Abstract
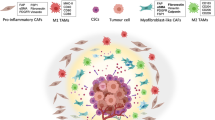
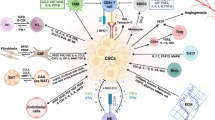
Tumor microenvironment (TME) is important in tumor development and may be a target for anti-cancer therapy. The genesis of TME is a dynamic process that is regulated by intrinsic and extrinsic factors and coordinated by multiple genes, cells, and signal pathways. Cancer anaerobic metabolism and various oncogenes may stimulate the genesis of TME. Tumor cells and cancer stem cells actively participate in the genesis of the cancer stem cell niche and tumor neovascularization, important in the initiation of the TME. Various cancer-associated stromal cells, derived niche factors, and tumor-associated macrophages may function as promoters in the genesis of the TME. Dicer1 gene-deleted stromal cells can induce generation of cancer stem cells and initiate tumorigenesis, suggesting that stromal cells also may promote the genesis of the TME. Therefore, the key features of TME include niche-driving oncogenes, cancer anaerobic metabolism, niche-driving cancer stem cells, neovascularization, tumor-associated inflammatory cells, and cancer-associated stromal cells. These features are potential targets for normalization of the malignant TME and effective anti-cancer therapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen M, Louise Jones J (2011) Jekyll and Hyde: the role of the microenvironment on the progression of cancer. J Pathol 223:162–176. doi:10.1002/path.2803, LID
Weber CE, Kuo PC (2011) The tumor microenvironment. Surg Oncol Sep 29
Borovski T, De Sousa E, Melo F, Vermeulen L, Medema JP (2011) Cancer stem cell niche: the place to be. Cancer Res 71:634–639
Paget S (1989) The distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast. Cancer Metastasis Rev 8:98–101
Bissell MJ, Hall HG, Parry G (1982) How does the extracellular matrix direct gene expression? J Theor Biol 99:31–68
Weinstein IB, Joe A (2008) Oncogene addiction. Cancer Res 68:3077–3080, discussion 3080
Croce CM (2008) Oncogenes and cancer. N Engl J Med 358:502–511
Sotgia F, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Howell A, Pestell RG, Pavlides S,Lisanti MP (2012) Caveolin-1 and Cancer Metabolism in the Tumor Microenvironment: Markers, Models, and Mechanisms. Annu Rev Pathol 7:423–467
Sengupta A, Cancelas JA (2010) Cancer stem cells: a stride towards cancer cure? J Cell Physiol 225:7–14
Cabarcas SM, Mathews LA,Farrar WL (2011) The cancer stem cell niche—there goes the neighborhood? Int J Cancer 129:2315–27 LID, doi:10.1002/ijc.26312
Zhang LZ, Zhang CQ, Yan ZY, Yang QC, Jiang Y,Zeng BF (2011) Tumor-initiating cells and tumor vascularization. Pediatr Blood Cancer 56:335–40 LID—doi:10.1002/pbc.22886
Medema JP, Vermeulen L (2011) Microenvironmental regulation of stem cells in intestinal homeostasis and cancer. Nature 474:318–26 LID—doi:10.1038/nature10212
Zhang WC, Shyh-Chang N, Yang H, Rai A, Umashankar S, Ma S, Soh BS, Sun LL, Tai BC, Nga ME, Bhakoo KK, Jayapal SR, Nichane M, Yu Q, Ahmed DA, Tan C, Sing WP, Tam J, Thirugananam A, Noghabi MS, Huei Pang Y, Ang HS, Robson P, Kaldis P, Soo RA, Swarup S, Lim EH, Lim B (2012) Glycine decarboxylase activity drives non-small cell lung cancer tumor-initiating cells and tumorigenesis. Cell 148:259–272
Zhang G, Shang B, Yang P, Cao Z, Pan Y, Zhou Q (2012) Induced pluripotent stem cell consensus genes: implication for the risk of tumorigenesis and cancers in induced pluripotent stem cell therapy. Stem Cells Dev 21(6):955–964
Sordella R, Bell DW, Haber DA, Settleman J (2004) Gefitinib-sensitizing EGFR mutations in lung cancer activate anti-apoptotic pathways. Science (New York, NY) 305:1163–1167
Aguirre A, Rubio ME, Gallo V (2010) Notch and EGFR pathway interaction regulates neural stem cell number and self-renewal. Nature 467:323–327
Wang SE, Yu Y, Criswell TL, Debusk LM, Lin PC, Zent R, Johnson DH, Ren X, Arteaga CL (2010) Oncogenic mutations regulate tumor microenvironment through induction of growth factors and angiogenic mediators. Oncogene 29:3335–3348
