Abstract
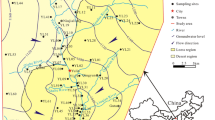
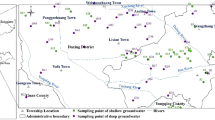
Intensive human activities have caused contamination to groundwater quality which consequently affects human health. In this study, an evaluation of groundwater quality was carried out for better understanding of the status of groundwater contamination and potential risks to local residents in an alluvial plain (China) where agricultural and industrial activities are intensive. Comprehensive water quality index was used for drinking water-quality assessment and sodium adsorption ratio, Na%, and residual sodium carbonate were applied for irrigation water-quality assessment. The human health risks caused by intake of the contaminated groundwater through the oral and dermal pathways were also assessed. The assessment results reveal that most of the water samples are generally suitable for irrigation purpose, but over 60 % of them are not fit for drinking, and the total hardness, NO3 −, NO2 −, TDS, SO4 2−, and F− are the main contaminants affecting its suitability for drinking purpose. Residents in the study area are at high health risk, and NO3 − originating mainly from industrial and agricultural pollution is the greatest contributory cause of the health risks. Furthermore, children in this area are at higher health risk than adults, and oral ingestion is the dominate exposure pathway of health risk. Therefore, urgent and efficient measures must be taken to combat groundwater pollution and reduce health risk in the area.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksoy AO, Scheytt T (2007) Assessment of groundwater pollution around Torbali, Izmir, Turkey. Environ Geol 53:19–25. doi:10.1007/s00254-006-0614-5
Alexakis D, Gotsis D, Giakoumakis S (2012) Assessment of drainage water quality in pre-and post-irrigation seasons for supplemental irrigation use. Environ Monit Assess 184:5051–5063. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-2321-2
Al-Rawabdeh AM, Al-Ansari NA, Al-Taani AA, Al-Khateeb FL, Knutsson S (2014) Modeling the risk of groundwater contamination using modified DRASTIC and GIS in Amman-Zerqa Basin. Cent Eur J Eng, Jordan. doi:10.2478/s13531-013-0163-0
Amiri V, Rezaei M, Sohrabi N (2014) Groundwater quality assessment using entropy weighted water quality index (EWQI) in Lenjanat. Iran. Environ Earth Sci 72:3479–3490. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3255-0
Angelopoulos K, Spiliopoulos IC, Mandoulaki A, Theodorakopoulou A, Kouvelas A (2009) Groundwater nitrate pollution in northern part of Achaia Prefecture. Desalination 248:852–858. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2008.11.007
Baba A, Tayfur G (2011) Groundwater contamination and its effect on health in Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 183:77–94. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-1907-z
Barroso MF, Ramalhosa MJ, Olhero A, Antão MC, Pina MF, Guimarães L, Teixeira J, Afonso MJ, Delerue-Matos C, Chaminé HI (2014) Assessment of groundwater contamination in an agricultural peri-urban area (NW Portugal): an integrated approach. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3297-3
Bouderbala A (2015) Assessment of groundwater quality and its suitability for agricultural uses in the Nador Plain, north of Algeria. Water Qual Expo Health. doi:10.1007/s12403-015-0160-z
Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision of China (1993) National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Quality Standard for Groundwater, GB/T 14848-93 (in Chinese)
Cai L-M, Xu Z-C, Qi J-Y, Feng Z-Z, Xiang T-S (2015) Assessment of exposure to heavy metals and health risks among residents near Tonglushan mine in Hubei, China. Chemosphere 127:127–135. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.01.027
Cheong J-Y, Hamm S-Y, Lee J-H, Lee K-S, Woo N-C (2012) Groundwater nitrate contamination and risk assessment in an agricultural area, South Korea. Environ Earth Sci 66:1127–1136. doi:10.1007/s12665-011-1320-5
Chidambaram S, Prasad MBK, Prasanna MV, Manivannan R, Anandhan P (2014) Evaluation of metal pollution in groundwater in the industrialized environs in and around Dindigul, Tamilnadu, India. Water Qual Expo Health. doi:10.1007/s12403-014-0150-6
Dar IA, Dar MA, Sankar K (2010) Nitrate contamination in groundwater of Sopore town and its environs, Kashmir, India. Arab J Geosci 3:267–272. doi:10.1007/s12517-009-0067-8
Davraz A, Özdemir A (2014) Groundwater quality assessment and its suitability in Çeltikçi plain (Burdur/Turkey). Environ Earth Sci 72:1167–1190. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-3036-1
Esteller MV, Domínguez-Mariani E, Garrido SE, Avilés M (2015) Groundwater pollution by arsenic and other toxic elements in an abandoned silver mine. Environ Earth Sci, Mexico. doi:10.1007/s12665-015-4315-9
