Abstract
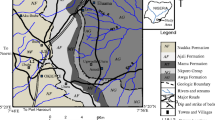
The sandstone outcrops in the Brega Area Two are designated as ‘Brega Sandstone Bed’ on the basis of the lithological similarities and stratigraphy of the region surrounding Brega. The ‘Brega Sandstone Bed’ is considered to be equivalent to the lower part of the Member V of the Sahabi Formation of the Pliocene age. The thinly bedded greyish to greenish sandstone interbedded with gravel and pebble beds exposed at the ‘Sea cliff section’ represents the upper part of Member V of the Sahabi Formation. Outcrops of Pleistocene-cemented marine dunes belong to the Ajdabiya Formation and are seen as patches of marine dunes of various shapes, lengths and heights that run parallel to the modern day Mediterranean Sea coastline. The Holocene sediments around Brega include coastal and inland sand dunes and sand sheets mixed with millions of 'beach balls'. The ichnofaunal assemblage of the ‘Brega Sandstone Bed’ is dominated by various types of vertical, oblique and horizontal burrows that are branched and unbranched. They are dominated by ichnogenera Ophiomorpha and Skolithos. The ichnocoenose dominated by these two ichnogenera belong to the marine soft ground Skolithos ichnofacies. Lithology of the ‘Brega Sandstone Bed’ and its ichnocoenose indicate a shallow marine, intertidal to shallow subtidal, moderate to high energy depositional environments.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashley GM (1990) Classification of large-scale subaqueous bedforms: a new look at the old problem. J Sediment Res 60:160-172
Barr FT, Walker BR (1973) Late Tertiary channel system in northern Libya and its implication on Mediterranean Sea level changes. Initial Rept Deep Sea Drill Proj 13:1244–1251
Boaz N T. 1996. Vertebrate palaeontology and terrestrial paleoecology of As Sahabi and the Sirt Basin. In: The Geology of Sirt Basin, vol. 1 (Eds.) M. J. Salem, A. J.Mouzughi and O. S. Hammuda. 531–539. Springer
Boaz NT, El-Arnauti A, Gaziry AW, Heinzelin JD, Boaz DD (1987) Neogene Paleontology and Geology of Sahabi. Alan R. Liss Inc., New York, 399p
Bromley RG (1990) Trace Fossils; Biology and Taphonomy Special Topics in Palaeontology. Unwin Hymen, London, 280 p
Buatois LA, Mangano MG (2011) Ichnology: Organism-substrate interactions in space and time. Cambridge Univ, Press, 358 p
Collinson JD Thompson DB (1989) Sedimentary structures. Unwin Hymen, London, 207 p
Curran HA (1994) The palaeobiology of ichnocoenoses in Quaternary, Bahamian-style carbonate environments: the modern to fossil transition. In: Donovan SK (ed) Palaeobiology of Trace Fossils, John Wiley & Sons. Ltd. Chichester, England, pp 83–104
Curran H A 2007 Chapter 14: Ichnofacies, Ichnocoenoses, and Ichnofabrics of Quaternary Shallow-Marine to Dunal Tropical Carbonates: A Model and Implications. In: Trace Fossils Concepts Problems Prospects (Ed. W. Miller, III) 232–247
Curran H A and Frey R W 1977. Pleistocene trace fossils from North Carolina (U. S. A.), and their Holocene analogues. In: (Ed. Crimes, T. P. and Harper, J. C.) Trace Fossils 2, Proc. Int. Symp. 25th Int. Geol. Cong. Sydney, Australia. Pp. 139–162
de Heinzelin J, El-Arnauti A (1982) Stratigraphy and geological history of the Sahabi and related formations. Garyounis Sci Bull Spec 4:5–12
de Heinzelin J, El-Arnauti A (1987) The Sahabi Formations and related deposits. In: Boaz NT et al (eds) Neogene Paleontology and Geology of Sahabi. Liss, New York, pp 1–21
Desio A (1931) Osservationi geologiche e geografiche compiute durante un nelle Sirtica, Boll. Soc Geogr 8:275–299