Rand V, Huang J, Stockwell T, Ferriera S, Buzko O, Levy S, Busam D, Li K, Edwards JB, Eberhart C, Murphy KM, Tsiamouri A, Beeson K, Simpson AJ, Venter JC, Riggins GJ, Strausberg RL (2005) Sequence survey of receptor tyrosine kinases reveals mutations in glioblastomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:14344–14349
Xiao S, Nalabolu SR, Aster JC, Ma J, Abruzzo L, Jaffe ES, Stone R, Weissman SM, Hudson TJ, Fletcher JA (1998) FGFR1 is fused with a novel zinc-finger gene, ZNF198, in the t(8;13) leukaemia/lymphoma syndrome. Nat Genet 18:84–87
Popovici C, Adelaide J, Ollendorff V, Chaffanet M, Guasch G, Jacrot M, Leroux D, Birnbaum D, Pebusque MJ (1998) Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 is fused to FIM in stem-cell myeloproliferative disorder with t(8;13). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:5712–5717
Hirota S, Isozaki K, Moriyama Y, Hashimoto K, Nishida T, Ishiguro S, Kawano K, Hanada M, Kurata A, Takeda M, Muhammad Tunio G, Matsuzawa Y, Kanakura Y, Shinomura Y, Kitamura Y (1998) Gain-of-function mutations of c-kit in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science (New York, NY) 279:577–580
Chi P, Chen Y, Zhang L, Guo X, Wongvipat J, Shamu T, Fletcher JA, Dewell S, Maki RG, Zheng D, Antonescu CR, Allis CD, Sawyers CL (2010) ETV1 is a lineage survival factor that cooperates with KIT in gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Nature 467:849–853
Charest A, Lane K, McMahon K, Park J, Preisinger E, Conroy H, Housman D (2003) Fusion of FIG to the receptor tyrosine kinase ROS in a glioblastoma with an interstitial del(6)(q21q21). Genes Chromosomes Cancer 37:58–71
Heisterkamp N, Stephenson JR, Groffen J, Hansen PF, de Klein A, Bartram CR, Grosveld G (1983) Localization of the c-ab1 oncogene adjacent to a translocation break point in chronic myelocytic leukaemia. Nature 306:239–242
Clark SS, McLaughlin J, Crist WM, Champlin R, Witte ON (1987) Unique forms of the abl tyrosine kinase distinguish Ph1-positive CML from Ph1-positive ALL. Science (New York, NY) 235:85–88
Graux C, Cools J, Melotte C, Quentmeier H, Ferrando A, Levine R, Vermeesch JR, Stul M, Dutta B, Boeckx N, Bosly A, Heimann P, Uyttebroeck A, Mentens N, Somers R, MacLeod RA, Drexler HG, Look AT, Gilliland DG, Michaux L, Vandenberghe P, Wlodarska I, Marynen P, Hagemeijer A (2004) Fusion of NUP214 to ABL1 on amplified episomes in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat Genet 36:1084–1089
Carpten JD, Faber AL, Horn C, Donoho GP, Briggs SL, Robbins CM, Hostetter G, Boguslawski S, Moses TY, Savage S, Uhlik M, Lin A, Du J, Qian YW, Zeckner DJ, Tucker-Kellogg G, Touchman J, Patel K, Mousses S, Bittner M, Schevitz R, Lai MH, Blanchard KL, Thomas JE (2007) A transforming mutation in the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT1 in cancer. Nature 448:439–444
Cha TL, Zhou BP, Xia W, Wu Y, Yang CC, Chen CT, Ping B, Otte AP, Hung MC (2005) Akt-mediated phosphorylation of EZH2 suppresses methylation of lysine 27 in histone H3. Science (New York, NY) 310:306–310
Nucera C, Lawler J, Parangi S (2011) BRAF(V600E) and microenvironment in thyroid cancer: a functional link to drive cancer progression. Cancer Res 71:2417–2422
Rajagopalan H, Bardelli A, Lengauer C, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Velculescu VE (2002) Tumorigenesis: RAF/RAS oncogenes and mismatch-repair status. Nature 418:934
Naoki K, Chen TH, Richards WG, Sugarbaker DJ, Meyerson M (2002) Missense mutations of the BRAF gene in human lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 62:7001–7003
Santos E, Martin-Zanca D, Reddy EP, Pierotti MA, Della Porta G, Barbacid M (1984) Malignant activation of a K-ras oncogene in lung carcinoma but not in normal tissue of the same patient. Science (New York, NY) 223:661–664
