Abstract
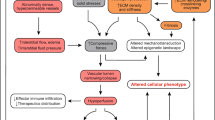
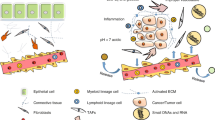
Reciprocal interactions between neoplastic cells and their microenvironment are crucial events in carcinogenesis and tumor progression. Pervasive stromal reprogramming and remodeling that transform a normal to a tumorigenic microenvironment modify numerous stromal cells functions, status redox, oxidative stress, pH, ECM stiffness and energy metabolism. These environmental factors allow selection of more aggressive cancer cells that develop important adaptive strategies. Subpopulations of cancer cells acquire new properties associating plasticity, stem-like phenotype, unfolded protein response, metabolic reprogramming and autophagy, production of exosomes, survival to anoikis, invasion, immunosuppression and therapeutic resistance. Moreover, by inducing vascular transdifferentiation of cancer cells and recruiting endothelial cells and pericytes, the tumorigenic microenvironment induces development of tumor-associated vessels that allow invasive cells to gain access to the tumor vessels and to intravasate. Circulating cancer cells can survive in the blood stream by interacting with the intravascular microenvironment, extravasate through the microvasculature and interact with the metastatic microenvironment of target organs. In this review, we will focus on many recent paradigms involved in the field of tumor progression.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- COX2:
-
Cyclooxygenase 2
- PDGF:
-
Release platelet-derived growth factor
- PDGFR:
-
Release platelet-derived growth factor receptor
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
- HIF-1:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1
- HGF:
-
Hepatocyte growth factor
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- FSP-1:
-
Fibroblast-specific protein 1
- SDF-1:
-
Stromal cell-derived factor 1
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- RANKL:
-
Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor beta
- FGF:
-
Fibroblast growth factors
- IFNs:
-
Interferons
- TNF1α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor 1 Alpha
- LOX:
-
Lysyl oxidase
- MCT1:
-
Monocarboxylate transporter 1
- MCT4:
-
Monocarboxylate transporter 4
- Shh:
-
Sonic Hedgehog
- LC3:
-
Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3
References
Mueller MM, Fusenig NE (2004) Friends or foes - bipolar effects of the tumour stroma in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 4(11):839–849
Cichon MA, Degnim AC, Visscher DW, Radisky DC (2010) Microenvironmental influences that drive progression from benign breast disease to invasive breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 15(4):389–397
Elshamy WM, Duhé RJ (2013) Overview: cellular plasticity, cancer stem cells and metastasis. Cancer Lett 341(1):2–8
Fulda S (2010) Evasion of apoptosis as a cellular stress response in cancer. Int J Cell Biol 2010:370835
Hanahan D, Coussens LM (2012) Accessories to the crime: functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 21(3):309–322
Byun JS, Gardner K (2013) Wounds that will not heal: pervasive cellular reprogramming in cancer. Am J Pathol 182(4):1055–1064
Mahadevan NR, Zanetti M (2011) Tumor stress inside out: cell-extrinsic effects of the unfolded protein response in tumor cells modulate the immunological landscape of the tumor microenvironment. J Immunol 187(9):4403–4409
Brosseau JP, Lucier JF, Nwilati H, Thibault P, Garneau D, Gendron D, Durand M, Couture S, Lapointe E, Prinos P, Klinck R, Perreault JP, Chabot B, Abou-Elela S (2013) Tumor microenvironment-associated modifications of alternative splicing. RNA 20(2):189–201
Orimo A, Weinberg RA (2006) Stromal fibroblasts in cancer: a novel tumor-promoting cell type. Cell Cycle 5(15):1597–1601
Hinz B, Phan SH, Thannickal VJ, Galli A, Bochaton-Piallat ML, Gabbiani G (2007) The myofibroblast: one function, multiple origins. Am J Pathol 170(6):1807–1816
Anderberg C, Li H, Fredriksson L, Andrae J, Betsholtz C, Li X, Eriksson U, Pietras K (2009) Paracrine signaling by platelet-derived growth factor-CC promotes tumor growth by recruitment of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cancer Res 69(1):369–378
Bochet L, Lehuédé C, Dauvillier S, Wang YY, Dirat B, Laurent V, Dray C, Guiet R, Maridonneau-Parini I, Le Gonidec S, Couderc B, Escourrou G, Valet P, Muller C (2013) Adipocyte-derived fibroblasts promote tumor progression and contribute to the desmoplastic reaction in breast cancer. Cancer Res 73(18):5657–5668
Wang YY, Lehuédé C, Laurent V, Dirat B, Dauvillier S, Bochet L, Le Gonidec S, Escourrou G, Valet P, Muller C (2012) Adipose tissue and breast epithelial cells: a dangerous dynamic duo in breast cancer. Cancer Lett 324(2):142–151
Kogan-Sakin I, Cohen M, Paland N, Madar S, Solomon H, Molchadsky A, Brosh R, Buganim Y, Goldfinger N, Klocker H, Schalken JA, Rotter V (2009) Prostate stromal cells produce CXCL-1, CXCL-2, CXCL-3 and IL-8 in response to epithelia-secreted IL-1. Carcinogenesis 30(4):698–705
Zhang J, Wang Y, Li D, Jing S (2013) Notch and TGF-β/Smad3 pathways are involved in the interaction between cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Tumour Biol 252(4):174–185
Tjomsland V, Spångeus A, Sandström P, Borch K, Messmer D, Larsson M (2010) Semi mature blood dendritic cells exist in patients with ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma owing to inflammatory factors released from the tumor. PLoS ONE 5(10):e13441
Teicher BA, Fricker SP (2010) CXCL12 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 16(11):2927–2931
Vannucci L (2014) Stroma as an Active Player in the Development of the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Microenviron
Chi Sabins N, Taylor JL, Fabian KP, Appleman LJ, Maranchie JK, Stolz DB, Storkus WJ (2013) DLK1: a novel target for immunotherapeutic remodeling of the tumor blood vasculature. Mol Ther 21(10):1958–1968
Cooke VG, LeBleu VS, Keskin D, Khan Z, O’Connell JT, Teng Y, Duncan MB, Xie L, Maeda G, Vong S, Sugimoto H, Rocha RM, Damascena A, Brentani RR, Kalluri R (2012) Pericyte depletion results in hypoxia-associated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis mediated by met signaling pathway. Cancer Cell 21(1):66–81
