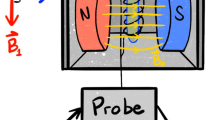
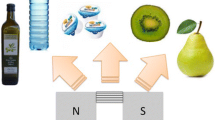
Abstract
Low-field bench top 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (LF-NMR) relaxometry instruments have been increasingly popular as analytical tools for engineering research. Magnetic resonance imaging, which is a more advanced approach to NMR technology, provides the researcher with images of the internal structure without any disruption to the sample and has been commonly used in medical applications in analysis of soft tissue. The non-invasive and non-destructive nature coupled with the high discriminative power of LF-NMR and MRI, makes them invaluable tools of analysis for a wide range of applications in food science. This review covers the basic concept behind NMR/MRI technology and discusses some of its most commonly used food applications. The review addresses the food scientist with no prior knowledge of NMR/MRI and aims to supply the reader with both the theory of the method and its fundamentals, as well as the practical uses in scientific research and industrial applications.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altan A, Lavenson DM, McCarthy MJ, McCarthy KL (2011) Oil migration in chocolate and almond product confectionery systems. J Food Sci 76(6):E489–E494. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02233.x
Altan A, Oztop MH, McCarthy KL, McCarthy MJ (2011) Monitoring changes in feta cheese during brining by magnetic resonance imaging and NMR relaxometry. J Food Eng 107(2):200–207. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2011.06.023
Astruc T (2014) MUSCLE FIBER TYPES AND MEAT QUALITY. In: Dikeman M, Devine C (eds) Encyclopedia of meat sciences, 2nd edn. Academic Press, Oxford, pp 442–448
Aursand IG, Erikson U, Veliyulin E (2010) Water properties and salt uptake in Atlantic salmon fillets as affected by ante-mortem stress, rigor mortis, and brine salting: a low-field H-1 NMR and H-1/Na-23 MRI study. Food Chem 120(2):482–489. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.10.041
Bajd F, Sersa I (2011) Continuous monitoring of dough fermentation and bread baking by magnetic resonance microscopy. Magn Reson Imaging 29(3):434–442. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2010.10.010
Bernstein MA, King KF, Zhou XJ (2004) Handbook of MRI pulse sequences. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam
Bertram HC, Rasmussen M, Busk H, Oksbjerg N, Karlsson AH, Andersen HJ (2002) Changes in porcine muscle water characteristics during growth—an in vitro low-field NMR relaxation study. J Magn Reson 157(2):267–276. doi:10.1006/jmre.2002.2600
Bertram HC, Wiking L, Nielsen JH, Andersen HJ (2005) Direct measurement of phase transitions in milk fat during cooling of cream—a low-field NMR approach. Int Dairy J 15(10):1056–1063. doi:10.1016/j.idairyj.2004.10.005
Bertsch F, Mattner J, Stehling MK, Müller-Lisse U, Peller M, Loeffler R et al (1998) Non-invasive temperature mapping using MRI: comparison of two methods based on chemical shift and T1-relaxation. Magn Reson Imaging 16(4):393–403. doi:10.1016/S0730-725X(97)00311-1
Bonny JM, Rouille J, Della Valle G, Devaux MF, Douliez JP, Renou JP (2004) Dynamic magnetic resonance microscopy of flour dough fermentation. Magn Reson Imaging 22(3):395–401. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2004.01.020
Bouhrara M, Clerjon S, Damez JL, Chevarin C, Portanguen S, Kondjoyan A, Bonny JM (2011) Dynamic MRI and thermal simulation to interpret deformation and water transfer in meat during heating. J Agric Food Chem 59(4):1229–1235. doi:10.1021/Jf103384d
Bouhrara M, Lehallier B, Clerjon S, Damez JL, Bonny JM (2012) Mapping of muscle deformation during heating: in situ dynamic MRI and nonlinear registration. Magn Reson Imaging 20(3):422–430. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2011.10.002
Castell-Palou A, Rossello C, Femenia A, Bon J, Simal S (2011) Moisture profiles in cheese drying determined by TD-NMR: mathematical modeling of mass transfer. J Food Eng 104(4):525–531. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2011.01.010