Sears R, Leone G, DeGregori J, Nevins JR (1999) Ras enhances Myc protein stability. Mol Cell 3:169–179
Barbie DA, Tamayo P, Boehm JS, Kim SY, Moody SE, Dunn IF, Schinzel AC, Sandy P, Meylan E, Scholl C, Frohling S, Chan EM, Sos ML, Michel K, Mermel C, Silver SJ, Weir BA, Reiling JH, Sheng Q, Gupta PB, Wadlow RC, Le H, Hoersch S, Wittner BS, Ramaswamy S, Livingston DM, Sabatini DM, Meyerson M, Thomas RK, Lander ES, Mesirov JP, Root DE, Gilliland DG, Jacks T, Hahn WC (2009) Systematic RNA interference reveals that oncogenic KRAS-driven cancers require TBK1. Nature 462:108–112
Alavi A, Hood JD, Frausto R, Stupack DG, Cheresh DA (2003) Role of Raf in vascular protection from distinct apoptotic stimuli. Science (New York, NY) 301:94–96
Muchemwa FC, Jinnin M, Wakasugi S, Sakamoto M, Inoue Y, Ishihara T, Ihn H (2010) A novel COL1A1 exon 14/PDGFB fusion gene in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Eur J Dermatol 20:390–391
Bhatia K, Huppi K, Spangler G, Siwarski D, Iyer R, Magrath I (1993) Point mutations in the c-Myc transactivation domain are common in Burkitt’s lymphoma and mouse plasmacytomas. Nat Genet 5:56–61
Morse B, Rotherg PG, South VJ, Spandorfer JM, Astrin SM (1988) Insertional mutagenesis of the myc locus by a LINE-1 sequence in a human breast carcinoma. Nature 333:87–90
Whitfield JR, Soucek L (2012) Tumor microenvironment: becoming sick of Myc. Cell Mol Life Sci 69:931–934
Sodir NM, Swigart LB, Karnezis AN, Hanahan D, Evan GI, Soucek L (2011) Endogenous Myc maintains the tumor microenvironment. Genes Dev 25:907–916
Cassago A, Ferreira AP, Ferreira IM, Fornezari C, Gomes ER, Greene KS, Pereira HM, Garratt RC, Dias SM, Ambrosio AL (2012) Mitochondrial localization and structure-based phosphate activation mechanism of Glutaminase C with implications for cancer metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:1092–1097
Luo YP, Zhou H, Krueger J, Kaplan C, Liao D, Markowitz D, Liu C, Chen T, Chuang TH, Xiang R, Reisfeld RA (2010) The role of proto-oncogene Fra-1 in remodeling the tumor microenvironment in support of breast tumor cell invasion and progression. Oncogene 29:662–673
Bronisz A, Godlewski J, Wallace JA, Merchant AS, Nowicki MO, Mathsyaraja H, Srinivasan R, Trimboli AJ, Martin CK, Li F, Yu L, Fernandez SA, Pecot T, Rosol TJ, Cory S, Hallett M, Park M, Piper MG, Marsh CB, Yee LD, Jimenez RE, Nuovo G, Lawler SE, Chiocca EA, Leone G, Ostrowski MC (2012) Reprogramming of the tumour microenvironment by stromal PTEN-regulated miR-320. Nat Cell Biol 14:159–67 LID—doi:10.1038/ncb2396
Camboni M, Hammond S, Martin LT, Martin PT (2012) Induction of a regenerative microenvironment in skeletal muscle is sufficient to induce embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma in p53-deficient mice. J Pathol 226:40–9 LID—doi:10.1002/path.2996
Kareva I (2011) Prisoner’s dilemma in cancer metabolism. PLoS One 6:e28576
Romero-Garcia S, Lopez-Gonzalez JS, Báez-Ez-Viveros JL, Aguilar-Cazares D, Prado-Garcia H (2011) Tumor cell metabolism: an integral view. Cancer Biol Ther 12:939–948
Dang CV, Le A, Gao P (2009) MYC-induced cancer cell energy metabolism and therapeutic opportunities. Clin Cancer Res 15:6479–6483
Cairns RA, Harris IS, Mak TW (2011) Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer 11:85–95
Levine AJ, Puzio-Kuter AM (2010) The control of the metabolic switch in cancers by oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Science (New York, NY) 330:1340–1344
Dang L, White DW, Gross S, Bennett BD, Bittinger MA, Driggers EM, Fantin VR, Jang HG, Jin S, Keenan MC, Marks KM, Prins RM, Ward PS, Yen KE, Liau LM, Rabinowitz JD, Cantley LC, Thompson CB, Vander Heiden MG, Su SM (2010) Cancer-associated IDH1 mutations produce 2-hydroxyglutarate. Nature 465:966
Clendening JW, Pandyra A, Boutros PC, El Ghamrasni S, Khosravi F, Trentin GA, Martirosyan A, Hakem A, Hakem R, Jurisica I, Penn LZ (2010) Dysregulation of the mevalonate pathway promotes transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:15051–15056