Ghosh A, Mukherjee K, Ghosh SK, Saha B (2013) Sources and toxicity of fluoride in the environment. Res Chem Intermed 39(7):2881–2915. doi:10.1007/s11164-012-0841-1
Giri S, Singh AK (2015) Human health risk assessment via drinking water pathway due to metal contamination in the groundwater of Subarnarekha River Basin, India. Environ Monit Assess 187:63. doi:10.1007/s10661-015-4265-4
Golekar RB, Patil SN, Baride MV (2013) Human health risk due to trace element contamination in groundwater from the Anjani and Jhiri river catchment area in northern Maharashtra. India. Earth Sci Res J 17(1):17–23
Guo Y, Li Z, Amo-Boateng M, Deng P, Huang P (2014) Quantitative assessment of the impact of climate variability and human activities on runoff changes for the upper reaches of Weihe River. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 28:333–346. doi:10.1007/s00477-013-0752-8
Han DM, Tong XX, Jin MG, Hepburn E, Tong CS, Song XF (2013) Evaluation of organic contamination in urban groundwater surrounding a municipal landfill, Zhoukou, China. Environ Monit Assess 185:3413–3444. doi:10.1007/s10661-012-2801-z
Huang S, Chang J, Huang Q, Wang Y, Chen Y (2014) Spatio-temporal changes in potential evaporation based on entropy across the Wei River Basin. Water Resour Manag 28(459):9–4613. doi:10.1007/s11269-014-0760-6
Huang S, Chang J, Huang Q, Chen Y (2015) Identification of abrupt changes of the relationship between rainfall and runoff in the Wei River Basin, China. Theor Appl Climatol 120:299–310. doi:10.1007/s00704-014-1170-7
Hudak PF (2010) Solutes and potential sources in a portion of the Trinity aquifer, Texas, USA. Carbonates Evaporites 25:15–20. doi:10.1007/s13146-010-0005-6
Jeelani GH, Shah RA, Hussain A (2014) Hydrogeochemical assessment of groundwater in Kashmir Valley, India. J Earth Syst Sci 123(5):1031–1043
Kim YS, Park HS, Kim JY, Park SK, Cho BW, Sung IH, Shin DC (2004) Health risk assessment for uranium in Korean groundwater. J Environ Radioact 77(1):77–85
Li P, Qian H (2011) Human health risk assessment for chemical pollutants in drinking water source in Shizuishan City, Northwest China. Iran J Environ Health Sci Eng 8(1):41–48
Li P, Qian H, Wu J (2010) Groundwater quality assessment based on improved water quality index in Pengyang County, Ningxia, Northwest China. E-J Chem 7(S1):S209–S216. doi:10.1155/2010/451304
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2012) Groundwater quality assessment based on rough sets attribute reduction and TOPSIS method in a semi-arid area, China. Environ Monit Assess 184:4841–4854. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-2306-1
Li P, Qian H, Wu J (2013a) Groundwater quality assessment based on entropy-weighted fuzzy WQI. Int J Environ Sci Eng Res 4(3):1–9
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2013b) Assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation purposes and identification of hydrogeochemical evolution mechanisms in Pengyang County, China. Environ Earth Sci 69:2211–2225. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-2049-5
Li P, Wu J, Qian H, Lyu X, Liu H (2014a) Origin and assessment of groundwater pollution and associated health risk: a case study in an industrial park, northwest China. Environ Geochem Health 36:693–712. doi:10.1007/s10653-013-9590-3
Li P, Qian H, Wu J, Chen J, Zhang Y, Zhang H (2014b) Occurrence and hydrogeochemistry of fluoride in alluvial aquifer of Weihe River, China. Environ Earth Sci 71(7):3133–3145. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2691-6
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2014c) Hydrogeochemistry and quality assessment of shallow groundwater in the southern part of the Yellow River alluvial plain (Zhongwei section), Northwest China. Earth Sci Res J 18(1):27–38
Liu S-Q, Li J-G, Mei M, Dong D-L (2007) Groundwater pollution from underground coal gasification. J China Univ Min Technol 17(4):0467–0472
López-Roldán R, Rubalcaba A, Martin-Alonso J, González S, MartíV Cortina JL (2015) Assessment of the water chemical quality improvement based on human health risk indexes: application to a drinking water treatment plant incorporating membrane technologies. Sci Total Environ. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.04.045
Lu X, Li LY, Lei K, Wang L, Zhai Y, Zhai M (2010) Water quality assessment of Wei River, China using fuzzy synthetic evaluation. Environ Earth Sci 60:1693–1699. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0303-2
Ma J, Ding Z, Wei G, Zhao H, Huang T (2009) Sources of water pollution and evolution of water quality in the Wuwei basin of Shiyang river, Northwest China. J Environ Manag 90:1168–1177. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.05.007
Manassaram DM, Backer LC, Moll DM (2006) A review of nitrates in drinking water: maternal exposure and adverse reproductive and developmental outcomes. Environ Health Perspect 114(3):320–327. doi:10.1289/ehp.8407