Bose A, Barik S, Banerjee S, Ghosh T, Mallick A, Bhattacharyya Majumdar S, Goswami KK, Bhuniya A, Banerjee S, Baral R, Storkus WJ, Dasgupta PS, Majumdar S (2013) Tumor-derived vascular pericytes anergize Th cells. J Immunol 191(2):971–981
Orlova VV, Drabsch Y, Freund C, Petrus-Reurer S, van den Hil FE, Muenthaisong S, Dijke PT, Mummery CL (2014) Functionality of endothelial cells and pericytes from human pluripotent stem cells demonstrated in cultured vascular plexus and zebrafish xenografts. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 34(1):177–186
Franses JW, Baker AB, Chitalia VC, Edelman ER (2011) Stromal endothelial cells directly influence cancer progression. Sci Transl Med 3(66):66ra5
Zamarron BF, Chen W (2011) Dual roles of immune cells and their factors in cancer development and progression. Int J Biol Sci 7(5):651–658
Coussens LM, Werb Z (2002) Inflammation and cancer. Nature 420(6917):860–867
Wei S, Kryczek I, Zou W (2006) Regulatory T-cell compartmentalization and trafficking. Blood 108(2):426–431
Littman DR, Rudensky AY (2010) Th17 and regulatory T cells in mediating and restraining inflammation. Cell 140(6):845–858
Lin SC, Chen KH, Lin CH, Kuo CC, Ling QD, Chan CH (2007) The quantitative analysis of peripheral blood FOXP3-expressing T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis patients. Eur J Clin Invest 37(12):987–996
O’Neill DW, Adams S, Bhardwaj N (2004) Manipulating dendritic cell biology for the active immunotherapy of cancer. Blood 104(8):2235–2246
Blom B, Ho S, Antonenko S, Liu YJ (2000) Generation of interferon alpha-producing predendritic cell (Pre-DC)2 from human CD34(+) hematopoietic stem cells. J Exp Med 192(12):1785–1796
Shurin MR, Shurin GV, Lokshin A, Yurkovetsky ZR, Gutkin DW, Chatta G, Zhong H, Han B, Ferris RL (2006) Intratumoral cytokines chemokines growth factors and tumor infiltrating dendritic cells: friends or enemies? Cancer Metastasis Rev 25(3):333–356
Steinman RM (2007) Dendritic cells: understanding immunogenicity. Eur J Immunol 37(Suppl 1):S53–S60
Ghirelli C, Zollinger R, Soumelis V (2010) Systematic cytokine receptor profiling reveals GM-CSF as a novel TLR-independent activator of human plasmacytoid predendritic cells. Blood 115(24):5037–5040
Cao W, Liu YJ (2007) Innate immune functions of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Curr Opin Immunol 19(1):24–30
Colonna M, Trinchieri G, Liu YJ (2004) Plasmacytoid dendritic cells in immunity. Nat Immunol 5(12):1219–1226
Pan PY, Ozao J, Zhou Z, Chen SH (2008) Advancements in immune tolerance. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60(2):91–105
Murdoch C, Muthana M, Coffelt SB, Lewis CE (2008) The role of myeloid cells in the promotion of tumour angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 8(8):618–631
Talmadge JE, Donkor M, Scholar E (2007) Inflammatory cell infiltration of tumors: Jekyll or Hyde. Cancer Metastasis Rev 26(3–4):373–400
Qian BZ, Pollard JW (2010) Macrophage diversity enhances tumor progression and metastasis. Cell 141(1):39–51
Mukhtar RA, Nseyo O, Campbell MJ, Esserman LJ (2011) Tumor-associated macrophages in breast cancer as potential biomarkers for new treatments and diagnostics. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 11(1):91–100
Porta C, Larghi P, Rimoldi M, Totaro MG, Allavena P, Mantovani A, Sica A (2009) Cellular and molecular pathways linking inflammation and cancer. Immunobiology 214(9–10):761–777
Friedl P, Wolf K (2003) Tumour-cell invasion and migration: diversity and escape mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer 3:362–374
Goc J, Fridman WH, Sautès-Fridman C, Dieu-Nosjean MC (2013) Characteristics of tertiary lymphoid structures in primary cancers. Oncoimmunology 2(12):e26836
Taddei ML, Giannoni E, Comito G, Chiarugi P (2013) Microenvironment and tumor cell plasticity: an easy way out. Cancer Lett 341(1):80–96
Shoulders MD, Raines RT (2009) Annu Collagen structure and stability. Rev Biochem 78:929–958
Carragher NO, Walker SM, Scott Carragher LA, Harris F, Sawyer TK, Brunton VG, Ozanne BW, Frame MC (2006) Calpain 2 and Src dependence distinguishes mesenchymal and amoeboid modes of tumour cell invasion: a link to integrin function. Oncogene 25(42):5726–5740
Friedl P, Wolf K (2010) Plasticity of cell migration: a multiscale tuning model. J Cell Biol 188(1):11–19
Wolf K, Wu YI, Liu Y, Geiger J, Tam E, Overall C, Stack MS, Friedl P (2007) Multi-step pericellular proteolysis controls the transition from individual to collective cancer cell invasion. Nat Cell Biol 9(8):893–904
Catalano V, Turdo A, Di Franco S, Dieli F, Todaro M, Stassi G (2013) Tumor and its microenvironment: a synergistic interplay. Semin Cancer Biol 23(6 Pt B):522–532
Erler JT, Bennewith KL, Nicolau M, Dornhöfer N, Kong C, Le QT, Chi JT, Jeffrey SS, Giaccia AJ (2006) Lysyl oxidase is essential for hypoxia-induced metastasis. Nature 440(7088):1222–1226
Semenza GL (2012) Hypoxia-inducible factors in physiology and medicine. Cell 148(3):399–408
Webb BA, Chimenti M, Jacobson MP, Barber DL (2011) Dysregulated pH: a perfect storm for cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer 11(9):671–677
Ilie M, Mazure NM, Hofman V, Ammadi RE, Ortholan C, Bonnetaud C, Havet K, Venissac N, Mograbi B, Mouroux J, Pouysségur J, Hofman P (2010) High levels of carbonic anhydrase IX in tumour tissue and plasma are biomarkers of poor prognostic in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 102(11):1627–1635
Swietach P, Patiar S, Supuran CT, Harris AL, Vaughan-Jones RD (2009) The role of carbonic anhydrase 9 in regulating extracellular and intracellular ph in three-dimensional tumor cell growths. J Biol Chem 284(30):20299–20310
Gatenby RA, Gawlinski ET, Gmitro AF, Kaylor B, Gillies RJ (2006) Acid-mediated tumor invasion: a multidisciplinary study. Cancer Res 66(10):5216–5223
Srivastava J, Barreiro G, Groscurth S, Gingras AR, Goult BT, Critchley DR, Kelly MJ, Jacobson MP, Barber DL (2008) Structural model and functional significance of pH-dependent talin-actin binding for focal adhesion remodeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(38):14436–14441
