Abstract
Background
Recent advances in nuclear myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) have made it possible to develop a dual-isotope protocol for high-speed acquisition with image quality and radiation delivery comparable to that obtained with conventional single isotope protocols. So far, no study has compared dual-isotope high-speed MPI to invasive coronary angiography (ICA) in a large cohort using a Cadmium-zinc-telluride SPECT system.
Methods
Over a 1-year period (May 2011 to April 2012), 1366 patients underwent dual-isotope high-speed MPI. Patients with ICA within 3 months after dual-isotope high-speed MPI were included together with patients with a low likelihood of coronary artery disease (CAD) in order to assess normalcy rate. Global summed stress score (SSS) and summed rest score (SRS) were calculated, and ICA results were analyzed independently. The main end point was a patient-based assessment of the diagnostic performance of dual-isotope high-speed MPI in detecting or ruling out significant CAD (>70% reduction in lumen diameter).
Results
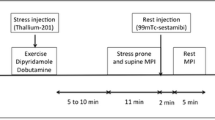
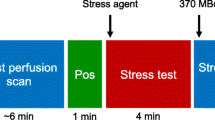
Inclusion criteria were fulfilled for 214 patients (143 men; age 60 ± 14 years; ICA, n = 104; low likelihood for CAD, n = 110). An exercise stress test was performed in 62% of patients and a pharmacological stress test was performed with either dipyridamole (32%) or dobutamine (6%). Average examination duration was 22.4 ± 4.5 minutes. Mean SSS, SRS, and SDS were 8.0 ± 4.9, 3.1 ± 4.3, and 5.0 ± 3.2, respectively. Prevalence of angiographic CAD was 75%. ICA detected stenosis in the left main trunk, left anterior descending artery, left circumflex artery, and right coronary artery in 4, 33, 31, and 42 patients, respectively. Sensitivity of dual-isotope high-speed MPI was 94%, normalcy rate was 92%, and accuracy was 83% for detecting CAD.
Conclusion
Dual-isotope high-speed MPI is reliable at detecting or ruling out CAD. NCT01785589





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herzog BA, Buechel RR, Katz R, Brueckner M, Husmann L, Burger IA, et al. Nuclear myocardial perfusion imaging with a cadmium-zinc-telluride detector technique: Optimized protocol for scan time reduction. J Nucl Med 2010;51:46-51.
Nkoulou R, Pazhenkottil AP, Kuest SM, Ghadri JR, Wolfrum M, Husmann L, et al. Semiconductor detectors allow low-dose-low-dose 1-day SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging. J Nucl Med 2011;52:1204-9.
Esteves FP, Raggi P, Folks RD, Keidar Z, Askew JW, Rispler S, et al. Novel solid-state-detector dedicated cardiac camera for fast myocardial perfusion imaging: Multicenter comparison with standard dual detector cameras. J Nucl Cardiol 2009;16:927-34.
Berman DS, Kang X, Tamarappoo B, Wolak A, Hayes SW, Nakazato R, et al. Stress thallium-201/rest technetium-99m sequential dual isotope high-speed myocardial perfusion imaging. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2009;2:273-82.
Underwood SR, Anagnostopoulos C, Cerqueira M, Ell PJ, Flint EJ, Harbinson M, et al. Myocardial perfusion scintigraphy: The evidence. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2004;31:261-91.
Fiechter M, Ghadri JR, Kuest SM, Pazhenkottil AP, Wolfrum M, Nkoulou RN, et al. Nuclear myocardial perfusion imaging with a novel cadmium-zinc-telluride detector SPECT/CT device: First validation versus invasive coronary angiography. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2011;38:2025-30.
Hendel RC, Berman DS, Di Carli MF, Heidenreich PA, Henkin RE, Pellikka PA, et al. ACCF/ASNC/ACR/AHA/ASE/SCCT/SCMR/SNM 2009 Appropriate use criteria for cardiac radionuclide imaging: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Appropriate Use Criteria Task Force, the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology, the American College of Radiology, the American Heart Association, the American Society of Echocardiography, the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography, the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, and the Society of Nuclear Medicine. J Am Coll Cardiol 2009;53:2201-29.
Valentin J. Radiation dose to patients from radiopharmaceuticals (addendum 2 to ICRP publication 53) ICRP publication 80. Ann ICRP 1998;28:1-126.
Radiation dose to patients from radiopharmaceuticals. A report of a Task Group of Committees 2 and 3 of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. Addendum 5 to ICRP Publication 53 (2001). http://www.icrp.org/docs/Add_5-7_to_P53.pdf. Accessed 8 Aug 2008.
Krahwinkel W, Herzog H, Feinendegen LE. Pharmacokinetics of thallium-201 in normal individuals after routine myocardial scintigraphy. J Nucl Med 1988;29:1582-6.
Thomas SR, Stabin MG, Castronovo FP. Radiation-absorbed dose from 201Tl-thallous chloride. J Nucl Med 2005;46:502-8.
Cerqueira MD, Weissman NJ, Dilsizian V, Jacobs AK, Kaul S, Laskey WK, et al. Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for tomographic imaging of the heart. A statement for healthcare professionals from the Cardiac Imaging Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology of the American Heart Association. Circulation 2002;105:539-42.
