Abstract
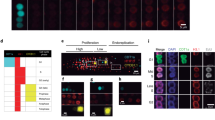
Embryogenesis in transgenic Arabidopsis plants with GFP:mTn, a chimeric fusion of soluble shifted green fluorescent protein and a mouse actin binding domain, was studied. Confocal laser scanning microscopy was used to determine patterns of formation and cellular responses during asymmetric cell division. Before such cells divide, the nucleus moves to the position where new cell walls are to be formed. The apical–basal axis of the embryo develops mainly at the zygote to octant stage, and these events are associated with asymmetric divisions of the zygote and hypophyseal cells. Formation of the radial axis is established from the dermatogen to the globular-stage embryo via tangential cell division within the upper tiers. Bilateral symmetry of the embryo primarily happens at the triangular stage through zig-zag cell divisions of initials of the cotyledonary primordia. All stages of embryogenesis are described in detail here.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
An G, Ebert P, Mitra A, Ha S (1988) Binary vectors. In: Gelvin SB, Schilperoot RA (eds) Plant molecular biology manual. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 1–19
Berleth T, Chatfield S (2002) The Arabidopsis book. American Society of Plant Biologists, Maryland
Berleth T, Jürgens G (1993) The role of the MONOPTEROS gene in organising the basal body region of the Arabidopsis embryo. Development 118:575–587
Bowman JL, Eshed Y (2000) Formation and maintenance of the shoot apical meristem. Trend Plant Sci 5:110–115
Brownlee C, Berger F (1995) Extracellular matrix and pattern in plant embryos: On the lookout for developmental information. Trends Gene 11:344–348
Casson S, Lindsey K (2006) The turnip mutant of Arabidopsis reveals the LEAFY COTYLEDON1 expression mediates the effects of auxin and sugars to promote embryonic cell identity. Plant Physiol 142:526–541
Casson S, Spencer M, Walker K, Lindsey K (2005) Laser capture microdissection for the analysis of gene expression during embryogenesis of Arabidopsis. Plant J 42:111–123
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Colette AH, Heidstra R (2007) Who begets whom? Plant cell fate determination by asymmetric cell division. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:1–8
Davis SJ, Vierstra RD (1998) Soluble, highly fluorescent variants of green fluorescent protein (GFP) for use in higher plants. Plant Mol Biol 36:1–8
Di Laurenzio L, Wysocka-Diller L, Malamy JE, Pysh L, Helariutta Y, Freshour G, Hahn MG, Feldmann KA, Benfey PN (1996) The SCARECROW gene regulates an asymmetric cell division that is essential for generating the radial organization of the Arabidopsis root. Cell 86:423–433
Friml J, Vieten A, Sauer M, Weijers D, Schwarz H, Hamann T, Offringa R, Jürgens G (2003) Efflux-dependent auxin gradients establish the apical-basal axis of Arabidopsis. Nature 426:147–153
Goldberg RB, de Paiva G, Yadegari R (1994) Plant embryogenesis: zygote to seed. Science 266:605–614
Haecker A, Gross-Hardt R, Geiges B, Sarkar A, Breuninger H, Herrmann A, Laux T (2004) Expression dynamics of Wox genes mark cell fate decisions during early embryonic patterning in Arabidopsis thaliana. Development 131:657–668
Hardtke CS, Berleth T (1998) The Arabidopsis gene MONOPTEROS encodes a transcription factor mediating embryo axis formation and vascular development. EMBO J 17:1405–1411
Haseloff J, Siemering KR, Prasher DC, Hodge S (1997) Removal of a cryptic intron and subcellular localization of green fluorescent protein are required to mark transgenic Arabidopsis plants brightly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:2122–2127
Helariutta Y, Fukaki H, Wysocka-Diller J, Nakajima K, Jung J, Sena G, Hauser MT, Benfey PN (2000) The SHORT-ROOT gene controls radial patterning of the Arabidopsis root through radial signaling. Cell 101:555–567
Jürgens G (1993) Apical-basal pattern formation in the Arabidopsis embryo: Studies on the role of the gnom gene. Development 117:149–162
Jürgens G (2001) Apical-basal pattern formation in Arabidopsis embryogenesis. EMBO J 20:3609–3616
Jürgens G, Mayer U (1994) Arabidopsis. In: Bard JBL (ed) Embryos, colour atlas of development. Wolfe, London, pp 7–21
Kim I (2007) Cell-to-cell transport of macromolecules during early plant development. J Plant Biol 50:266–273
Kost B, Spielhofer P, Chua N-H (1998) A GFP-mouse talin fusion protein labels plant actin filaments in vivo and visualizes the actin cytoskeleton in growing pollen tubes. Plant J 16:393–401
Laux T, Jürgens G (1997) Embryogenesis: a new start in life. Plant Cell 9:989–1000
Laux T, Würschum T, Breuninger H (2004) Genetic regulation of embryonic pattern formation. Plant Cell 16:190–202
Liu C-M, Xu Z-H, Chua N-H (1993) Auxin polar transport is essential for the establishment of bilateral symmetry during early plant embryogenesis. Plant Cell 5:621–630
Long TA, Ohno C, Smith ZR, Meyerowitz EM (2006) TOPLESS regulates apical embryonic fate in Arabidopsis. Science 312:1520–1523