Giannoni E, Bianchini F, Masieri L, Serni S, Torre E, Calorini L, Chiarugi P (2010) Reciprocal activation of prostate cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts stimulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stemness. Cancer Res 70(17):6945–6956
Justus CR, Dong L, Yang LV (2013) Acidic tumor microenvironment and pH-sensing G protein-coupled receptors. Front Physiol 4:354
Gerald D, Berra E, Frapart YM, Chan DA, Giaccia AJ, Mansuy D, Pouysségur J, Yaniv M, Mechta-Grigoriou F (2004) JunD reduces tumor angiogenesis by protecting cells from oxidative stress. Cell 118(6):781–794
Liu LZ, Hu XW, Xia C, He J, Zhou Q, Shi X, Fang J, Jiang BH (2006) Reactive oxygen species regulate epidermal growth factor-induced vascular endothelial growth factor and hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression through activation of AKT and P70S6K1 in human ovarian cancer cells. Free Radic Biol Med 41(10):1521–1533
Storz P (2005) Reactive oxygen species in tumor progression. Front Biosci 10:1881–1896
Fessler E, Dijkgraaf FE, De Sousa E, Melo F, Medema JP (2013) Cancer stem cell dynamics in tumor progression and metastasis: is the microenvironment to blame? Cancer Lett 341(1):97–104
Costa A, Scholer-Dahirel A, Mechta-Grigoriou F (2014) The role of reactive oxygen species and metabolism on cancer cells and their microenvironment. Semin Cancer Biol
Erez N, Truitt M, Olson P, Arron ST, Hanahan D (2010) Cancer-associated fibroblasts are activated in incipient neoplasia to orchestrate tumor-promoting inflammation in an NF-kappa B-dependent manner. Cancer Cell 17(2):135–147
Atsumi T, Singh R, Sabharwal L, Bando H, Meng J, Arima Y, Yamada M, Harada M, Jiang JJ, Kamimura D, Ogura H, Hirano T, Murakami M (2014) Inflammation amplifier, a new paradigm in cancer biology. Cancer Res 74(1):8–14
Nakaya Y, Sheng G (2013) EMT in developmental morphogenesis. Cancer Lett 341(1):9–15
Samatov TR, Tonevitsky AG, Schumacher U (2013) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: focus on metastatic cascade, alternative splicing, non-coding RNAs and modulating compounds. Mol Cancer 12(1):107
Valastyan S, Weinberg RA (2011) Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell 147(2):275–292
Bednarz-Knoll N, Alix-Panabières C, Pantel K (2012) Plasticity of disseminating cancer cells in patients with epithelial malignancies. Cancer Metastasis Rev 31(3–4):673–687
De Craene B, Berx G (2013) Regulatory networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat Rev Cancer 13(2):97–110
Espinoza I, Miele L (2013) Deadly crosstalk: Notch signaling at the intersection of EMT and cancer stem cells. Cancer Lett 341(1):41–45
Morrison CD, Parvani JG, Schiemann WP (2013) The relevance of the TGF-β Paradox to EMT-MET programs. Cancer Lett 341(1):30–40
Tam WL, Weinberg RA (2013) The epigenetics of epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in cancer. Nat Med 19(11):1438–1449
Li M, Liu GH, Izpisua Belmonte JC (2013) Navigating the epigenetic landscape of pluripotent stem cells. Nat Med 19(11):1438–1449
Liu B, Sun L, Song E (2013) Non-coding RNAs regulate tumor cell plasticity. Sci China Life Sci 56(10):886–890
D’Amato NC, Howe EN, Richer JK (2013) MicroRNA regulation of epithelial plasticity in cancer. Cancer Lett 341(1):46–55
Ying L, Chen Q, Wang Y, Zhou Z, Huang Y, Qiu F (2012) Upregulated MALAT-1 contributes to bladder cancer cell migration by inducing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Mol Biosyst 8(9):2289–2294
Gupta PB, Fillmore CM, Jiang G, Shapira SD, Tao K, Kuperwasser C, Lander ES (2011) Stochastic state transitions give rise to phenotypic equilibrium in populations of cancer cells. Cell 146(4):633–644
Sell S (2004) Stem cell origin of cancer and differentiation therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 51(1):1–28
Magee JA, Piskounova E, Morrison SJ (2012) Cancer stem cells: impact, heterogeneity, and uncertainty. Cancer Cell 21(3):283–296
Chang JT, Mani SA (2013) Sheep, wolf, or werewolf: cancer stem cells and the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett 341(1):16–23
May CD, Sphyris N, Evans KW, Werden SJ, Guo W, Mani SA (2011) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells: a dangerously dynamic duo in breast cancer progression. Breast Cancer Res 13(1):202
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, Campbell LL, Polyak K, Brisken C, Yang J, Weinberg RA (2008) The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 133(4):704–715
Yasuda H, Soejima K, Watanabe H, Kawada I, Nakachi I, Yoda S, Nakayama S, Satomi R, Ikemura S, Terai H, Sato T, Suzuki S, Matsuzaki Y, Naoki K, Ishizaka A (2010) Distinct epigenetic regulation of tumor suppressor genes in putative cancer stem cells of solid tumors. Int J Oncol 37(6):1537–1546
Reya T, Clevers H (2005) Wnt signalling in stem cells and cancer. Nature 434(7035):843–850
Vermeulen L, De Sousa E, Melo F, van der Heijden M, Cameron K, de Jong JH, Borovski T, Tuynman JB, Todaro M, Merz C, Rodermond H, Sprick MR, Kemper K, Richel DJ, Stassi G, Medema JP (2010) Wnt activity defines colon cancer stem cells and is regulated by the microenvironment. Nat Cell Biol 12(5):468–476
Vincent A, Van Seuningen I (2012) On the epigenetic origin of cancer stem cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1826(1):83–88
Tagliavacca L, Caretti A, Bianciardi P, Samaja M (2012) In vivo up-regulation of the unfolded protein response after hypoxia. Biochim Biophys Acta 1820(7):900–906
Chakrabarti A, Chen AW, Varner JD (2011) A review of the mammalian unfolded protein response. Biotechnol Bioeng 108(12):2777–2793
Vandewynckel YP, Laukens D, Geerts A, Bogaerts E, Paridaens A, Verhelst X, Janssens S, Heindryckx F, Van Vlierberghe H (2013) The paradox of the unfolded protein response in cancer. Anticancer Res 33(11):4683–4694
Bauer DE, Harris MH, Plas DR, Lum JJ, Hammerman PS, Rathmell JC, Riley JL, Thompson CB (2004) Cytokine stimulation of aerobic glycolysis in hematopoietic cells exceeds proliferative demand. FASEB J 18:1303–1305