Sun Q, Chen X, Ma J, Peng H, Wang F, Zha X, Wang Y, Jing Y, Yang H, Chen R, Chang L, Zhang Y, Goto J, Onda H, Chen T, Wang MR, Lu Y, You H, Kwiatkowski D, Zhang H (2011) Mammalian target of rapamycin up-regulation of pyruvate kinase isoenzyme type M2 is critical for aerobic glycolysis and tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:4129–4134
Israelsen WJ, Vander Heiden MG (2010) ATP consumption promotes cancer metabolism. Cell 143:669–671
Chun SY, Johnson C, Washburn JG, Cruz-Correa MR, Dang DT, Dang LH (2010) Oncogenic KRAS modulates mitochondrial metabolism in human colon cancer cells by inducing HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha target genes. Mol Cancer 9:293
Goldberg MS, Sharp PA (2012) Pyruvate kinase M2-specific siRNA induces apoptosis and tumor regression. J Exp Med 209:217–224
Chiavarina B, Whitaker-Menezes D, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Witkiewicz AK, Birbe RC, Howell A, Pestell RG, Smith J, Daniel R, Sotgia F, Lisanti MP (2011) Pyruvate kinase expression (PKM1 and PKM2) in cancer-associated fibroblasts drives stromal nutrient production and tumor growth. Cancer Biol Ther 12
Sotgia F, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Pavlides S, Howell A, Pestell RG, Lisanti MP (2011) Understanding the Warburg effect and the prognostic value of stromal caveolin-1 as a marker of a lethal tumor microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res 13:213
Chen SY, Huang YC, Liu SP, Tsai FJ, Shyu WC, Lin SZ (2011) An overview of concepts for cancer stem cells. Cell Transplant 20:113–120
D’Angelo RC, Wicha MS (2010) Stem cells in normal development and cancer. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 95:113–158
Gao JX (2008) Cancer stem cells: the lessons from pre-cancerous stem cells. J Cell Mol Med 12:67–96
Menakuru SR, Brown NJ, Staton CA, Reed MW (2008) Angiogenesis in pre-malignant conditions. Br J Cancer 99:1961–1966
Dieter SM, Ball CR, Hoffmann CM, Nowrouzi A, Herbst F, Zavidij O, Abel U, Arens A, Weichert W, Brand K, Koch M, Weitz J, Schmidt M, von Kalle C, Glimm H (2011) Distinct types of tumor-initiating cells form human colon cancer tumors and metastases. Cell Stem Cell 9:357–65 LID—doi:10.1016/j.stem.2011.08.010
Hong D, Gupta R, Ancliff P, Atzberger A, Brown J, Soneji S, Green J, Colman S, Piacibello W, Buckle V, Tsuzuki S, Greaves M, Enver T (2008) Initiating and cancer-propagating cells in TEL-AML1-associated childhood leukemia. Science (New York, N Y) 319:336–339
Davies EJ, Marsh V, Clarke AR (2011) Origin and maintenance of the intestinal cancer stem cell. Mol Carcinog 50:254–63 LID—doi:10.1002/mc.20631
Floor S, van Staveren WC, Larsimont D, Dumont JE, Maenhaut C (2011) Cancer cells in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and tumor-propagating-cancer stem cells: distinct, overlapping or same populations. Oncogene 30:4609–21 LID—doi:10.1038/onc.2011.184
Tellez CS, Juri DE, Do K, Bernauer AM, Thomas CL, Damiani LA, Tessema M, Leng S, Belinsky SA (2011) EMT and stem cell-like properties associated with miR-205 and miR-200 epigenetic silencing are early manifestations during carcinogen-induced transformation of human lung epithelial cells. Cancer Res 71:3087–3097
Hotz HG, Hotz B, Buhr HJ (2011) Genes associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition: possible therapeutic targets in ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma? Anticancer Agents Med Chem 11:448–454
Said NA, Williams ED (2011) Growth factors in induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. Cells Tissues Organs 193:85–97
Hill RP, Marie-Egyptienne DT, Hedley DW (2009) Cancer stem cells, hypoxia and metastasis. Semin Radiat Oncol 19:106–111
Potente M, Gerhardt H, Carmeliet P (2011) Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis. Cell 146:873–887