Chassagne-Berces S, Leitner M, Melado A, Barreiro P, Correa EC, Blank I, Chanvrier H (2011) Effect of fibers and whole grain content on quality attributes of extruded cereals. Procedia Food Sci 1:17–23. doi:10.1016/j.profoo.2011.09.004
Chayaprasert W, Stroshine R (2005) Rapid sensing of internal browning in whole apples using a low-cost, low-field proton magnetic resonance sensor. Postharvest Biol Technol 36(3):291–301. doi:10.1016/j.postharvbio.2005.02.006
Chen FL, Wei YM, Zhang B (2010) Characterization of water state and distribution in textured soybean protein using DSC and NMR. J Food Eng 100(3):522–526. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2010.04.040
Choi YJ, McCarthy KL, McCarthy MJ, Kim MH (2007) Oil migration in chocolate. Appl Magn Reson 32(1–2):205–220. doi:10.1007/s00723-007-0013-4
Ciampa A, Dell’Abate MT, Masetti O, Valentini M, Sequi P (2010) Seasonal chemical–physical changes of PGI Pachino cherry tomatoes detected by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Food Chem 122(4):1253–1260. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.03.078
Cioica N, Fechete R, Cota C, Nagy EM, David L, Cozar O (2013) NMR relaxation investigation of the native corn starch structure with plasticizers. J Mol Struct 1044:128–133. doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2013.01.037
Clark CJ, MacFall JS (2003) Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging of ‘Fuyu’ persimmon fruit during development and ripening. Magn Reson Imaging 21(6):679–685
Collewet G, Bogner P, Allen P, Busk H, Dobrowolski A, Olsen E, Davenel A (2005) Determination of the lean meat percentage of pig carcasses using magnetic resonance imaging. Meat Sci 70(4):563–572. doi:10.1016/j.meatsci.205.02.005
Collewet G, Bugeon J, Idier J, Quellec S, Quittet B, Cambert M, Haffray P (2013) Rapid quantification of muscle fat content and subcutaneous adipose tissue in fish using MRI. Food Chem 138(2–3):2008–2015. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.09.131
Cornillon P, Salim LC (2000) Characterization of water mobility and distribution in low- and intermediate-moisture food systems. Magn Reson Imaging 18(3):335–341. doi:10.1016/S0730-725x(99)00139-3
d’Avila MA, Powell RL, Phillips RJ, Shapley NC, Walton JH, Dungan SR (2005) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): a technique to study flow an microstructure of concentrated emulsions. Braz J Chem Eng 22(1):49–60. doi:10.1590/S0104-66322005000100006
Defraeye T, Lehmann V, Gross D, Holat C, Herremans E, Verboven P, Nicolai BM (2013) Application of MRI for tissue characterisation of ‘Braeburn’ apple. Postharvest Biol Technol 75:96–105. doi:10.1016/j.postharvbio.2012.08.009
Derossi A, De Pilli T, Severini C, McCarthy MJ (2008) Mass transfer during osmotic dehydration of apples. J Food Eng 86(4):519–528. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2007.11.007
El-Bakry M, Duggan E, O’Riordan ED, O’Sullivan M (2010) Effects of emulsifying salts reduction on imitation cheese manufacture and functional properties. J Food Eng 100(4):596–603. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2010.05.007
El-Bakry M, Duggan E, O’Riordan ED, O’Sullivan M (2011) Casein hydration and fat emulsification during manufacture of imitation cheese, and effects of emulsifying salts reduction. J Food Eng 103(2):179–187. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2010.10.014
El-Bakry M, Duggan E, O’Riordan ED, O’Sullivan M (2011) Effect of cation, sodium or potassium, on casein hydration and fat emulsification during imitation cheese manufacture and post-manufacture functionality. LWT Food Sci Technol 44(10):2012–2018. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2011.07.007
Esveld DC, van der Sman RGM, Witek MM, Windt CW, van As H, van Duynhoven JPM, Meinders MBJ (2012) Effect of morphology on water sorption in cellular solid foods. Part II: sorption in cereal crackers. J Food Eng 109(2):311–320. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2011.08.023
Fan D, Ma S, Wang L, Zhao H, Zhao J, Zhang H, Chen W (2013) (1)H NMR studies of starch–water interactions during microwave heating. Carbohydr Polym 97(2):406–412. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.05.021