DeBerardinis RJ, Lum JJ, Hatzivassiliou G, Thompson CB (2008) The biology of cancer: metabolic reprogramming fuels cell growth and proliferation. Cell Metab 7(1):11–20
Ward PS, Thompson CB (2012) Metabolic reprogramming: a cancer hallmark even warburg did not anticipate. Cancer Cell 21(3):297–308
Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Curry JM, Ko YH, Lin Z, Tuluc M, Cognetti D, Birbe RC, Pribitkin E, Bombonati A, Pestell RG, Howell A, Sotgia F, Lisanti MP (2013) Oncogenes and inflammation rewire host energy metabolism in the tumor microenvironment: RAS and NFκB target stromal MCT4. Cell Cycle 12(16):2580–2597
Liu W, Beck BH, Vaidya KS, Nash KT, Feeley KP, Ballinger SW, Pounds KM, Denning WL, Diers AR, Landar A, Dhar A, Iwakuma T, Welch DR (2014) Metastasis suppressor KISS1 seems to reverse the Warburg effect by enhancing mitochondrial biogenesis. Cancer Res 74(3):954–963
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144(5):646–674
Mazurek S (2011) Pyruvate kinase type M2: a key regulator of the metabolic budget system in tumor cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 43(7):969–980
Possemato R, Marks KM, Shaul YD, Pacold ME, Kim D, Birsoy K, Sethumadhavan S, Woo HK, Jang HG, Jha AK, Chen WW, Barrett FG, Stransky N, Tsun ZY, Cowley GS, Barretina J, Kalaany NY, Hsu PP, Ottina K, Chan AM, Yuan B, Garraway LA, Root DE, Mino-Kenudson M, Brachtel EF, Driggers EM, Sabatini DM (2011) Functional genomics reveal that the serine synthesis pathway is essential in breast cancer. Nature 476(7360):346–350
Gross S, Cairns RA, Minden MD, Driggers EM, Bittinger MA, Jang HG, Sasaki M, Jin S, Schenkein DP, Su SM, Dang L, Fantin VR, Mak TW (2010) Cancer-associated metabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate accumulates in acute myelogenous leukemia with isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 and 2 mutations. J Exp Med 207(2):339–344
Figueroa ME, Abdel-Wahab O, Lu C, Ward PS, Patel J, Shih A, Li Y, Bhagwat N, Vasanthakumar A, Fernandez HF, Tallman MS, Sun Z, Wolniak K, Peeters JK, Liu W, Choe SE, Fantin VR, Paietta E, Löwenberg B, Licht JD, Godley LA, Delwel R, Valk PJ, Thompson CB, Levine RL, Melnick A (2010) Leukemic IDH1 and IDH2 mutations result in a hypermethylation phenotype, disrupt TET2 function, and impair hematopoietic differentiation. Cancer Cell 18(6):553–567
Tsuchihara K, Fujii S, Esumi H (2009) Autophagy and cancer: dynamism of the metabolism of tumor cells and tissues. Cancer Lett 278(2):130–138
Rosenfeldt MT, Ryan KM (2009) The role of autophagy in tumour development and cancer therapy. Expert Rev Mol Med 11:e36
Xu Y, Xia X, Pan H (2013) Active autophagy in the tumor microenvironment: a novel mechanism for cancer metastasis. Oncol Lett 5(2):411–416
Rouschop KM, Wouters BG (2009) Regulation of autophagy through multiple independent hypoxic signaling pathways. Curr Mol Med 9(4):417–424
Parolini I, Federici C, Raggi C, Lugini L, Palleschi S, De Milito A, Coscia C, Iessi E, Logozzi M, Molinari A, Colone M, Tatti M, Sargiacomo M, Fais S (2009) Microenvironmental pH is a key factor for exosome traffic in tumor cells. J Biol Chem 284(49):34211–34222
Kucharzewska P, Belting M (2013) Emerging roles of extracellular vesicles in the adaptive response of tumour cells to microenvironmental stress. J Extracell Vesicles 2
Van Doormaal FF, Kleinjan A, Di Nisio M, Büller HR, Nieuwland R (2009) Cell-derived microvesicles and cancer. Neth J Med 67(7):266–273
Grange C, Tapparo M, Collino F, Vitillo L, Damasco C, Deregibus MC, Tetta C, Bussolati B, Camussi G (2011) Microvesicles released from human renal cancer stem cells stimulate angiogenesis and formation of lung premetastatic niche. Cancer Res 71(15):5346–5356
Abd Elmageed ZY, Yang Y, Thomas R, Ranjan M, Mondal D, Moroz K, Fang Z, Rezk BM, Moparty K, Sikka SC, Sartor O, Abdel-Mageed AB (2014) Neoplastic reprogramming of patient-derived adipose stem cells by prostate cancer cell-associated exosomes. Stem Cells 32(4):983–997
Cho JA, Park H, Lim EH, Kim KH, Choi JS, Lee JH, Shin JW, Lee KW (2011) Exosomes from ovarian cancer cells induce adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells to acquire the physical and functional characteristics of tumor-supporting myofibroblasts. Gynecol Oncol 123(2):379–386
Gross JC, Chaudhary V, Bartscherer K, Boutros M (2012) Active Wnt proteins are secreted on exosomes. Nat Cell Biol 14(10):1036–1045
Friedl P, Weigelin B (2008) Interstitial leukocyte migration and immune function. Nat Immunol 9(9):960–969
Friedl P, Maaser K, Klein CE, Niggemann B, Krohne G, Zänker KS (1997) Migration of highly aggressive MV3 melanoma cells in 3-dimensional collagen lattices results in local matrix reorganization and shedding of alpha2 and beta1 integrins and CD44. Cancer Res 57(10):2061–2070
Friedl P, Wolf K (2009) Proteolytic interstitial cell migration: a five-step process. Cancer Metastasis Rev 28(1–2):129–135
Sanz-Moreno V, Marshall CJ (2010) The plasticity of cytoskeletal dynamics underlying neoplastic cell migration. Curr Opin Cell Biol 22(5):690–696
Lorentzen A, Bamber J, Sadok A, Elson-Schwab I, Marshall CJ (2011) An ezrin-rich, rigid uropod-like structure directs movement of amoeboid blebbing cells. J Cell Sci 124(Pt 8):1256–1267
Beaty BT, Condeelis J (2014) Digging a little deeper: The stages of invadopodium formation and maturation. Eur J Cell Biol
Saykali BA, El-Sibai M (2014) Invadopodia, regulation, and assembly in cancer cell invasion. Cell Commun Adhes 21(4):207–212
McNiven MA (2013) Breaking away: matrix remodeling from the leading edge. Trends Cell Biol 23(1):16–21
Assaker G, Ramel D, Wculek SK, González-Gaitán M, Emery G (2010) Spatial restriction of receptor tyrosine kinase activity through a polarized endocytic cycle controls border cell migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(52):22558–22563
Ramel D, Wang X, Laflamme C, Montell DJ, Emery G (2013) Rab11 regulates cell-cell communication during collective cell movements. Nat Cell Biol 15(3):317–324
Laflamme C, Assaker G, Ramel D, Dorn JF, She D, Maddox PS, Emery G (2012) Evi5 promotes collective cell migration through its Rab-GAP activity. J Cell Biol 198(1):57–67