Marghade D, Malpe DB, Zade AB (2011) Geochemical characterization of groundwater from northeastern part of Nagpur urban, Central India. Environ Earth Sci 62:1419–1430. doi:10.1007/s12665-010-0627-y
Metwaly M, Elawadi E, Moustafa SSR, Arifi NA, Alfy ME, Zaharani EA (2013) Groundwater contamination assessment in Al-Quwy’yia area of central Saudi Arabia using transient electromagnetic and 2D electrical resistivity tomography. Environ Earth Sci. 71(2):827–835. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2485-x
Ministry of Environmental Protection of the PRC (2011a) National Plan of Groundwater Pollution Prevention (2011–2020). Available at http://www.zhb.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/bwj/201111/W020111109376922920938.pdf, Accessed 18 April 2015 (in Chinese)
Ministry of Environmental Protection of the PRC (2011b) Technical guidelines for environmental impact assessment groundwater environment, HJ 610-2011. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Ministry of Environmental Protection of the PRC (2014) Technical guidelines for risk assessment of contaminated sites, HJ 25.3-2014. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Ministry of Health of the PRC, Standardization Administration of the PRC (2006) Standards for drinking water quality, GB5749–2006. China Standard Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Momot O, Synzynys B (2005) Toxic aluminium and heavy metals in groundwater of middle Russia: health risk assessment. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2(2):214–218
Navoni JA, De Pietri D, Olmos V, Gimenez C, Bovi Mitre G, de Titto E, Villaamil Lepori EC (2014) Human health risk assessment with spatial analysis: study of a population chronically exposed to arsenic through drinking water from Argentina. Sci Total Environ 499:166–174. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.08.058
Ni F-Q, Liu G-D, Tan Y-S, Deng Y (2010) Spatial variation of health risk of groundwater for drinking water supply in Mingshan County, Ya’an City, China. Water Sci Eng 3(4):454–466. doi:10.3882/j.issn.1674-2370.2010.04.008
Nunes LM, Cunha MDC, Ribeiro L (2013) Coverage methods for early groundwater contamination detection. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 90:531–536. doi:10.1007/s00128-013-0971-1
Rajesh R, Brindha K, Elango L (2015) Groundwater quality and its hydrochemical characteristics in a shallow weathered rock aquifer of Southern India. Water Qual Expo Health. doi:10.1007/s12403-015-0166-6
Rao GT, Rao VVSG, Sarma VS, Dhakate R, Surinaidu L, Mahesh J, Ramesh G (2012) Hydrogeochemical parameters for assessment of groundwater quality in a river sub-basin. Int J Environ Sci Technol 9:297–310. doi:10.1007/s13762-012-0024-z
Rao GT, Rao VVSG, Padalu G, Dhakate R, Sarma VS (2013) Application of electrical resistivity tomography methods for delineation of groundwater contamination and potential zones. Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-013-0835-3
Rice EW, Baird RB, Eaton AD, Clesceri LS (2012) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 22nd edn. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and Water Environment Federation, Washington, DC
Sirat M (2013) Neural network assessment of groundwater contamination of US Mid-continent. Arab J Geosci 6:3149–3160. doi:10.1007/s12517-012-0570-1
Srinivasamoorthy K, Gopinath M, Chidambaram S, Vasanthavigar M, Sarma VS (2014) Hydrochemical characterization and quality appraisal of groundwater from Pungar sub basin, Tamilnadu, India. J King Saud Univ 26:37–52. doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2013.08.001
Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress of the PRC (2014) Environmental protection law of the People’s Republic of China. China Legal Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Su X, Wang H, Zhang Y (2013) Health risk assessment of nitrate contamination in groundwater: a case study of an agricultural area in Northeast China. Water Resour Manag 27:3025–3034. doi:10.1007/s11269-013-0330-3
Subba Rao N (2014) Spatial control of groundwater contamination, using principal component analysis. J Earth Syst Sci 123(4):715–728
Suthar S, Bishnoi P, Singh S, Mutiyar PK, Nema AK, Patil NS (2009) Nitrate contamination in groundwater of some rural areas of Rajasthan, India. J Hazard Mater 171:189–199. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.111
Thilagavathi R, Chidambaram S, Prasanna MV, Thivya C, Singaraja C (2012) A study on groundwater geochemistry and water quality in layered aquifers system of Pondicherry region, southeast India. Appl Water Sci 2(4):253–269. doi:10.1007/s13201-012-0045-2
USSL (United States Salinity Laboratory) (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. US Dept of Agriculture (USDA), Agriculture Handbook 60, Washington, pp 69–81