Desio A (1932) Nuovi dati sulla geologia della Libia. Mem Geol Geogr Di G Danielli, Firenze 3:203–227
Desio A 1935 Studi geologici sulla Cirenaica, sul deserto Libico, sulla Tripolitania e sul Fezzan orientale. Missone scientifica della R. Acad. d’Italie a Cufra, (1931), Roma, v. 1, 480p
Desio A (1971) Outlines and problems of the geomorphological evolution of Libya from the Tertiary to the present day. In: Gray C (ed) First Symp. on the Geol. of Libya. Faculty of Scienec, University of Tripoli, Tripoli, pp 11–36
El-Arnauti A, El Sogher A (2004) Geology of East Libya. Short notes and guidebook on The Geology of Qasr As Sahabi Area. Sedimentary Basins of Libya, 3rd Symposium. Gutenberg Press, Malta, p 95
Frey RW, Pemberton SG (1987) The Psilonichnus ichnocoenose and its relationship to adjacent marine and nonmarine ichnocoenoses along the Georgia coast. Bull Can Petrol Geol 35:333–357
Frey RW, Seilacher A (1980) Uniformity in marine invertebrate ichnology. Lethaia 13:183–207
Garlan, T. GIS and mapping of marine sand dunes. (website 1)
Giglia G (1984) Sheet Ajdabiaya (NH-34), Geological map of Libya, scale 1: 250,000, Explanatory Booklet. Industrial Research Center, Tripoli
Goudarzi G H (1970) Geology and mineral resources of Libya – a reconnaissance. U. S. Geol. Surv. Prof. pap. 660, 104 p
Gregory JW (1911) Contributions to the geology of Cyrnaica. Q J Geol Soc 67:572–615
Hallett D 2002 Petroleum Geology of Libya. Elsevier, 503 p
de Heinzelin J, El-Arnauti A, Gaziry, W 1980 A preliminary revision of the Sahabi Formation. In: M. J. Salem and M. T. Busrewil (eds), The Geology of Libya, 1:127–126
Kumar A 2014 Origin and distribution of “Beach Balls” (Egagropili) of Brega, Libya, “Kedron Balls” of New Brunswick,Canada, and Carboniferous “Coal Balls”. Earth Science India, Popular Issue, VII (III): 1–12. (www.earthscienceindia.info)
Le Bot S, Trentesaux A, Garlan T, Berné S, Chamley H (2000) Influence des tempêtes sur la mobilité des dunes tidales dans le détroit du Pas-de-Calais. Oceanol Acta 23(2):129–141
MacEachern J A, Bann K L, Gingras M K, Zonneveld J P, Dashtgard S E, Pemberton S G 2012 Chapter 4: The Ichnofacies Paradigm. In, Trace Fossils as Indicators of Sedimentary Environments (Eds. D. Knaust and R. G. Bromley). Developments in Sedimentology 64, 103–138. Elsevier
McBurney C B M, Hey R W 2009 Prehistory and Pleistocene Geology in Cyrenaican Libya. Cambridge University Press
Pemberton S G, Spila M, Pulham A J, Saunders T, MacEachern J A, Robbins D, Sinclair I K 2001 Ichnology and Sedimentology of Shallow to Marginal Marine Systems. Ben Nevis & Avalon Reservoirs Jeanne d’Arc Basin. Geological Association of Canada, Short Course Notes v. 15, 341 p
Petrocchi C 1943 Il giacimento fossilifero di Sahabi. Coll. Doc. Scientif. A Cura Min Afr. Ital., 9, 172p
Tawadros E (2012) The Geology of North Africa. Balkema, London
Wennekers J H N, Wallace F K, Abugres Y I 1996 The geology and hydrocarbons of the Sirt Basin: a synopsis. In: The Geology of Sirt Basin, (Eds.) Salem M J, Mouzughi A J, Hammuda O S. vol. 1, part 1:3–56
Acknowledgments
I am grateful to two anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments. I thank my colleagues Sajal Sharma, James Lonappan and Moazzam Hussain for helping me during the field work. I also thank my son Anshuman Kumar for the linguistic improvements to this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A. Geology of the Brega area and the ichnofauna of the ‘Brega Sandstone Bed’ (Pliocene), Libya. Arab J Geosci 8, 5337–5349 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1656-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1656-8