Frías JM, Foucat L, Bimbenet JJ, Bonazzi C (2002) Modeling of moisture profiles in paddy rice during drying mapped with magnetic resonance imaging. Chem Eng J 86(1–2):173–178. doi:10.1016/S1385-8947(01)00285-6
Fukuoka M, Mihori T, Watanabe H (2000) MRI observation and mathematical model simulation of water migration in wheat flour dough during boiling. J Food Sci 65(8):1343–1348. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.2000.tb10609.x
Ghosh PK, Jayas DS, Smith EA, Gruwel MLH, White NDG (2008) Mathematical modelling of wheat kernel drying with input from moisture movement studies using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), Part II: model comparison with published studies. Biosyst Eng 100(4):547–554. doi:10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2008.04.014
Ghosh PK, Jayas DS, Smith EA, Gruwel MLH, White NDG, Zhilkin PA (2008) Mathematical modelling of wheat kernel drying with input from moisture movement studies using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), Part I: model development and comparison with MRI observations (vol 100, pg 389, 2008). Biosyst Eng 101(1):143. doi:10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2008.07.001
Gonera A, Cornillon P (2002) Gelatinization of Starch/Gum/Sugar Systems Studied by using DSC, NMR, and CSLM. Starch 54(11):508–516. doi:10.1002/1521-379X(200211)54:11<508:AID-STAR508>3.0.CO;2-K
Grenier A, Lucas T, Collewet G, Le Bail A (2003) Assessment by MRI of local porosity in dough during proving. Theoretical considerations and experimental validation using a spin-echo sequence. Magn Reson Imaging 21(9):1071–1086. doi:10.1016/s0730-725x(03)00194-2
Grimault S, Lucas T, Quellec S, Mariette F (2004) Quantitative measurement of temperature by proton resonance frequency shift at low field: a general method to correct non-linear spatial and temporal phase deformations. J Magn Reson 170(1):79–87. doi:10.1016/j.jmr.2004.06.001
Gudjonsdottir M, Gunnlaugsson VN, Finnbogadottir GA, Sveinsdottir K, Magnusson H, Arason S, Rustad T (2010) Process control of lightly salted wild and farmed atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) by Brine injection, brining, and freezing—a low field NMR study. J Food Sci 75(8):E527–E536. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2010.01808.x
Gudjonsdottir M, Jonsson A, Bergsson AB, Arason S, Rustad T (2011) Shrimp processing assessed by low field nuclear magnetic resonance, near infrared spectroscopy, and physicochemical measurements—the effect of polyphosphate content and length of prebrining on shrimp muscle. J Food Sci 76(4):E357–E367. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02112.x
Hall LD, Evans SD, Nott KP (1998) Measurement of textural changes of food by MRI relaxometry. Magn Reson Imaging 16(5–6):485–492. doi:10.1016/S0730-725x(98)00116-7
Harbourne N, Jacquier JC, O’Riordan D (2011) Effects of addition of phenolic compounds on the acid gelation of milk. Int Dairy J 21(3):185–191. doi:10.1016/j.idairyj.2010.10.003
Hashemi RH, Bradley WG, Lisanti CJ (2010) MRI: the basics. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore
Heil JR, Ozilgen M, McCarthy MJ (1993) Magnetic resonance imaging analysis of water migration and void formation in baking biscuits. Food Dehydration 89(297):39–45
Hills B (2010) Food properties, applications of NMR. In: Lindon JC (ed) Encyclopedia of spectroscopy and spectrometry, 2nd edn. Academic Press, Oxford, pp 671–679
Hills BP, Wright KM, Belton PS (1989) Proton N.M.R. studies of chemical and diffusive exchange in carbohydrate systems. Mol Phys 67(6):1309–1326. doi:10.1080/00268978900101831
Hong SW, Yan ZY, Otterburn MS, McCarthy MJ (1996) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of a cookie in comparison with time-lapse photographic analysis (TLPA) during baking process. Magn Reson Imaging 14(7–8):923–927. doi:10.1016/S0730-725X(96)00183-X
Horigane AK, Takahashi H, Maruyama S, Ohtsubo KI, Yoshida M (2006) Water penetration into rice grains during soaking observed by gradient echo magnetic resonance imaging. J Cereal Sci 44(3):307–316. doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2006.07.014
Hulbert GJ, Litchfield JB, Schmidt SJ (1997) Determination of convective heat transfer coefficients using 2D MRI temperature mapping and finite element modeling. J Food Eng 34(2):193–201. doi:10.1016/S0260-8774(97)00058-7