Lotan T, Ohto M-A, Yee KM, West MA, Lo R, Kwong RW, Yamagishi K, Fischer RL, Goldberg RB, Harada JJ (1998) Arabidopsis LEAFY COTYLEDON1 is sufficient to induce embryo development in vegetative cells. Cell 93:1195–1205
Lyndon RF (1990) Plant development—the cellular basis. Unwin Hyman, Boston
Mansfield SG, Briaty LG (1991) Early embryogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. II. The developing embryo. Can J Bot 69:461–476
Mayer U, Büttner G, Jürgens G (1993) Apical-basal pattern formation in the Arabidopsis embryo: studies on the role of the gnom gene. Development 117:149–162
McCann RO, Craig SW (1997) The I/LWEQ module: a conserved sequence that signifies F-actin binding in functionally diverse proteins from yeast to mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:5679–5684
Mòl R, Matthys-Rochon E, Dumas PC (1994) The kinetics of cytological events during double fertilization in Zea mays L. Plant J 5:197–206
Nakajima K, Sena G, Nawy T, Benfey PN (2001) Intercellular movement of the putative transcription factor SHR in root patterning. Nature 413:307–311
Nawy T, Lukowitz W, Bayer M (2008) Talk global, act local-patterning the Arabidopsis embryo. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11:28–33
Ogas J, Kaufmann S, Henderson J, Somerville C (1999) PICKLE is a CHD3 chromatin-remodeling factor that regulates the transition from embryonic to vegetative development in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:13839–13844
Przemeck GKH, Mattsson J, Hardtke CS, Sung ZR, Berleth T (1996) Studies on the role of the Arabidopsis gene MONOPTEROS in vascular development and plant axialization. Planta 200:229–237
Scheres B, Wolkenfelt H, Willemsen V, Terlouw M, Lawson E, Dean C, Weisbeek P (1994) Embryonic origin of the Arabidopsis primary root and root meristem initials. Development 120:2475–2487
Scheres B, Di Laurenzio L, Willemsen V, Hauser MT, Janmaat K, Weisbeek P, Benfey PN (1995) Mutations affecting the radial organisation of the Arabidopsis root display specific defects throughout the embryonic axis. Development 121:53–62
Song SK, Clark SE (2005) POL and related phosphatases and are dosage-sensitive regulators of meristem and organ development in Arabidopsis. Dev Biol 285:272–284
Spencer MW, Casson SA, Lindsey K (2007) Transcriptional profiling of the Arabidopsis embryo. Plant Physiol 143:924–940
Steeves TA, Sussex IM (1989) Experimental investigation on the shoot apex. In: Steeves TA, Sussex IM, Ed 2. Patterns in plant development. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 86–99
Steinmann T, Geldner N, Grebe M, Mangold S, Jackson CL, Paris S, Galweiler L, Palme K, Jürgens G (1999) Coordinated polar localization of auxin efflux carrier PIN1 by GNOM ARF GEF. Science 286:316–318
Takada S, Hibara K, Ishida T, Tasaka M (2001) The CUP-SHAPED COTYLEDON1 gene of Arabidopsis regulates shoot apical meristem formation. Development 128:1127–1135
Torres-Ruiz RA, Jürgens G (1994) Mutations in the FASS gene uncouple pattern formation and morphogenesis in Arabidopsis development. Development 120:2967–2978
Vernon DM, Meinke DW (1994) Embryonic transformation of the suspensor in twin a polyembryonic mutant of Arabidopsis. Dev Biol 165:566–573
Vroemen CW, Langeveld S, Mayer U, Ripper G, Jürgens G, van Kammen A, De Vries SC (1996) Pattern formation in the Arabidopsis embryo revealed by position-specific lipid transfer gene expression. Plant Cell 8:783–791
Webb MC, Gunning BES (1991) The microtubular cytoskeleton during development of the zygote, proembryo, and free-nuclear endosperm in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Planta 184:187–195
Willemsen V, Wolkenfelt H, de Vrieze G, Weisbeek P, Scheres B (1998) The HOBBIT gene is required for formation of the root meristem in the Arabidopsis embryo. Development 125:521–531
Wysocka-Diller JW, Helariutta Y, Fukaki H, Malamy JE, Benfey PN (2000) Molecular analysis of SCARECROW function reveals a radial patterning mechanism common to root and shoot. Development 127:595–603
Xiang C, Han P, Lutziger I, Wang K, Oliver DJ (1999) A mini binary vector series for plant transformation. Plant Mol Biol 40:711–717
Yadegari R, de Paiva GR, Laux T, Koltunow AM, Apuya N, Zimmerman JL, Fischer RL, Harada JJ, Goldberg RB (1994) Cell differentiation and morphogenesis are uncoupled in Arabidopsis raspberry embryos. Plant Cell 6:1713–1729
Yeung EC, Sussex IM (1979) Embryogeny of Phaseolus coccineus: the suspensor and the growth of the embryo-proper in vitro. Z Pflanzenphysiol 91:423–433
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank Dr. S.E. Clark, Dr. S.K. Song, and Mr. M. Hymes for their generous support of this work. This research was funded by the Korea Research Foundation (KRF-2007-030107008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Whang, S.S. Confocal Microscopy Study of Arabidopsis Embryogenesis Using GFP:mTn. J. Plant Biol. 52, 312–318 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-009-9039-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-009-9039-5