Abstract
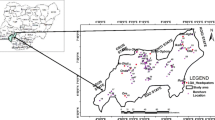
Theory of data-driven evidential belief function (EBF) is based on generalized Bayesian probabilities. It computes the reliability of evidences according to the presence or absence of known indices. This method has a reliable performance even in the case of limitation of data layers diversity. The study aims to detect the most probable regions for copper and gold mineralization in Takhte-h-Soleiman, Iran using EBF method. The available data layers including lithological map, faults, geochemical anomalies and known indices maps were processed to generate a potential map for the study area. The “belief”, “disbelief”, “uncertainty” and “plausibility” functions were therefore calculated based on data-driven EBF for each pattern of evidences in two different classification types. The data layers were then combined with the use of the EBF AND-OR operators, and the “belief” map was proposed as a target recognition map for following detail explorations. As a validation criterion, the ratio of indices number to the total area of the most favourable regions in each map was computed. According to the highest ratio for the belief map resulted by integrated AND-OR operators on equal interval classification (0.62), it was selected as the target map for primary explorations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedi M, Torabi S, Norouzi G (2013) Application of fuzzy AHP method to integrate geophysical data in a prospect scale, a case study: seridune copper deposit. Boll Geofis Teor Appl 54(2):145–164
Agterberg FP, Cheng Q (2002) Conditional independence test for weights-of-evidence modelling. Nat Resour Res 11(4):249–255
Althuwaynee OF, Pradhan B, Lee S (2012) Application of an evidential belief function model in landslide susceptibility mapping. Comput Geosci 44:120–135
An P, Moon W, Bonham-Carter G (1994) An object-oriented knowledge representation structure for exploration data integration. Non-renewable Resources 3(2):132–145
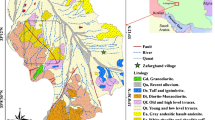
Babakhani Aajg (1991)1/100000 map of Takhte-Soleiman, Geological Survey and Mineral Explorations
Bonham C (1994) Geographic information system for geoscientists, Pergamon (modelling with GIS), Ontario
Brown WM, Gedeon T, Groves D, Barnes R (2000) Artificial neural networks: a new method for mineral prospectivity mapping. Aust J Earth Sci 47(4):757–770
Bui DT, Pradhan B, Lofman O, Revhaug I, Dick OB (2012) Spatial prediction of landslide hazards in Hoa Binh province (Vietnam): a comparative assessment of the efficacy of evidential belief functions and fuzzy logic models. Catena 96:28–40
Carranza EJM (2004) Weights of evidence modelling of mineral potential: a case study using small number of prospects, Abra, Philippines. Nat Resour Res 13(3):173–187
Carranza EJM (2008) Geochemical anomaly and mineral prospectivity mapping in GIS. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Carranza EJM (2014) Data-driven evidential belief modelling of mineral potential using few prospects and evidence with missing values. Nat Resour Res 24:291–304
Carranza EJM, Hale M (2001) Geologically constrained fuzzy mapping of gold mineralization potential, Baguio district, Philippines. Nat Resour Res 10(2):125–136
Carranza E, Hale M (2002) Wildcat mapping of gold potential, Baguio district, Philippines. Applied Earth Science: Transactions of the Institutions of Mining and Metallurgy: Section B 111(2):100–105
Carranza EJM, Hale M (2003) Evidential belief functions for data-driven geologically constrained mapping of gold potential, Baguio district, Philippines. Ore Geol Rev 22(1):117–132
Carranza EJM, Sadeghi M (2010) Predictive mapping of prospectivity and quantitative estimation of undiscovered VMS deposits in Skellefte district (Sweden). Ore Geol Rev 38(3):219–241