Hwang S-S, Cheng Y-C, Chang C, Lur H-S, Lin T-T (2009) Magnetic resonance imaging and analyses of tempering processes in rice kernels. J Cereal Sci 50(1):36–42. doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2008.10.012
Ishida N, Naito S, Kano H (2004) Loss of moisture from harvested rice seeds on MRI. Magn Reson Imaging 22(6):871–875. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2004.01.054
Janas S, Boutry S, Malumba P, Vander Elst L, Béra F (2010) Modelling dehydration and quality degradation of maize during fluidized-bed drying. J Food Eng 100(3):527–534. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2010.05.001
Jin X, van der Sman RGM, Gerkema E, Vergeldt FJ, van As H, van Boxtel AJB (2011) Moisture distribution in broccoli: measurements by MRI hot air drying experiments. 11th Int Congress Eng Food (Icef11) 1:640–646. doi:10.1016/j.profoo.2011.09.096
Kara S, Mueller JJ, Liese A (2011) Online analysis methods for monitoring of bioprocesses. Chem Today 29(2):38–41
Kirtil E, Oztop MH, Sirijariyawat A, Ngamchuachit P, Barrett DM, McCarthy MJ (2014) Effect of pectin methyl esterase (PME) and CaCl2 infusion on the cell integrity of fresh-cut and frozen-thawed mangoes: an NMR relaxometry study. Food Res Int 66:409–416. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2014.10.006
Knoerzer K, Regier M, Schubert H (2006) Microwave heating: a new approach of simulation and validation. Chem Eng Technol 29(7):796–801. doi:10.1002/ceat.200600038
Koizumi M, Naito S, Ishida N, Haishi T, Kano H (2008) A dedicated MRI for food science and agriculture. Food Sci Technol Res 14(1):74–82. doi:10.3136/Fstr.14.74
Konez O (2011) Manyetik Rezonans Görüntüleme: Temel Bilgiler. http://konez.com/
Kotwaliwale N, Curtis E, Othman S, Naganathan GK, Subbiah J (2012) Magnetic resonance imaging and relaxometry to visualize internal freeze damage to pickling cucumber. Postharvest Biol Technol 68:22–31. doi:10.1016/j.postharvbio.2011.12.022
Lai H-M, Hwang S-C (2004) Water status of cooked white salted noodles evaluated by MRI. Food Res Int 37(10):957–966. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2004.06.008
Lee WL, McCarthy MJ, McCarthy KL (2010) Oil migration in 2-component confectionery systems. J Food Sci 75(1):E83–E89. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2009.01454.x
Li WM, Wang P, Xu XL, Xing T, Zhou GH (2014) Use of low-field nuclear magnetic resonance to characterize water properties in frozen chicken breasts thawed under high pressure. Eur Food Res Technol 239(2):183–188. doi:10.1007/s00217-014-2189-9
Li ZG, Thomas C (2014) Quantitative evaluation of mechanical damage to fresh fruits. Trends Food Sci Technol 35(2):138–150. doi:10.1016/j.tifs.2013.12.001
Lopes-Da-Silva JA, Santos DMJ, Freitas A, Brites C, Gil AM (2007) Rheological and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) study of the hydration and heating of undeveloped wheat doughs. J Agric Food Chem 55(14):5636–5644. doi:10.1021/Jf070379+
Lucas T, Doursat C, Grenier D, Wagner M, Trystram G, Flick D (2015) Modeling of bread baking with a new, multi-scale formulation of evaporation–condensation–diffusion and evidence of compression in the outskirts of the crumb. J Food Eng 149:24–37. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2014.07.020
Lucas T, Grenier A, Quellec S, Collewet G, Le Bail A, Davenel A (2005) Use of MRI for the characterization of bread processes. In: Cauvain SP, Salmon SS, Young LS (eds) Using cereal science and technology for the benefit of consumers: proceedings of the 12th international ICC cereal and bread congress, 24–26th May, 2004, Harrogate, UK. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 199–203
Lucas T, Grenier A, Quellec S, Le Bail A, Davenel A (2005) MRI quantification of ice gradients in dough during freezing or thawing processes. J Food Eng 71(1):98–108. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2004.07.027
Lucas T, Grenier D, Bornert M, Challois S, Quellec S (2010) Bubble growth and collapse in pre-fermented doughs during freezing, thawing and final proving. Food Res Int 43(4):1041–1048. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2010.01.014