Kim KJ, Godarova A, Seedle K, Kim MH, Ince TA, Wells SI, Driscoll JJ, Godar S (2013) Rb suppresses collective invasion, circulation and metastasis of breast cancer cells in CD44-dependent manner. PLoS ONE 8(12):e80590
Bussolino F, Mantovani A, Persico G (1997) Molecular mechanisms of blood vessel formation. Trends Biochem Sci 22:251–256
Hillen F, Griffioen AW (2007) Tumour vascularization: sprouting angiogenesis and beyond. Cancer Metastasis Rev 26(3–4):489–502
Maniotis AJ, Folberg R, Hess A, Seftor EA, Gardner LM, Pe’er J, Trent JM, Meltzer PS, Hendrix MJ (1999) Vascular channel formation by human melanoma cells in vivo and in vitro: vasculogenic mimicry. Am J Pathol 155(3):739–752
Hendrix MJ, Seftor EA, Meltzer PS, Gardner LM, Hess AR, Kirschmann DA, Schatteman GC, Seftor RE (2001) Expression and functional significance of VE-cadherin in aggressive human melanoma cells: role in vasculogenic mimicry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(14):8018–8023
Folberg R, Hendrix MJ, Maniotis AJ (2000) Vasculogenic mimicry and tumor angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 156(2):361–381
Van der Schaft DW, Hillen F, Pauwels P, Kirschmann DA, Castermans K, Egbrink MG, Tran MG, Sciot R, Hauben E, Hogendoorn PC, Delattre O, Maxwell PH, Hendrix MJ, Griffioen AW (2005) Tumor cell plasticity in Ewing sarcoma, an alternative circulatory system stimulated by hypoxia. Cancer Res 65(24):11520–11528
Shirakawa K, Furuhata S, Watanabe I, Hayase H, Shimizu A, Ikarashi Y, Yoshida T, Terada M, Hashimoto D, Wakasugi H (2002) Induction of vasculogenesis in breast cancer models. Br J Cancer 87(12):1454–1461
Ponti D, Costa A, Zaffaroni N, Pratesi G, Petrangolini G, Coradini D, Pilotti S, Pierotti MA, Daidone MG (2005) Isolation and in vitro propagation of tumorigenic breast cancer cells with stem progenitor cell properties. Cancer Res 65(13):5506–5511
Su M, Feng YJ, Yao LQ, Cheng MJ, Xu CJ, Huang Y, Zhao YQ, Jiang H (2008) Plasticity of ovarian cancer cell SKOV3ip and vasculogenic mimicry in vivo. Int J Gynecol Cancer 18(3):476–486
Wang W, Lin P, Han C, Cai W, Zhao X, Sun B (2010) Vasculogenic mimicry contributes to lymph node metastasis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 29:60
Lin P, Wang W, Sun BC, Cai WJ, Li L, Lu HH, Han CR, Zhang JM (2012) Vasculogenic mimicry is a key prognostic factor for laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma: a new pattern of blood supply. Chin Med J (Engl) 125(19):3445–3449
Upile T, Jerjes W, Radhi H, Al-Khawalde M, Kafas P, Nouraei S, Sudhoff H (2011) Vascular mimicry in cultured head and neck tumour cell lines. Head Neck Oncol 3:55
El Hallani S, Boisselier B, Peglion F, Rousseau A, Colin C, Idbaih A, Marie Y, Mokhtari K, Thomas JL, Eichmann A, Delattre JY, Maniotis AJ, Sanson M (2010) A new alternative mechanism in glioblastoma vascularization: tubular vasculogenic mimicry. Brain 133(Pt 4):973–982
Francescone R, Scully S, Bentley B, Yan W, Taylor SL, Oh D, Moral L, Shao R (2012) Glioblastoma-derived tumor cells induce vasculogenic mimicry through Flk-1 protein activation. J Biol Chem 287(29):24821–24831
Liu Z, Li Y, Zhao W, Ma Y, Yang X (2011) Demonstration of vasculogenic mimicry in astrocytomas and effects of Endostar on U251 cells. Pathol Res Pract 207(10):645–651
Kieda C (2013) Heterogeneity of endothelial cells–role in vessel specialization and cooperation in vasculogenic mimicry. Postepy Biochem 59(4):372–378
Yao XH, Ping YF, Bian XW (2011) Contribution of cancer stem cells to tumor vasculogenic mimicry. Protein Cell 2(4):266–272
Pezzolo A, Parodi F, Corrias MV, Cinti R, Gambini C, Pistoia V (2007) Tumor origin of endothelial cells in human neuroblastoma. J Clin Oncol 25(4):376–383
Shen G, Shen F, Shi Z, Liu W, Hu W, Zheng X, Wen L, Yang X (2008) Identification of cancer stem-like cells in the C6 glioma cell line and the limitation of current identification methods. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 44(7):280–289
Bjerkvig R, Tysnes BB, Aboody KS, Najbauer J, Terzis AJ (2005) Opinion: the origin of the cancer stem cell: current controversies and new insights. Nat Rev Cancer 5(11):899–904
Fan YL, Zheng M, Tang YL, Liang XH (2013) A new perspective of vasculogenic mimicry: EMT and cancer stem cells. Oncol Lett 6(5):1174–1180
Weiss L (2000) Metastasis of cancer: a conceptual history from antiquity to the 1990s. Cancer Metastasis Rev 19(3–4):193–383
Roussos ET, Balsamo M, Alford SK, Wyckoff JB, Gligorijevic B, Wang Y, Pozzuto M, Stobezki R, Goswami S, Segall JE, Lauffenburger DA, Bresnick AR, Gertler FB, Condeelis JS (2011) Mena invasive (MenaINV) promotes multicellular streaming motility and transendothelial migration in a mouse model of breast cancer. J Cell Sci 124:2120–2131
Reymond N, Im JH, Garg R, Vega FM, Borda d’Agua B, Riou P, Cox S, Valderrama F, Muschel RJ, Ridley AJ (2012) Cdc42 promotes transendothelial migration of cancer cells through β1 integrin. J Cell Biol 199(4):653–668
Fröhlich C, Klitgaard M, Noer JB, Kotzsch A, Nehammer C, Kronqvist P, Berthelsen J, Blobel C, Kveiborg M, Albrechtsen R, Wewer UM (2013) ADAM12 is expressed in the tumour vasculature and mediates ectodomain shedding of several membrane-anchored endothelial proteins. Biochem J 452(1):97–109
Anderberg C, Cunha SI, Zhai Z, Cortez E, Pardali E, Johnson JR, Franco M, Páez-Ribes M, Cordiner R, Fuxe J, Johansson BR, Goumans MJ, Casanovas O, ten Dijke P, Arthur HM, Pietras K (2013) Deficiency for endoglin in tumor vasculature weakens the endothelial barrier to metastatic dissemination. J Exp Med 210(3):563–579
Lu P, Takai K, Weaver VM, Werb Z (2011) Extracellular matrix degradation and remodeling in development and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3
Levental KR, Yu H, Kass L, Lakins JN, Egeblad M, Erler JT, Fong SF, Csiszar K, Giaccia A, Weninger W, Yamauchi M, Gasser DL, Weaver VM (2009) Matrix crosslinking forces tumor progression by enhancing integrin signaling. Cell 139(5):891–906
De Bock K, Cauwenberghs S, Carmeliet P (2011) Vessel abnormalization: another hallmark of cancer? Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Curr Opin Genet Dev 21:73–79
Condon MS (2005) The role of the stromal microenvironment in prostate cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 15(2):132–137
