Abstract
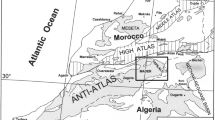
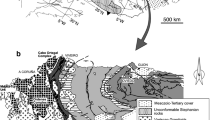
Depositional sequences and paleogeographic evolution of the Miocene deposits have been studied in the Zibane zone (Saharan Atlas, Algeria) located at the north of the African platform. During the Miocene, this region corresponded to a fault-bounded collapse area and filled by diversified deposits, showing important lateral facies and thicknesses variations. The studied deposits are divided into five depositional sequences separated by major unconformities. These depositional sequences are well developed in the whole basin and testify a paleogeographic differentiation from E–W, induced by a set of NW-SE-trending old faults inherited from the Atlasic orogeny. The organization and the development of those sequences make it possible to correlate them better to the basin scale, which is integrated in a model of restricted platform intersected by NW-SE faults where the tectonic-sedimentation duality is predominant. These new data point to a paleogeographic evolution different from the one usually admitted environment for this region during Miocene time and plead in favour of a reconsideration of the depositional environments of the post-Burdigalian formations in the Zibane zone of the Algerian Atlasic domain.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aissaoui D (1984) Les structures liées à l’accident sud-atlasique entre Biskra et le Djebel Manndra, Algérie. Evolution géométrique et cinématique. Thèse 3ème cycle, Université de Strasbourg
Amirshahkarami M (2013) Microfacies correlation analysis of the Oligocene-Miocene Asmari formation, in the central part of the Rag-eSafid anticlinal oil field, Zagros basin, south-west Iran. Turk J Earth Sci 22:204–219
Anis A K, Shahnawaz S R (2012) Sedimentary Facies and Depositional Environment of Early Triassic Pachmarhi Formation, Satpura Gondwana Basin, Central India, Madhya Pradesh. Internat. J. Sci Res. Pub 2(12):1–11
Bracène R, de Frizon LD (2002) The origin of intraplate deformation in the atlas system of western and central Algeria: from Jurassic rifting to Cenozoic–quaternary inversion. Tectonophysics 357:207–226
Chebbah M (2007) Lithostratigraphie, Sédimentologie et Modèles de Bassins des dépôts néogènes de la région de Biskra, de part et d’autre de l’Accident Sud Atlasique (Zibans, Algérie). Thèse Doctorat d’Etat, Univ. Constantine.
Chebbah M, Lamouroux C (2012) La Fosse Sud Aurèsienne au Néogène (Domaine pré-saharien, Algérie): séquences de dépôt, propositions de corrélations et évolution sédimentaires. Bull Serv Géol Nat, Alger 23:1–21
Delfaut J (1974) La sédimentation deltaïque ancienne. Exemples Nord sahariens. Bull Cent Rech de Pau 8(1):24–62
Folk RL, Ward WC (1957) Brazos river bar: a study in the significance of grain size parameters. J Sediment Petrol 27:3–26
Fournel H (1849) Richesse minérale de l’Algérie accompagnée d’éclaircissements géographiques et historiques sur cette partie de l’Algérie septentrionale. Tomme I, Paris
Ghandriche H (1991) Modalités de la superposition de structures de plissements-chevauchements d’âge alpin dans les Aurès (Algérie). Thèse ès Sci Université Paris XI
Gouskov N (1962) Notice explicative de la carte géologique au 1/200 000 de Biskra. PubServGéol Algérie
Guiraud R (1973) Evolution post-Triasique de l’Avant pays de la chaîne alpine en Algérie d’après l’étude du bassin du Hodna et des régions voisines. Thèse Sci. Université de Nice
Guiraud R (1990) Evolution post-triasique de l’avant pays de la chaîne alpine en Algérie d’après l’étude du bassin du Hodna et des régions voisines. Pub. Office National de la Géologie, Alger