Lucas T, Le Ray D, Barey P, Mariette F (2005) NMR assessment of ice cream: effect of formulation on liquid and solid fat. Int Dairy J 15(12):1225–1233. doi:10.1016/j.idairyj.2004.06.012
Lucas T, Le Ray D, Mariette F (2007) Kinetics of water absorption and solute leaching during soaking of breakfast cereals. J Food Eng 80(2):377–384. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2005.11.006
Lucas T, Musse M, Bornert M, Davenel A, Quellec S (2012) Temperature mapping in bread dough using SE and GE two-point MRI methods: experimental and theoretical estimation of uncertainty. Magn Reson Imaging 30(3):431–445. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2011.09.004
Luyts A, Wilderjans E, Waterschoot J, Van Haesendonck I, Brijs K, Courtin CM, Delcour JA (2013) Low resolution 1H NMR assignment of proton populations in pound cake and its polymeric ingredients. Food Chem 139(1–4):120–128. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.01.062
Maeda I, Horigane AK, Yoshida M, Aikawa Y (2009) Water diffusion in buckwheat noodles and wheat noodles during boiling and holding as determined from MRI and rectangular cylinder diffusion model. Food Sci Technol Res 15(2):107–116. doi:10.3136/fstr.15.107
Maehara M, Ikeda K, Kurokawa H, Ohmura N, Ikeda S, Hirokawa Y, Sawada S (2014) Diffusion-weighted echo-planar imaging of the head and neck using 3-T MRI: investigation into the usefulness of liquid perfluorocarbon pads and choice of optimal fat suppression method. Magn Reson Imaging 32(5):440–445. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2014.01.011
Mannina L, Sobolev AP, Viel S (2012) Liquid state 1H high field NMR in food analysis. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 66:1–39. doi:10.1016/j.pnmrs.2012.02.001
Marcone MF, Wang S, Albabish W, Nie S, Somnarain D, Hill A (2013) Diverse food-based applications of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) technology. Food Res Int 51(2):729–747. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2012.12.046
Mariette F (2009) Investigations of food colloids by NMR and MRI. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 14(3):203–211. doi:10.1016/j.cocis.2008.10.006
Mariette F, Collewet G, Davenel A, Lucas T, Musse M (2007) Quantitative MRI in food science and food engineering eMagRes. Wiley, New York
McCarthy KL, McCarthy MJ (2008) Oil migration in chocolate–peanut butter paste confectionery as a function of chocolate formulation. J Food Sci 73(6):E266–E273. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2008.00797.x
McDaniel KA, White BL, Dean LL, Sanders TH, Davis JP (2012) Compositional and mechanical properties of peanuts roasted to equivalent colors using different time/temperature combinations. J Food Sci 77(12):C1292–C1298. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2012.02979.x
Melado A, Barreiro P, Rodríguez-Sinobas L, Fernández-Valle ME, Ruíz-Cabello J, Chassagne-Berces S, Chanvrier H (2011) MRI texture analysis as means for addressing rehydration and milk diffusion in cereals. Procedia Food Sci 1:625–631. doi:10.1016/j.profoo.2011.09.094
Mikac U, Sepe A, Sersa I (2015) MR microscopy for noninvasive detection of water distribution during soaking and cooking in the common bean. Magn Reson Imaging 33(3):336–345. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2014.12.001
Milczarek RR, Saltveit ME, Garvey TC, McCarthy MJ (2009) Assessment of tomato pericarp mechanical damage using multivariate analysis of magnetic resonance images. Postharvest Biol Technol 52(2):189–195. doi:10.1016/j.postharvbio.2009.01.002
Mohoric A, Vergeldt F, Gerkema E, de Jager A, van Duynhoven J, van Dalen G, Van As H (2004) Magnetic resonance imaging of single rice kernels during cooking. J Magn Reson 171(1):157–162. doi:10.1016/j.jmr.2004.08.013
Motwani T, Lanagan M, Anantheswaran RC (2012) State of water in starch–water systems in the gelatinization temperature range as investigated using dielectric relaxation spectroscopy. Carbohydr Polym 87(1):24–31. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.06.057