Miura M, Numaguchi Y, Ishii M, Kubota R, Takeuchi T, Imamura A, Murakami R, Kondo T, Okumura K, Murohara T (2009) Differentiation capacity of endothelial progenitor cells correlates with endothelial function in healthy young men. Circ J 73(7):1324–1329
Rattigan YI, Patel BB, Ackerstaff E, Sukenick G, Koutcher JA, Glod JW, Banerjee D (2012) Lactate is a mediator of metabolic cooperation between stromal carcinoma associated fibroblasts and glycolytic tumor cells in the tumor microenvironment. Exp Cell Res 318:326–335
Shields JD, Kourtis IC, Tomei AA, Roberts JM, Swartz MA (2010) Induction of lymphoid like stroma and immune escape by tumors that express the chemokine CCL21. Science 328(5979):749–752
Räsänen K, Vaheri A (2010) TGF-beta1 causes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in HaCaT derivatives, but induces expression of COX-2 and migration only in benign, not in malignant keratinocytes. J Dermatol Sci 58(2):97–104
Ksiazkiewicz M, Gottfried E, Kreutz M, Mack M, Hofstaedter F, Kunz-Schughart LA (2010) Importance of CCL2-CCR2A 2B signaling for monocyte migration into spheroids of breast cancer-derived fibroblasts. Immunobiology 215(9–10):737–747
Han EC, Lee J, Ryu SW, Choi C (2014) Tumor-conditioned Gr-1(+)CD11b(+) myeloid cells induce angiogenesis through the synergistic action of CCL2 and CXCL16 in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 443(4):1218–1225
Smith C (2013) Cancer shows strength through diversity. Nature 499:505–508
Shree T, Olson OC, Elie BT, Kester JC, Garfall AL, Simpson K, Bell-McGuinn KM, Zabor EC, Brogi E, Joyce JA (2011) Macrophages and cathepsin proteases blunt chemotherapeutic response in breast cancer. Genes Dev 25:2465–2479
Chen Q, Zhang XH, Massague J (2011) Macrophage binding to receptor VCAM-1 transmits survival signals in breast cancer cells that invade the lungs. Cancer Cell 20:538–549
Klein CA (2009) Parallel progression of primary tumours and metastases. Nat Rev Cancer 9:302–312
Ruffell B, DeNardo DG, Affara NI, Coussens LM (2010) Lymphocytes in cancer development: polarization towards pro-tumor immunity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 21:3–10
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2011) Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature 47:298–307
Semenza GL (2013) Cancer-stromal cell interactions mediated by hypoxia-inducible factors promote angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, and metastasis. Oncogene 32:4057–4063
Chaffer CL, Weinberg RA (2011) A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science 331:1559–1564
Ashworth TR (1869) A case of cancer in which cells similar to those in the tumours were seen in the blood after death. Australian Med J 14:146–147
Ryall C (1908) The technique of cancer operations, with reference to the danger of cancer infection. BMJ 2:1005–1008
Christopherson W (1965) Cancer cells in the peripheral blood: a second look. Acta Cytol 9:169–174
Jansa P (1971) Tumor cells in peripheral blood. Crit Rev Vnitr Lek 17(8):803–811
Romsdahl MM, Valaitis J, McGrath RG, McGrew EA (1965) Circulating tumor cells in patients with carcinoma. Method and recent studies. JAMA 193(13):1087–1090
Cardozo PL (1970) Tumor cells in peripheral blood. Med Klin 65(48):2095–2096
Paterlini-Brechot P, Benali NL (2007) Circulating tumor cells (CTC) detection: clinical impact and future directions. Cancer Lett 253(2):180–204
Kim MY, Oskarsson T, Acharyya S, Nguyen DX, Zhang XH, Norton L, Massagué J (2009) Tumor self-seeding by circulating cancer cells. Cell 139(7):1315–1326
Ross JS, Slodkowska EA (2009) Circulating and disseminated tumor cells in the management of breast cancer. Am J Clin Pathol 132(2):237–245
Braun S, Vogl FD, Naume B, Janni W, Osborne MP, Coombes RC, Schlimok G, Diel IJ, Gerber B, Gebauer G, Pierga JY, Marth C, Oruzio D, Wiedswang G, Solomayer EF, Kundt G, Strobl B, Fehm T, Wong GY, Bliss J, Vincent-Salomon A, Pantel K (2005) A pooled analysis of bone marrow micrometastasis in breast cancer. N Engl J Med 353(8):793–802
Lang JM, Casavant BP, Beebe DJ (2012) Circulating tumor cells: getting more from less. Sci Transl Med 4(141):141ps13
Danila DC, Fleisher M, Scher HI (2011) Circulating tumor cells as biomarkers in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 17(12):3903–3912
Balic M, Lin H, Young L, Hawes D, Giuliano A, McNamara G, Datar RH, Cote RJ (2006) Most early disseminated cancer cells detected in bone marrow of breast cancer patients have a putative breast cancer stem cell phenotype. Clin Cancer Res 12(19):5615–5621
Liu R, Wang X, Chen GY, Dalerba P, Gurney A, Hoey T, Sherlock G, Lewicki J, Shedden K, Clarke MF (2007) The prognostic role of a gene signature from tumorigenic breast-cancer cells. N Engl J Med 356(3):217–226
Nagrath S, Sequist LV, Maheswaran S, Bell DW, Irimia D, Ulkus L, Smith MR, Kwak EL, Digumarthy S, Muzikansky A, Ryan P, Balis UJ, Tompkins RG, Haber DA, Toner M (2007) Isolation of rare circulating tumour cells in cancer patients by microchip technology. Nature 450(7173):1235–1239
Labelle M, Begum S, Hynes RO (2011) Direct signaling between platelets and cancer cells induces an epithelial-mesenchymal-like transition and promotes metastasis. Cancer Cell 20(5):576–590
Hermann PC, Huber SL, Herrler T, Aicher A, Ellwart JW, Guba M, Bruns CJ, Heeschen C (2007) Distinct populations of cancer stem cells determine tumor growth and metastatic activity in human pancreatic cancer. Cell Stem Cell 1(3):313–323
Zhang SS, Han ZP, Jing YY, Tao SF, Li TJ, Wang H, Wang Y, Li R, Yang Y, Zhao X, Xu XD, Yu ED, Rui YC, Liu HJ, Zhang L, Wei LX (2012) CD133(+)CXCR4(+) colon cancer cells exhibit metastatic potential and predict poor prognosis of patients. BMC Med 10:85
Hofman VJ, Ilie MI, Bonnetaud C, Selva E, Long E, Molina T, Vignaud JM, Fléjou JF, Lantuejoul S, Piaton E, Butori C, Mourad N, Poudenx M, Bahadoran P, Sibon S, Guevara N, Santini J, Vénissac N, Mouroux J, Vielh P, Hofman PM (2011) Cytopathologic detection of circulating tumor cells using the isolation by size of epithelial tumor cell method: promises and pitfalls. Am J Clin Pathol 135(1):146–156