Guiraud R, Bellion Y (1995) Late Carboniferous to recent geodynamic evolution of the West Gondwanian cratonic Thethyan margins. In: Nairn A, Dercourt J, Vrirlynck B (eds) The ocean basins and margins, the Tethys ocean, vol 8. Plenum, New York, pp 101–124
Haq BU, Hardenbold S, Vail PM (1988) Mesozoic and Cenozoic chronostratigraphy and cycles of sea-level change. In: C.K. Wilgus, B.S. Hastings, H.W. Posamentier, J. Van Wagoner, C.A. Ross and C.G.St. Kendall, Editors, Sea level Changes: An Integrated Approach. SEPM Special Publication 42: 71–108
Heiden KA, Holmes MA (1998) Grain size and significance of clay and clay-sized minerals in Eocene to Holocene sediments from sites 918 and 919 in the Irminger basin. In: Saunders, A.D., Larsen, H.C., and Wise, S.W., Jr. (Eds.) Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol. 152
Herkat M (1999) La sédimentation de haut niveau marin du Crétacé supérieur de l’Atlas saharien oriental et des Aurès : stratigraphie séquentielle, analyse quantitative des biocénoses, évolution paléogéographique et contexte géodynamique, Thèse ès Sciences. USTHB, Alger
Kazi Tani N (1986) Evolution géodynamique de la bordure Nord-africaine : le domaine intraplaque nord-algérien. Approche megaséquentielle. Thèse ès Sci. Université de Pau
Kendall A (1988) Aspects of evaporite basin stratigraphy. In: Schreiber BC (ed) Evaporites and hydrocarbons. Columbia Univ Press, New York, pp 11–65
Kendall A, Harwood GM (1996) Marine evaporites: arid shore-lines and basins. In: Reading HG (ed) Sedimentary environments: processes, facies and stratigraphy, 3rd edn. Blackwell Science, Oxford, pp 281–324
Laffitte R (1939) Etude géologique de l’Aurès. Bull. Serv. Carte géol. 2ème série, Stratigr. Descript. Région, Algérie
Miall AD (1978) Fluvial sedimentology. Can Soc Petrol Geol Mem 5
Miall AD (1988) Architectural elements and bounding surfaces in fluvial deposits: anatomy of the Kagenta Formation (Lower Jurasssic), southwest Colorado. Sediment Geol 55:233–262
Miall AD (1996) The geology of stratigraphic sequences. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Moissette P, Cornée JJ, Mannaï-Tayech B, Rabhi M, André JP, Koskeridou E, Méon H (2010) The western edge of the Mediterranean pelagian platform: a Messinian mixed siliciclastic–carbonate ramp in northern Tunisia. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 285:85–103
Neurdin-Trescartes J (1992) Le remplissage sédimentaire du bassin néogène du Chélif : Modèle de référence de bassins intramontagneux. Thèse Doct.ès Sci., Université de Pau
Piqué A, Tricart P, Guiraud R, Laville E, Bouaziz MA, Ait Ouali R (2002) The Mesozoic-Cenozoic atlas belt (North Africa : on overview. Geodin Acta 15:185–208
Pye K, Blott SJ (2004) Particle size analysis of sediments, soils and related particulate materials for forensic purposes using laser granulometry. Forensic Sci Int 144:19–27
Toshifumi K, Satoru K , Kento H, Reishi T , Yukari , Masahiro O, Hajime N, Phuong H. T, Phong D. N, Huyen T. D , Truong N. D , Hung H. N , Susumu S, Kunio K, Peter Königshof (2014) Devonian–Carboniferous transition containing a Hangenberg Black Shale equivalent in the Pho Han Formation on Cat Ba Island, northeastern Vietnam. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 404:30–43
Trindde MJ, Rocha F, Diasi MI, Prudencio MI (2013) Mineralogy and grain-size distribution of clay-rich rock units of the Algarve Basin (South Portugal). Clay Miner 48:59–83
Vail PR, Mitchum RM, Todd RG, Widmier JM, Thomson SB, Angree JB, Bubb JN, Hatler IDW (1977) Seismic stratigraphy and global changes in sea level. In Payton C.E. AAPG Mem 26:49–212
Vail PR, Audemard F, Bowman SA, Eisner P, Perez-Cruz C (1991) Cycles and events in stratigraphy. Springer Verlag, Berlin, pp 617–665
Walker RG (1990) Facies modeling and sequence stratigraphy. J Sediment Petrol 60:777–786