Nestor G, Bankefors J, Schlechtriem C, Brannas E, Pickova J, Sandstrom C (2010) High-resolution H-1 magic angle spinning NMR spectroscopy of intact arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus) muscle. Quantitative analysis of n-3 fatty acids, EPA and DHA. J Agric Food Chem 58(20):10799–10803. doi:10.1021/Jf103338j
Nicolai BM, Bulens I, Baerdemaeker JD, Ketelaere BD, Hertog MLATM, Verboven P, Lammertyn J (2009) Chapter 15—Non-destructive evaluation: detection of external and internal attributes frequently associated with quality and damage. In: Prussia EBJFLSBE (ed) Postharvest handling, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 421–441
Nott KP, Hall LD (2005) Validation and cross-comparison of MRI temperature mapping against fibre optic thermometry for microwave heating of foods. Int J Food Sci Technol 40(7):723–730. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.2005.00992.x
Nott KP, Halla LD, Bows JR, Hale M, Patrick ML (2000) MRI phase mapping of temperature distributions induced in food by microwave heating. Magn Reson Imaging 18(1):69–79. doi:10.1016/S0730-725X(99)00103-4
Nutrition Facts (2014) Peanuts, all types, oil-roasted, with salt. http://nutritiondata.self.com/facts/legumes-and-legume-products/4357/2
Nutrition Facts (2014) Raisins, seedless. http://nutritiondata.self.com/facts/fruits-and-fruit-juices/2050/2
Otero L, Prestamo G (2009) Effects of pressure processing on strawberry studied by nuclear magnetic resonance. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 10(4):434–440. doi:10.1016/j.ifset.2009.04.004
Oztop MH, Bansal H, Takhar P, McCarthy KL, McCarthy MJ (2014) Using multi-slice-multi-echo images with NMR relaxometry to assess water and fat distribution in coated chicken nuggets. LWT Food Sci Technol 55(2):690–694. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2013.10.031
Oztop MH, Rosenberg M, Rosenberg Y, McCarthy KL, McCarthy MJ (2010) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and relaxation spectrum analysis as methods to investigate swelling in whey protein gels. J Food Sci 75(8):E508–E515. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2010.01788.x
Pearce KL, Rosenvold K, Andersen HJ, Hopkins DL (2011) Water distribution and mobility in meat during the conversion of muscle to meat and ageing and the impacts on fresh meat quality attributes—a review. Meat Sci 89(2):111–124. doi:10.1016/j.meatsci.2011.04.007
Pedersen HT, Munck L, Engelsen SB (2000) Low-field (1)H nuclear magnetic resonance and chemometrics combined for simultaneous determination of water, oil, and protein contents in oilseeds. J Am Oil Chem Soc 77(10):1069–1076. doi:10.1007/s11746-000-0168-4
Pykett IL (2000) NMR—a powerful tool for industrial process control and quality assurance. IEEE Trans Appl Supercond 10(1):721–723. doi:10.1109/77.828333
Rakesh V, Seo Y, Datta AK, McCarthy KL, McCarthy MJ (2010) Heat transfer during microwave combination heating: computational modeling and MRI experiments. AIChE J 56(9):2468–2478. doi:10.1002/Aic.12162
Regier M, Hardy EH, Knoerzer K, Leeb CV, Schuchmann HP (2007) Determination of structural and transport properties of cereal products by optical scanning, magnetic resonance imaging and Monte Carlo simulations. J Food Eng 81(2):485–491. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2006.11.025
Renou JP, Foucat L, Bonny JM (2003) Magnetic resonance imaging studies of water interactions in meat. Food Chem 82(1):35–39. doi:10.1016/S0308-8146(02)00582-4
Rieke V, Pauly KB (2008) MR Thermometry. J Magn Res Imaging JMRI 27(2):376–390. doi:10.1002/jmri.21265
Ritota M, Gianferri R, Bucci R, Brosio E (2008) Proton NMR relaxation study of swelling and gelatinisation process in rice starch–water samples. Food Chem 110(1):14–22. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.01.048
Ruiz-Altisent M, Ruiz-Garcia L, Moreda GP, Lu RF, Hernandez-Sanchez N, Correa EC, Garcia-Ramos J (2010) Sensors for product characterization and quality of specialty crops—a review. Comput Electron Agric 74(2):176–194. doi:10.1016/j.compag.2010.07.002
Ruiz-Cabrera MA, Gou P, Foucat L, Renou JP, Daudin JD (2004) Water transfer analysis in pork meat supported by NMR imaging. Meat Sci 67(1):169–178. doi:10.1016/j.meatsci.2003.10.005
Rumsey TR, McCarthy KL (2012) Modeling oil migration in two-layer chocolate-almond confectionery products. J Food Eng 111(1):149–155. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2012.01.006