Gibbons RJ, Balady GJ, Bricker JT, Chaitman BR, Fletcher GF, Froelicher VF, et al. ACC/AHA 2002 guideline update for exercise testing: Summary article. A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Committee to Update the Exercise Testing Guidelines). J Am Coll Cardiol 1997;2002(40):1531-40.
Steele PP, Kirch DL, Koss JE. Comparison of simultaneous dual-isotope multipinhole SPECT with rotational SPECT in a group of patients with coronary artery disease. J Nucl Med 2008;49:1080-9.
Salerno M, Beller GA. Noninvasive assessment of myocardial perfusion. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 2009;2:412-24.
Leppo JA, Meerdink DJ. Comparison of the myocardial uptake of a technetium-labeled isonitrile analogue and thallium. Circ Res 1989;65:632-9.
Udelson JE, Coleman PS, Metherall J, Pandian NG, Gomez AR, Griffith JL, et al. Predicting recovery of severe regional ventricular dysfunction. Comparison of resting scintigraphy with 201Tl and 99mTc-sestamibi. Circulation 1994;89:2552-61.
Duvall WL, Sweeny JM, Croft LB, Ginsberg E, Guma KA, Henzlova MJ. Reduced stress dose with rapid acquisition CZT SPECT MPI in a non-obese clinical population: Comparison to coronary angiography. J Nucl Cardiol 2012;19:19-27.
Nakazato R, Tamarappoo BK, Kang X, Wolak A, Kite F, Hayes SW, et al. Quantitative upright-supine high-speed SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging for detection of coronary artery disease: Correlation with invasive coronary angiography. J Nucl Med 2010;51:1724-31.
Duvall WL, Sweeny JM, Croft LB, Barghash MH, Kulkarni NK, Guma KA, et al. Comparison of high efficiency CZT SPECT MPI to coronary angiography. J Nucl Cardiol 2011;18:595-604.
Gimelli A, Bottai M, Genovesi D, Giorgetti A, Di Martino F, Marzullo P. High diagnostic accuracy of low-dose gated-SPECT with solid-state ultrafast detectors: Preliminary clinical results. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2012;39:83-90.
Neill J, Prvulovich EM, Fish MB, Berman DS, Slomka PJ, Sharir T, et al. Initial multicentre experience of high-speed myocardial perfusion imaging: Comparison between high-speed and conventional single-photon emission computed tomography with angiographic validation. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2013;40:1084-94.
Gimelli A, Bottai M, Quaranta A, Giorgetti A, Genovesi D, Marzullo P. Gender differences in the evaluation of coronary artery disease with a cadmium-zinc telluride camera. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2013;40:1542-8.
Duvall WL, Slomka PJ, Gerlach JR, Sweeny JM, Baber U, Croft LB, et al. High-efficiency SPECT MPI: Comparison of automated quantification, visual interpretation, and coronary angiography. J Nucl Cardiol 2013;20:763-73.
Hindorf C, Oddstig J, Hedeer F, Hansson MJ, Jögi J, Engblom H. Importance of correct patient positioning in myocardial perfusion SPECT when using a CZT camera. J Nucl Cardiol 2014;21:695-702.
Kim JC, Anderson S, Kaye W, Zhang F, Zhu Y, Kaye SJ, et al. Charge sharing in common-grid pixelated CdZnTe detectors. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res A 2011;654:233-43.
Machecourt J, Longère P, Fagret D, Vanzetto G, Wolf JE, Polidori C, et al. Prognostic value of thallium-201 single-photon emission computed tomographic myocardial perfusion imaging according to extent of myocardial defect. Study in 1,926 patients with follow-up at 33 months. J Am Coll Cardiol 1994;23:1096-106.
Jneid H, Anderson JL, Wright RS, Adams CD, Bridges CR, Casey DE Jr, et al. 2012 ACCF/AHA focused update of the guideline for the management of patients with unstable angina/non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (updating the 2007 guideline and replacing the 2011 focused update): A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 2012;60:645-81.
Hoffmann U, Bamberg F, Chae CU, Nichols JH, Rogers IS, Seneviratne SK, et al. Coronary computed tomography angiography for early triage of patients with acute chest pain: The ROMICAT (Rule Out Myocardial Infarction using Computer Assisted Tomography) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 2009;53:1642-50.
Tonino PA, Fearon WF, De Bruyne B, Oldroyd KG, Leesar MA, Ver Lee PN, et al. Angiographic versus functional severity of coronary artery stenoses in the FAME study fractional flow reserve versus angiography in multivessel evaluation. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010;55:2816-21.
Cerqueira MD, Allman KC, Ficaro EP, Hansen CL, Nichols KJ, Thompson RC, et al. Recommendations for reducing radiation exposure in myocardial perfusion imaging. J Nucl Cardiol 2010;17:709-18.
Conflict of interest
The authors have indicated that they have no financial conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barone-Rochette, G., Leclere, M., Calizzano, A. et al. Stress thallium-201/rest technetium-99m sequential dual-isotope high-speed myocardial perfusion imaging validation versus invasive coronary angiography. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 22, 513–522 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12350-014-0016-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12350-014-0016-0