Xiaowei L, Meiyi Y, Daniel JL, Jonathan LP, Brian MK, Marcello M (2011) Factors controlling carbonate platform asymmetry: preliminary results from the great bank of Guizhou, an isolated Permian–Triassic platform in the Nanpanjiang basin, South China. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 15–16:158–171
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix A
Appendix B
a The early Miocene clays (sequence 1 and sequence 2) in the SE sector (Branis) a Greenish brown clays with gypsum (sequence 1) unconformably overlies the anti-Miocene formations (substratum) and overlain by greenish brown clays with oysters (the basis of sequence 2), b Brown clays with echinoids (the summit of sequence 2). b a. The Burdigalian limestones (sequence 2) in the central sector (El Outaya, East Oued Biskra) overlain by the sequence 3 (Middle Miocene), b Close-up of the sequences 3 and 4 in the central sector (El Outaya, East Oued Biskra) c a Yellow-green gypseous clays (sequence 1) unconformably overlies the anti-Miocene formations (substratum) and overlain by alternation of conglomerate bars and clays (sequence 2), b Close-up of the sequence 2 where conglomerate bars showing a clear stratification
a General view of sequence 3, clays-gypsum alternation; beds of gypsum draw a clear parallel stratification in this sequence, NE sector. b The Messinian unconformity overlies the Tortonian which in turn unconformably overlain by the Pliocene in the NE sector. c General view of the Miocene showing various unconformities registered in the SE sector
Some sedimentological features of the Miocene deposits in the Zibane zone. a Clay facies containing gypsum crystals (arrows), sequence 1, NE sector (Branis). b Clay facies showing a synsedimentary deformation, sequence 3, SE sector (Droh). c Sandstone facies with erosive contact (arrows) showing large parallel stratifications, sequence 4, West Oued Biskra, El Outaya. d Close-up of sandstones with conglomerate base, sequence 4, SE sector, Chetma. e Sandstones with parallel to slightly wavy stratifications, NE sector, Branis. f Sandstone facies showing large parallel stratifications, central sector. g Parallel then cross-bedded stratification of the sandstones, sequence 4, East Oued Biskra, El Outaya. h Erosive contact between clay facies-SD4 (below) and sand facies with conglomerate base SD5 (above) in the SE sector (Lahbel). i Parallel then oblique stratification in the sandstones, sequence 4, SE sector, Lahbel. j General view of conglomerate facies in the NE sector. k Sandy-conglomeratic facies association showing trough cross-bedded stratifications, SE sector (Chetma)
Some sedimentological features of the Miocene deposits in the Zibane zone (following). a Sandstones with conglomeratic crossings, sequence 4, West Oued Biskra, El Outaya. b Alternation of clays and sandstones, sequence 4, SE sector, Lahbel. c Large parallel stratifications in the sandstones, sequence 3, East Oued Biskra, El outaya. d Clay facies, sequence 3, SE sector, Droh. e Cross-bedded sandstone facies, sequence 5, SE sector, Chetma. f Trough-cross stratifications in the sandstones, sequence 5, Lahbel. h and g Current figures in the sandstones, sequence 5, SE sector, Droh. i sandstones with parallel laminations, sequence 3, El Outaya, West Oued Biskra. j Oblique stratifications in the sandstones, sequence 4, SE sector, Chetma
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chebbah, M. A Miocene-restricted platform of the Zibane zone (Saharan Atlas, Algeria), depositional sequences and paleogeographic reconstruction. Arab J Geosci 9, 151 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2132-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2132-9