Carranza E, Woldai T, Chikambwe E (2005) Application of data-driven evidential belief functions to prospectivity mapping for aquamarine-bearing pegmatites, Lundazi district, Zambia. Nat Resour Res 14(1):47–63
Carranza EJM, Van Ruitenbeek F, Hecker C, van der Meijde M, van der Meer FD (2008) Knowledge-guided data-driven evidential belief modelling of mineral prospectivity in Cabo de Gata, SE Spain. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 10(3):374–387
Carver SJ (1991) Integrating multi-criteria evaluation with geographical information systems. International Journal of Geographical Information System 5(3):321–339
De Quadros TF, Koppe JC, Strieder AJ, Costa JF (2006) Mineral-potential mapping: a comparison of weights-of-evidence and fuzzy methods. Nat Resour Res 15(1):49–65
Dempster AP (1967) Upper and lower probabilities induced by a multivalued mapping. Ann Math Stat 38:325–339
Eastman JR, Jin W, Keym P, Toledano J (1995) Raster procedures for multi-criteria/multi-objective decisions. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 61(5):539–547
Harris D, Pan G (1999) Mineral favourability mapping: a comparison of artificial neural networks, logistic regression, and discriminant analysis. Nat Resour Res 8(2):93–109
Harris J, Wilkinson L, Heather K, Fumerton S, Bernier M, Ayer J, Dahn R (2001) Application of GIS processing techniques for producing mineral prospectivity maps—a case study: mesothermal Au in the Swayze Greenstone Belt, Ontario, Canada. Nat Resour Res 10(2):91–124
Lee S, Hwang J, Park I (2013) Application of data-driven evidential belief functions to landslide susceptibility mapping in Jinbu, Korea. Catena 100:15–30
Lee S, Oh H-J, Heo C-H, Park I (2014) A case study for the integration of predictive mineral potential maps. Open Geosciences 6(3):373–392
Liu Y, Cheng Q, Xia Q, Wang X (2014) Mineral potential mapping for tungsten polymetallic deposits in the Nanling metallogenic belt, South China. J Earth Sci 25(4):689–700
Mohebi A, Mirnejad H, Lentz D, Behzadi M (2014) Using AHP method in GIS for PCDs potential mapping in southeast of Iran. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition) 88(s2):1222–1224
Pazand K, Hezarkhani A, Ataei M, Ghanbari Y (2011) Combining AHP with GIS for predictive Cu porphyry potential mapping: a case study in Ahar Area NW, Iran. Nat Resour Res 20(4):251–262
Porwal A, Carranza E, Hale M (2003a) Artificial neural networks for mineral-potential mapping: a case study from Aravalli Province, Western India. Nat Resour Res 12(3):155–171
Porwal A, Carranza E, Hale M (2003b) Knowledge-driven and data-driven fuzzy models for predictive mineral potential mapping. Nat Resour Res 12(1):1–25
Porwal A, Gonzalez-Alvarez I, Markwitz V, McCuaig T, Mamuse A (2010) Weights-of-evidence and logistic regression modelling of magmatic nickel sulfide prospectivity in the Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia. Ore Geol Rev 38(3):184–196
Porwal A, R D Das, B Chaudhary, I Gonzalez-Alvarez and O Kreuzer (2014) Fuzzy inference systems for prospectivity modelling of mineral systems and a case-study for prospectivity mapping of surficial uranium in Yeelirrie Area, Western Australia. Ore Geol Rev
Rigol-Sanchez J, Chica-Olmo M, Abarca-Hernandez F (2003) Artificial neural networks as a tool for mineral potential mapping with GIS. Int J Remote Sens 24(5):1151–1156
Shafer G (1976) A mathematical theory of evidence. Princeton University press, Princeton
Thiart C, de Wit M (2000) Linking spatial statistics to GIS: exploring potential gold and tin models of Africa. S Afr J Geol 103(3–4):215–230
Yousefi M, Carranza EJM (2015) Fuzzification of continuous-value spatial evidence for mineral prospectivity mapping. Comput Geosci 74:97–109
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oskouei, M.M., Soltani, F. Mapping of potential Cu and Au mineralization using EBF method. Appl Geomat 9, 13–25 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-016-0178-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-016-0178-3