Abstract
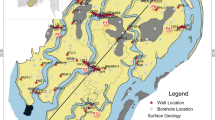
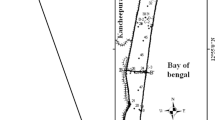
Kharg Island with an area about 21.3 km2 is located between 29° 12′ 22″ to 29° 16′ 29″ northern latitudes and 50° 16′ 54″ to 50° 20′ 12″ eastern longitudes. It is located 58 km to the northwest of Bushehr City in the southwest of Iran. The target of present paper is determination of origin and distribution of salt water in the shallow Kharg aquifer using hydrochemical and geophysical tools. More than 50 % of the island’s surface is covered by limestone. General direction of groundwater flow in the aquifer is from highlands to the eastern and the northern coasts. Exploitation of groundwater is carried out by shallow wells on the eastern part of Kharg Island. Sampling operations were conducted in 27 wells in May 2010. Saltwater intrusion mapping was conducted on the aquifer through combining the results of geophysical and hydrochemical studies. Hydrochemical factors such as bromide, bicarbonate, carbonate and chloride ions, electrical conductivity, and chloride to strontium ratio in addition to apparent resistivity confirmed similar seawater intrusion pattern in different parts of the aquifer. The results show that seawater is the main source of groundwater salinity but via two difference mechanism. The first mechanism of seawater intrusion is taking place in shore line. The second one is due to upconing as a result of extraordinary exploitation of product wells located in the west part of Kharg aquifer.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedelrahem Allow K (2011) Seawater intrusion in Syrian coastal aquifers, past, present and future, case study. Arab J Geosci. 645–653
Barbieri G, Barrocu G, Uras Gand Vernier A (1992) Study and modeling of saltwater intrusion into aquifers. Proceedings 12th saltwater intrusion meeting Barcelona
Barlow Paul M, Reichard Eric G (2010) Saltwater intrusion in coastal regions of North America. Hydrogeol J 18:247–260. doi:10.1007/s10040-009-0514-3
Bennetts DA, Webb JA, Stone DJM, Hill DM (2006) Understanding the salinisation process for groundwater in an area of south-eastern Australia, using hydrochemical and isotopic evidence. J Hydrol 323:178–192
Central Mining Research Institute (CMRI) (2007) Geo-hydrological studies for Kovaya Limestone Mine of UltraTech Cement: a technical report. Australia, Ref. No GC/MT/N/18/05–06 103
Cook RE (1958) Kharg Island groundwater investigation. P. E. D. Division/Geology & Exploration Department Tehran Iran
El Moujabber M, Bou Samra B, Darwish T, Atallah T (2006) Comparison of different indicators for groundwater contamination by seawater intrusion on the Lebanese coast. Water Resour Manag 20:161–180
Elkrail AB, Obied BA (2013) Hydrochemical characterization and groundwater quality in Delta Tokar alluvial plain, Red Sea coast—Sudan. Arab J Geosci 6(8):3133–3138
EPA (1995) Superfund program representative sampling guidance
Jones BF, Vengosh A, Rosenthal E, Yechieli Y (1999) Geochemical investigations in seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers—concepts, methods and practices, Bear, J., Cheng, AHD, Sorek, S, Ouazar D and Herrera, I (eds) Kluwer Academic Publications, Dordrecht, Boston, London 51–71
Jørgensen NO, Holm PM (1995) Strontium-isotope studies of chloride-contaminated groundwater Denmark. Hydrogeol J 3(2):52–57
Mercado A (1985) The use of hydrogeochemical patterns in carbonate sand and sandstone aquifers to identify intrusion and flushing of saline waters. Groundwater 23(5):635–645
Morell, Medina J, Pulido A, Fernandez-Rubio R (1986) The use of bromide and strontium ions as indicators of marine intrusion in the aquifer of Oropesa-Torreblanca (Castellon, Spain). Proc, 9th SWIM, 629-640, Delft
Park SC, Yun ST, Chae GT, Yoo IS, Shin KS, Heo CH, Lee SK (2005) Regional hydrochemical study on salinization of coastal aquifers, western coastal area of South Korea. J Hydrol 313:182–194
Petalas C, Lambrakis N (2006) Simulation of intense salinization phenomena in coastal aquifers—the case of the coastal aquifers of Thrace. J Hydrol 324:51–64
Revelle R (1941) Criteria for recognition of sea water in groundwaters. Trans Am Geophys Union 22:593–597
Roy S, Fouillac AM (2004) Uncertainties related to sampling and their impact on the chemical analysis of groundwater. Trends Anal Chem 23(3):185–193
Sajil Kumar PJ, Elango L, James J (2013) Assessment of hydrochemistry and groundwater quality in the coastal area of South Chennai, India. Arab J Geosci
Saxena VK, Mondal NC, Singh VS (2004) Evaluation of hydrogeochemical parameters to delineate fresh groundwater zones in coastal aquifers. J Appl Geochem 6:245–254
Singaraja C, Chidambaram S, Anandhan P, Prasanna MV, Thivya C, Thilagavathi R, Sarathidasan J (2014) Hydrochemistry of groundwater in a coastal region and its repercussion on quality, a case study—Thoothukudi district, Tamil Nadu. India Arab J Geosci 7(3):939–950
Soni Abhay K, Pujari Paras R (2012) Sea -water intrusion studies for coastal aquifers: some points to ponder. Open Hydrol J 6:24–30
Soni AK, Pujari PR (2010) Ground water vis-a-vis sea water intrusion analysis for a part of limestone tract of Gujarat Coast. India J Water Resour 2:462–468
Spechler Rick M (1994) Saltwater intrusion and quality of water in the Floridan aquifer system, Northeastern Florida. U.S. geological survey water-resources investigations Report 92-4174
Srinivasamoorthy K, Vasanthavigar M, Vijayaraghavan K, Sarathidasan R, Gopinath S (2013) Hydrochemistry of groundwater in a coastal region of Cuddalore district, Tamilnadu. India Implication Qual Assess Arab J Geosci 6(2):441–454
Tremblay JJ, D’Cruz J, Anger H (1973) Salt water intrusion in the Summerside area. Ground Water 11:21–27
Zesheng Y (1992) Study on the saltwater intrusion in coast region of Laizhou Gulf. Ocean Press, Beijing, pp 58–59
Zhumei L, Pihal N (1996) Study on monitoring sea water intrusion by geoexploration technics. Disaster of salt water intrusion and combatting. Shangdong Science and Technology Press, Jinan, pp 80–85
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahsavari, A.A., Khodaei, K., Asadian, F. et al. Determination of origin and distribution of saline water in the aquifer of Kharg Island, Iran. Arab J Geosci 8, 3129–3137 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1450-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1450-7