Hofman V, Bonnetaud C, Ilie MI, Vielh P, Vignaud JM, Fléjou JF, Lantuejoul S, Piaton E, Mourad N, Butori C, Selva E, Poudenx M, Sibon S, Kelhef S, Vénissac N, Jais JP, Mouroux J, Molina TJ, Hofman P (2011) Preoperative circulating tumor cell detection using the isolation by size of epithelial tumor cell method for patients with lung cancer is a new prognostic biomarker. Clin Cancer Res 17(4):827–835
Zong C, Lu S, Chapman AR, Xie XS (2012) Genome-wide detection of single-nucleotide and copy-number variations of a single human cell. Science 338(6114):1622–1626
Heitzer E, Auer M, Gasch C, Pichler M, Ulz P, Hoffmann EM, Lax S, Waldispuehl-Geigl J, Mauermann O, Lackner C, Höfler G, Eisner F, Sill H, Samonigg H, Pantel K, Riethdorf S, Bauernhofer T, Geigl JB, Speicher MR (2013) Complex tumor genomes inferred from single circulating tumor cells by array-CGH and next-generation sequencing. Cancer Res 73(10):2965–2975
Wirtz D, Konstantopoulos K, Searson PC (2011) The physics of cancer: the role of physical interactions and mechanical forces in metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 11(7):512–522
Phillipson M, Kubes P (2011) The neutrophil in vascular inflammation. Nat Med 17(11):1381–1390
Teramukai S, Kitano T, Kishida Y, Kawahara M, Kubota K, Komuta K, Minato K, Mio T, Fujita Y, Yonei T, Nakano K, Tsuboi M, Shibata K, Furuse K, Fukushima M (2009) Pretreatment neutrophil count as an independent prognostic factor in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: an analysis of Japan Multinational Trial Organisation LC00-03. Eur J Cancer 45(11):1950–1958
Lee YY, Choi CH, Kim HJ, Kim TJ, Lee JW, Lee JH, Bae DS, Kim BG (2012) Pretreatment neutrophil: lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor in cervical carcinoma. Anticancer Res 32(4):1555–1561
Gondo T, Nakashima J, Ohno Y, Choichiro O, Horiguchi Y, Namiki K, Yoshioka K, Ohori M, Hatano T, Tachibana M (2012) Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and establishment of novel preoperative risk stratification model in bladder cancer patients treated with radical cystectomy. Urology 79(5):1085–1091
McDonald B, Spicer J, Giannais B, Fallavollita L, Brodt P, Ferri LE (2009) Systemic inflammation increases cancer cell adhesion to hepatic sinusoids by neutrophil mediated mechanisms. Int J Cancer 125(6):1298–1305
Spicer JD, McDonald B, Cools-Lartigue JJ, Chow SC, Giannias B, Kubes P, Ferri LE (2012) Cancer Neutrophils promote liver metastasis via Mac-1-mediated interactions with circulating tumor cells. Cancer Res 72(16):3919–3927
Auguste P, Fallavollita L, Wang N, Burnier J, Bikfalvi A, Brodt P (2007) The host inflammatory response promotes liver metastasis by increasing tumor cell arrest and extravasation. Am J Pathol 170(5):1781–1792
Huh SJ, Liang S, Sharma A, Dong C, Robertson GP (2010) Transiently entrapped circulating tumor cells interact with neutrophils to facilitate lung metastasis development. Cancer Res 70(14):6071–6082
Slattery MJ, Dong C (2003) Neutrophils influence melanoma adhesion and migration under flow conditions. Int J Cancer 106(5):713–722
Liang S et al (2008) Two-dimensional kinetics of beta 2-integrin and ICAM-1 bindings between neutrophils and melanoma cells in a shear flow. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 294(3):C743–C753
Liang S, Hoskins M, Khanna P, Kunz RF, Dong C (2008) Effects of the tumor-leukocyte microenvironment on melanoma-neutrophil adhesion to the endothelium in a shear flow. Cell Mol Bioeng 1(2–3):189–200
De Larco JE, Wuertz BR, Furcht LT (2004) The potential role of neutrophils in promoting the metastatic phenotype of tumors releasing interleukin-8. Clin Cancer Res 10(15):4895–4900
Houghton AM et al (2010) Neutrophil elastase-mediated degradation of IRS-1 accelerates lung tumor growth. Nat Med 16(2):219–223
Chen HC et al (2004) Neutrophil elastase induces IL-8 synthesis by lung epithelial cells via the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Biomed Sci 11(1):49–58
Brinkmann V et al (2004) Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 303(5663):1532–1535
Fuchs TA et al (2007) Novel cell death program leads to neutrophil extracellular traps. J Cell Biol 176(2):231–241
Pilsczek FH et al (2010) A novel mechanism of rapid nuclear neutrophil extracellular trap formation in response to Staphylococcus aureus. J Immunol 185(12):7413–7425
Metzler KD et al (2011) Myeloperoxidase is required for neutrophil extracellular trap formation: implications for innate immunity. Blood 117(3):953–959
Cools-Lartigue J, Spicer J, McDonald B, Gowing S, Chow S, Giannias B, Bourdeau F, Kubes P, Ferri L (2013) Neutrophil extracellular traps sequester circulating tumor cells and promote metastasis. J Clin Invest
Lian L, Li W, Li ZY, Mao YX, Zhang YT, Zhao YM, Chen K, Duan WM, Tao M (2013) Inhibition of MCF-7 breast cancer cell-induced platelet aggregation using a combination of antiplatelet drugs. Oncol Lett 5(2):675–680
Egan K, Crowley D, Smyth P, O’Toole S, Spillane C, Martin C, Gallagher M, Canney A, Norris L, Conlon N, McEvoy L, Ffrench B, Stordal B, Keegan H, Finn S, McEneaney V, Laios A, Ducrée J, Dunne E, Smith L, Berndt M, Sheils O, Kenny D, O’Leary J (2011) Platelet adhesion and degranulation induce pro-survival and pro-angiogenic signalling in ovarian cancer cells. PLoS ONE 6(10):e26125
Finn SP, CD Spillane CD, Conlon N, Cooke N, O’Toole SA, Martin CM, Smyth PC, Sheils OM, O’Leary JJ (2012) The relationship between Circulating Tumour Cells (CTCs), platelets and Epithelial-Mesenchymal-Transition (EMT). 19th Annual PCF scientific retreat – October 25-27, Abstract
Balic M, Williams A, Lin H, Datar R, Cote RJ (2013) Circulating tumor cells: from bench to bedside. Annu Rev Med 64:31–44
Wang H, Fu W, Im JH, Zhou Z, Santoro SA, Iyer V, DiPersio CM, Yu QC, Quaranta V, Al-Mehdi A, Muschel RJ (2004) Tumor cell alpha3beta1 integrin and vascular laminin-5 mediate pulmonary arrest and metastasis. J Cell Biol 164(6):935–941
Bacac M, Stamenkovic I (2008) Metastatic cancer cell. Annu Rev Pathol 3:221–247
Al-Mehdi AB, Tozawa K, Fisher AB, Shientag L, Lee A, Muschel RJ (2000) Intravascular origin of metastasis from the proliferation of endothelium-attached tumor cells: a new model for metastasis. Nat Med 6(1):100–102