Salomonsen T, Sejersen MT, Viereck N, Ipsen R, Engelsen SB (2007) Water mobility in acidified milk drinks studied by low-field H-1 NMR. Int Dairy J 17(4):294–301. doi:10.1016/j.idairyj.2006.04.003
Sanchez-Alonso I, Martinez I, Sanchez-Valencia J, Careche M (2012) Estimation of freezing storage time and quality changes in hake (Merluccius merluccius, L.) by low field NMR. Food Chem 135(3):1626–1634. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.06.038
Sanchez-Alonso I, Moreno P, Careche M (2014) Low field nuclear magnetic resonance (LF-NMR) relaxometry in hake (Merluccius merluccius, L.) muscle after different freezing and storage conditions. Food Chem 153:250–257. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.12.060
Sekiyama Y, Horigane AK, Ono H, Irie K, Maeda T, Yoshida M (2012) T2 distribution of boiled dry spaghetti measured by MRI and its internal structure observed by fluorescence microscopy. Food Res Int 48(2):374–379. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2012.05.019
Shaarani SM, Nott KP, Hall LD (2006) Combination of NMR and MRI quantitation of moisture and structure changes for convection cooking of fresh chicken meat. Meat Sci 72(3):398–403. doi:10.1016/j.meatsci.2005.07.017
Sorland GH, Larsen PM, Lundby F, Rudi AP, Guiheneuf T (2004) Determination of total fat and moisture content in meat using low field NMR. Meat Sci 66(3):543–550. doi:10.1016/S0309-1740(03)00157-8
Steglich T, Bernin D, Röding M, Nydén M, Moldin A, Topgaard D, Langton M (2014) Microstructure and water distribution of commercial pasta studied by microscopy and 3D magnetic resonance imaging. Food Res Int 62:644–652. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2014.04.004
Tananuwong K, Reid D (2004) DSC and NMR relaxation studies of starch–water interactions during gelatinization. Carbohydr Polym 58(3):345–358. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2004.08.003
Tao F, Zhang L, McCarthy MJ, Beckles DM, Saltveit M (2014) Magnetic resonance imaging provides spatial resolution of chilling injury in micro-tom tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) fruit. Postharvest Biol Technol 97:62–67. doi:10.1016/j.postharvbio.2014.06.005
Thybo AK, Szczypinski PM, Karlsson AH, Donstrup S, Stodkilde-Jorgensen HS, Andersen HJ (2004) Prediction of sensory texture quality attributes of cooked potatoes by NMR-imaging (MRI) of raw potatoes in combination with different image analysis methods. J Food Eng 61(1):91–100. doi:10.1016/S0260-8774(03)00190-0
Troutman MY, Mastikhin IV, Balcom BJ, Eads TM, Ziegler GR (2001) Moisture migration in soft-panned confections during engrossing and aging as observed by magnetic resonance imaging. J Food Eng 48(3):257–267. doi:10.1016/S0260-8774(00)00167-9
Tsukakoshi Y, Naito S, Ishida N (2008) Fracture intermittency during a puncture test of cereal snacks and its relation to porous structure. Food Res Int 41(9):909–917. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2007.11.010
Van As H, van Duynhoven J (2013) MRI of plants and foods. J Magn Reson 229:25–34. doi:10.1016/j.jmr.2012.12.019
van Duynhoven J, Voda A, Witek M, Van As H (2010) Chapter 3—Time-domain NMR applied to food products. In: Graham AW (ed) Annual reports on NMR spectroscopy, vol 69. Academic Press, New York, pp 145–197
Vanin FM, Lucas T, Trystram G (2009) Crust formation and its role during bread baking. Trends Food Sci Technol 20(8):333–343. doi:10.1016/j.tifs.2009.04.001
Vereecken J, Foubert I, Smith KW, Sassano GJ, Dewettinck K (2010) Crystallization of model fat blends containing symmetric and asymmetric monounsaturated triacylglycerols. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 112(2):233–245. doi:10.1002/ejlt.200900037
Voda A, Homan N, Witek M, Duijster A, van Dalen G, van der Sman R, van Duynhoven J (2012) The impact of freeze-drying on microstructure and rehydration properties of carrot. Food Res Int 49(2):687–693. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2012.08.019
Wagner M, Quellec S, Trystram G, Lucas T (2008) MRI evaluation of local expansion in bread crumb during baking. J Cereal Sci 48(1):213–223. doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2007.09.006