Venkatramanan S, Chung SY, Kim TH, Prasanna MV, Hamm SY (2014) Assessment and distribution of metals contamination in groundwater: a case study of Busan City. Water Qual Expo Health, Korea. doi:10.1007/s12403-014-0142-6
Vetrimurugan E, Elango L (2014) Groundwater chemistry and quality in an intensively cultivated river delta. Water Qual Expo Health. doi:10.1007/s12403-014-0133-7
Vetrimurugan E, Elango L, Rajmohan N (2013) Sources of contaminants and groundwater quality in the coastal part of a river delta. Int J Environ Sci Technol 10(3):473–486. doi:10.1007/s13762-012-0138-3
Wang W-L, Wu Q-Y, Wang C, He T, Hu H-Y (2014) Health risk assessment of phthalate esters (PAEs) in drinking water sources of China. Environ Sci Pollut Res. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3615-z
Wang LN, Zhu QK, Zhao WJ, Zhao XK (2015) The drought trend and its relationship with rainfall intensity in the Loess Plateau of China. Nat Hazards. doi:10.1007/s11069-015-1594-0
WHO (1997) Guideline for drinking water quality. Recommendations (vol 1), 2nd edn. WHO, Geneva
Wilcox LV (1948) The quality of water for irrigation use. US Dept of Agriculture Tech Bull 1962, Washington
Wongsanit J, Teartisup P, Kerdsueb P, Tharnpoophasiam P, Worakhunpiset S (2015) Contamination of nitrate in groundwater and its potential human health: a case study of lower Mae Klong river basin. Environ Sci Pollut Res, Thailand. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-4347-4
Wongsasuluk P, Chotpantarat Siriwong W, Robson M (2013) Heavy metal contamination and human health risk assessment in drinking water from shallow groundwater wells in an agricultural area in Ubon Ratchathani province. Environ Geochem Health, Thailand. doi:10.1007/s10653-013-9537-8
Wu J, Li P, Qian H (2012) Study on the hydrogeochemistry and non-carcinogenic health risk induced by fluoride in Pengyang County, China. Int J Environ Sci 2(3):1127–1134
Wu J, Li P, Qian H, Duan Z, Zhang X (2014) Using correlation and multivariate statistical analysis to identify hydrogeochemical processes affecting the major ion chemistry of waters: a case study in Laoheba phosphorite mine in Sichuan, China. Arab J Geosci 7:3973–3982. doi:10.1007/s12517-013-1057-4
Yang M, Fei Y, Ju Y, Ma Z, Li H (2012) Health risk assessment of groundwater pollution—a case study of typical city in North China Plain. J Earth Sci 23(3):335–348. doi:10.1007/s12583-012-0260-7
Yang X, Duan J, Wang L, Li W, Guan J, Beecham S, Mulcahy D (2015) Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment in the Wei River in China. Environ Monit Assess 187:111. doi:10.1007/s10661-014-4202-y
Zhang H (2014) Early-warning of nitrogen pollution in groundwater source in Huaxian, China. A Dissertation Submitted for the Degree of Master, Chang’an Univeristy, Xi’an (in Chinese)
Zhang H, Xu WL, Hiscock KM (2013) Application of MT3DMS and geographic information system to evaluation of groundwater contamination in the Sherwood sandstone aquifer, UK. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1438. doi:10.1007/s11270-013-1438-z
Zhang X, Zhuang D, Ma X, Jiang D (2014a) Esophageal cancer spatial and correlation analyses: water pollution, mortality rates, and safe buffer distances in China. J Geogr Sci 24(1):46–58. doi:10.1007/s11442-014-1072-8
Zhang Y, Ma R, Li Z (2014b) Human health risk assessment of groundwater in Hetao Plain (Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China). Environ Monit Assess 186:4669–4684. doi:10.1007/s10661-014-3729-2
Zumlot T, Batayneh A, Nazal Y, Ghrefat H, Mogren S, Zaman H, Elawadi E, Laboun A, Qaisy S (2013) Using multivariate statistical analyses to evaluate groundwater contamination in the northwestern part of Saudi Arabia. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2392-1
Zuo D, Xu Z, Wu W, Zhao J, Zhao F (2014) Identification of streamflow response to climate change and human activities in the Wei River Basin, China. Water Resour Manag 28:833–851. doi:10.1007/s11269-014-0519-0
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Doctoral Postgraduate Technical Project of Chang’an University (2014G5290001), the Special Fund for Basic Scientific Research of Central Colleges (310829151072), the Special Fund for Scientific Research on Public Interest of the Ministry of Water Resources (201301084), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41172212). The authors are grateful to the anonymous reviewers and the editors who helped us in improving the quality of the paper.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Sun, Z. Evaluation of Shallow Groundwater Contamination and Associated Human Health Risk in an Alluvial Plain Impacted by Agricultural and Industrial Activities, Mid-west China. Expo Health 8, 311–329 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-015-0170-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-015-0170-x