatric patients: decision making and timing. Transplant Proc 2012;44:478–480.
Bellary S, Hassanein T, Van Thiel DH. Liver transplantation for Wilson’s disease. J Hepatol 1995;23:373–381.
Jhang JS, Schilsky ML, Lefkowitch JH, Schwartz J. Therapeutic plasmapheresis as a bridge to liver transplantation in fulminant Wilson disease. J Clin Apher 2007;22:10–14.
Chiu A, Tsoi NS, Fan ST. Use of the molecular adsorbents recirculating system as a treatment for acute decompensated Wilson disease. Liver Transpl 2008;14:1512–1516.
Collins KL, Roberts EA, Adeli K, Bohn D, Harvey EA. Single pass albumin dialysis (SPAD) in fulminant Wilsonian liver failure: a case report. Pediatr Nephrol 2008;23:1013–1016.
Rodríguez Fariña E, Tremosa Llurba G, Xiol Quingles X, Lores Obradors A, Castellote Alonso J, Gornals Soler JB, et al. D-penicillamine and plasmapheresis in acute liver failure secondary to Wilson’s disease. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2003;95:60–62, 63-65.
Nagata Y, Uto H, Hasuike S, Ido A, Hayashi K, Eto T, et al. Bridging use of plasma exchange and continuous hemodiafiltration before living donor liver transplantation in fulminant Wilson’s disease. Intern Med 2003;42:967–970.
Morgan SM, Zantek ND. Therapeutic plasma exchange for fulminant hepatic failure secondary to Wilson’s disease. J Clin Apher 2012;27:282–286.
Asfaha S, Almansori M, Qarni U, Gutfreund KS. Plasmapheresis for hemolytic crisis and impending acute liver failure in Wilson disease. J Clin Apher 2007;22:295–298.
Kiss JE, Berman D, Van Thiel D. Effective removal of copper by plasma exchange in fulminant Wilson’s disease. Transfusion 1998;38:327–331.
Matsumura A, Hiraishi H, Terano A. Plasma exchange for hemolytic crisis in Wilson disease. Ann Intern Med 1999;131:866.
Xu SQ, Li XF, Zhu HY, Liu Y, Fang F, Chen L. Clinical efficacy and safety of chelation treatment with typical penicillamine in cross combinationwith DMPS repeatedly for Wilson’s disease. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci 2013;33:743–747.
Akdogan M, Camci C, Gurakar A, Gilcher R, Alamian S, Wright H, et al. The effect of total plasma exchange on fulminant hepatic failure. J Clin Apher 2006;21:96–99.
Eisenbach C, Sieg O, Stremmel W, Encke J, Merle U. Diagnostic criteria for acute liver failure due to Wilson disease. World J Gastroenterol 2007;13:1711–1714.
Kasahara M, Sakamoto S, Horikawa R, Koji U, Mizuta K, Shinkai M, et al. Living donor liver transplantation for pediatric patients with metabolic disorders: the Japanese multicenter registry. Pediatr Transplant 2014;18:6–15.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Y., Gong, GZ., Yang, X. et al. Diagnosis and management of fulminant Wilson’s disease: a single center’s experience. World J Pediatr 12, 209–214 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-015-0026-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-015-0026-2