Wagner MJ, Loubat M, Sommier A, Le Ray D, Collewet G, Broyart B, Lucas T (2008) MRI study of bread baking: experimental device and MRI signal analysis. Int J Food Sci Technol 43(6):1129–1139. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.2007.01633.x
Wagner MJ, Lucas T, Le Ray D, Trystram G (2007) Water transport in bread during baking. J Food Eng 78(4):1167–1173. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2005.12.029
Wang YJ, Assaad E, Ispas-Szabo P, Mateescu MA, Zhu XX (2011) NMR imaging of chitosan and carboxymethyl starch tablets: swelling and hydration of the polyelectrolyte complex. Int J Pharm 419(1–2):215–221. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.08.008
Watanabe H, Fukuoka M, Tomiya A, Mihori T (2001) A new non-Fickian diffusion model for water migration in starchy food during cooking. J Food Eng 49(1):1–6. doi:10.1016/S0260-8774(00)00175-8
Węglarz WP, Hemelaar M, van der Linden K, Franciosi N, van Dalen G, Windt C, Van As H (2008) Real-time mapping of moisture migration in cereal based food systems with Aw contrast by means of MRI. Food Chem 106(4):1366–1374. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.04.077
Weglarz* WP, Goudappel GJW, van Dalen G, Blonk H, van Duynhoven J (2007) Real-time assessment of the internal porous structure of cereal materials under high-moisture conditions using 3D MRI and XRT. Magn Reson Imaging 25(4):590. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2007.01.145
Whitworth MB, Alava JM (2005) Non-destructive imaging of bread and cake structure during baking. In: Cauvain SP, Salmon SS, Young LS (eds) Using cereal science and technology for the benefit of consumers: proceedings of the 12th international ICC cereal and bread congress, 24–26th May, 2004, Harrogate, UK. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 456–460
Yahia EM, De Jesus Ornelas-Paz J, Elansari A (2011) 5—Postharvest technologies to maintain the quality of tropical and subtropical fruits. In: Yahia EM (ed) Postharvest biology and technology of tropical and subtropical fruits. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, pp 142–195e
Ye X, Ruan R, Chen P, Doona C (2004) Simulation and verification of ohmic heating in static heater using MRI temperature mapping. LWT Food Sci Technol 37(1):49–58. doi:10.1016/s0023-6438(03)00133-6
Yuan-hui L, Miao-yun L, Gai-ming Z, Qiu-hui Z, Yan-xia L, Xiao-ping G (2013) Effects of freeze-thaw cycle on quality of chicken flesh and bones. J Henan Agric Univ 2:187–191
Zehl M, Braunberger C, Conrad J, Crnogorac M, Krasteva S, Vogler B, Krenn L (2011) Identification and quantification of flavonoids and ellagic acid derivatives in therapeutically important Drosera species by LC-DAD, LC-NMR, NMR, and LC-MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 400(8):2565–2576. doi:10.1007/s00216-011-4690-3
Zhang L, Lucas T, Doursat C, Flick D, Wagner M (2007) Effects of crust constraints on bread expansion and CO2 release. J Food Eng 80(4):1302–1311. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2006.10.008
Zhang L, McCarthy MJ (2012) Black heart characterization and detection in pomegranate using NMR relaxometry and MR imaging. Postharvest Biol Technol 67:96–101. doi:10.1016/j.postharvbio.2011.12.018
Zhang L, McCarthy MJ (2012) Measurement and evaluation of tomato maturity using magnetic resonance imaging. Postharvest Biol Technol 67:37–43. doi:10.1016/j.postharvbio.2011.12.004
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Bilkent University National Magnetic Center (UMRAM), Ankara, Turkey, for providing the opportunity to use the MRI scanner.
Compliance with ethical standards
In this review, principles of ethical and professional conduct have been followed. This study does not involve research on human participants and/or animals.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirtil, E., Oztop, M.H. 1H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Relaxometry and Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Applications in Food Science and Processing. Food Eng Rev 8, 1–22 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12393-015-9118-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12393-015-9118-y