Weis SM, Cheresh DA (2005) Pathophysiological consequences of VEGF-induced vascular permeability. Nature 437(7058):497–504
Schumacher D, Strilic B, Sivaraj KK, Wettschureck N, Offermanns S (2013) Platelet-derived nucleotides promote tumor-cell transendothelial migration and metastasis via P2Y2 receptor. Cancer Cell 24(1):130–137
Lukanidin E, Sleeman JP (2012) Building the niche: the role of the S100 proteins in metastatic growth. Semin Cancer Biol 22:216–225
Psaila B, Lyden D (2009) The metastatic niche: adapting the foreign soil. Nat Rev Cancer 9:285–293
Sceneay J, Smyth MJ, Möller A (2013) The pre-metastatic niche: finding common ground. Cancer Metastasis Rev 32:449–464
Fazilaty H, Gardaneh M, Bahrami T, Salmaninejad A, Behnam B (2013) Crosstalk between breast cancer stem cells and metastatic niche: emerging molecular metastasis pathway? Tumour Biol 34:2019–2030
Kaplan RN, Riba RD, Zacharoulis S, Bramley AH, Vincent L, Costa C, MacDonald DD, Jin DK, Shido K, Kerns SA, Zhu Z, Hicklin D, Wu Y, Port JL, Altorki N, Port ER, Ruggero D, Shmelkov SV, Jensen KK, Rafii S, Lyden D (2005) VEGFR1-positive haematopoietic bone marrow progenitors initiate the pre-metastatic niche. Nature 438:820–827
Wong CC, Gilkes DM, Zhang H, Chen J, Wei H, Chaturvedi P, Fraley SI, Wong CM, Khoo US, Ng IO, Wirtz D, Semenza GL (2011) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a master regulator of breast cancer metastatic niche formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:16369–16374
Huang Y, Song N, Ding Y, Yuan S, Li X, Cai H et al (2009) Pulmonary vascular ‘destabilization in the premetastatic phase facilitates lung metastasis. Cancer Res 69:7529–7537
Hiratsuka S et al (2002) MMP9 induction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 is involved in lung-specific metastasis. Cancer Cell 2:289–300
Hiratsuka S, Watanabe A, Aburatani H, Maru Y (2006) Tumour-mediated upregulation of chemoattractants and recruitment of myeloid cells predetermines lung metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 8:1369–1375
Chioda M et al (2011) Myeloid cell diversification and complexity: an old concept with new turns in oncology. Cancer Metastasis Rev 30:27–43
Hynes RO (2011) Metastatic cells will take any help they can get. Cancer Cell 20:689–690
Mishra A, Shiozawa Y, Pienta KJ, Taichman RS (2011) Homing of cancer cells to the bone. Cancer Microenviron 4(3):221–235
Paget S (1889) The distribution of secondary growth in cancer of the breast. Lancet 133(3421):571–573
Fidler IJ (2003) The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: the ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev Cancer 3(6):453–458
Gassmann P, Haier J, Schlüter K, Domikowsky B, Wendel C, Wiesner U, Kubitza R, Engers R, Schneider SW, Homey B, Müller A (2009) CXCR4 regulates the early extravasation of metastatic tumor cells in vivo. Neoplasia 11(7):651–661
Martin MD, Kremers GJ, Short KW, Rocheleau JV, Xu L, Piston DW, Matrisian LM, Gorden DL (2010) Rapid extravasation and establishment of breast cancer micrometastases in the liver microenvironment. Mol Cancer Res 8(10):1319–1327
Favaro E, Amadori A, Indraccolo S (2008) Cellular interactions in the vascular niche: implications in the regulation of tumor dormancy. APMIS 116(7–8):648–659
Koebel CM, Vermi W, Swann JB, Zerafa N, Rodig SJ, Old LJ, Smyth MJ, Schreiber RD (2007) Adaptive immunity maintains occult cancer in an equilibrium state. Nature 450(7171):903–907
Quesnel B, Disis ML, Stanton SE (2013) Can immunity to breast cancer eliminate residual micrometastases? Clin Cancer Res 19(23):6398–6403
Aguirre-Ghiso JA (2007) Models, mechanisms and clinical evidence for cancer dormancy. Nat Rev Cancer 7(11):834–846
Brabletz T (2012) To differentiate or not–routes towards metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 12:425–436
Ocaña OH, Córcoles R, Fabra A, Moreno-Bueno G, Acloque H, Vega S, Barrallo-Gimeno A, Cano A, Nieto MA (2012) Metastatic colonization requires the repression of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition inducer Prrx1. Cancer Cell 22:709–724
Tsai JH, Donaher JL, Murphy DA, Chau S, Yang J (2012) Spatiotemporal regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition is essential for squamous cell carcinoma metastasis. Cancer Cell 22:725–736
Chao YL, Shepard CR, Wells A (2010) Breast carcinoma cells re-express E-cadherin during mesenchymal to epithelial reverting transition. Mol Cancer 9:179
Gunasinghe NP, Wells A, Thompson EW, Hugo HJ (2012) Mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) as a mechanism for metastatic colonisation in breast cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 31:469–478
Bendorait A, Knouf EC, Garg KS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, O’Briant KC, Ventura AP, Godwin AK, Karlan BY, Drescher CW, Urban N, Knudsen BS, Tewari M (2010) Regulation of miR-200 family microRNAs and ZEB transcription factors in ovarian cancer: evidence supporting a mesothelial-to-epithelial transition. Gynecol Oncol 116:117–125
Pinedo HM, Verheul HM, D’Amato RJ, Folkman J (1998) Involvement of platelets in tumour angiogenesis? Lancet 352:1775–1777
Bragado P, Sosa MS, Keely P, Condeelis J, Aguirre-Ghiso JA (2012) Microenvironments dictating tumor cell dormancy. Recent Results Cancer Res 195:25–39
Aguirre-Ghiso JA (2010) On the theory of tumor self-seeding: implications for metastasis progression in humans. Breast Cancer Res 12(2):304
Mocellin S, Nitti D (2013) CTLA-4 blockade and the renaissance of cancer immunotherapy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1836(2):187–196
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grant INCa-DGOS-4654.
Disclosure–Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meseure, D., Drak Alsibai, K. & Nicolas, A. Pivotal Role of Pervasive Neoplastic and Stromal Cells Reprogramming in Circulating Tumor Cells Dissemination and Metastatic Colonization. Cancer Microenvironment 7, 95–115 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12307-014-0158-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12307-014-0158-2