Ping YF, Bian XW (2011) Consice review: Contribution of cancer stem cells to neovascularization Stem Cells (Dayton, Ohio) 29:888–94 LID—doi:10.1002/stem.650
Maniotis AJ, Folberg R, Hess A, Seftor EA, Gardner LM, Pe’er J, Trent JM, Meltzer PS, Hendrix MJ (1999) Vascular channel formation by human melanoma cells in vivo and in vitro: vasculogenic mimicry. Am J Pathol 155:739–752
Hendrix MJ, Seftor EA, Hess AR, Seftor RE (2003) Vasculogenic mimicry and tumour-cell plasticity: lessons from melanoma. Nat Rev Cancer 3:411–421
Wang R, Chadalavada K, Wilshire J, Kowalik U, Hovinga KE, Geber A, Fligelman B, Leversha M, Brennan C, Tabar V (2010) Glioblastoma stem-like cells give rise to tumour endothelium. Nature 468:829–833
Ricci-Vitiani L, Pallini R, Biffoni M, Todaro M, Invernici G, Cenci T, Maira G, Parati EA, Stassi G, Larocca LM, De Maria R (2010) Tumour vascularization via endothelial differentiation of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Nature 468:824–828
Hida K, Hida Y, Amin DN, Flint AF, Panigrahy D, Morton CC, Klagsbrun M (2004) Tumor-associated endothelial cells with cytogenetic abnormalities. Cancer Res 64:8249–8255
Coffelt SB, Hughes R, Lewis CE (2009) Tumor-associated macrophages: effectors of angiogenesis and tumor progression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1796:11–18
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2011) Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature 473:298–307
Zhou Q, Cao Z, Shang B, Zhang G, Pan Y, Guo P (2011) The molecular and celluar progress of tumor-cell- mediated angiogenesis and vasculogenesis. Blood 118(21):1405–1406
Zhou Q, Kiosses WB, Liu J, Schimmel P (2008) Tumor endothelial cell tube formation model for determining anti-angiogenic activity of a tRNA synthetase cytokine. Methods (San Diego, Calif) 44:190–195
Zhou Q, Kapoor M, Guo M, Belani R, Xu X, Kiosses WB, Hanan M, Park C, Armour E, Do MH, Nangle LA, Schimmel P, Yang XL (2010) Orthogonal use of a human tRNA synthetase active site to achieve multifunctionality. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17:57–61
Melero-Martin JM, Dudley AC (2011) Concise review: vascular stem cells and tumor angiogenesis. Stem Cells (Dayton, Ohio) 29:163–8 LID—doi:10.1002/stem.583
Zhao Y, Bao Q, Renner A, Camaj P, Eichhorn M, Ischenko I, Angele M, Kleespies A, Jauch KW, Bruns C (2011) Cancer stem cells and angiogenesis. Int J Dev Biol 55:477–482
Charles N, Holland EC (2010) The perivascular niche microenvironment in brain tumor progression. Cell Cycle (Georgetown, Tex) 9:3012–3021
Doan PL, Chute JP (2012) The vascular niche: home for normal and malignant hematopoietic stem cells. Leukemia 26:54–62 LID—doi:10.1038/leu.2011.236
Zhu TS, Costello MA, Talsma CE, Flack CG, Crowley JG, Hamm LL, He X, Hervey-Jumper SL, Heth JA, Muraszko KM, DiMeco F, Vescovi AL, Fan X (2011) Endothelial cells create a stem cell niche in glioblastoma by providing NOTCH ligands that nurture self-renewal of cancer stem-like cells. Cancer Res 71:6061–6072
Siveen KS, Kuttan G (2009) Role of macrophages in tumour progression. Immunol Lett 123:97–102
De Palma M, Naldini L (2009) Tie2-expressing monocytes (TEMs): novel targets and vehicles of anticancer therapy? Biochim Biophys Acta 1796:5–10
Ria R, Piccoli C, Cirulli T, Falzetti F, Mangialardi G, Guidolin D, Tabilio A, Di Renzo N, Guarini A, Ribatti D, Dammacco F, Vacca A (2008) Endothelial differentiation of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells from patients with multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res 14:1678–1685
Scavelli C, Nico B, Cirulli T, Ria R, Di Pietro G, Mangieri D, Bacigalupo A, Mangialardi G, Coluccia AM, Caravita T, Molica S, Ribatti D, Dammacco F, Vacca A (2008) Vasculogenic mimicry by bone marrow macrophages in patients with multiple myeloma. Oncogene 27:663–674
Raaijmakers MH (2011) Niche contributions to oncogenesis: emerging concepts and implications for the hematopoietic system. Haematologica 96:1041–1048
Raaijmakers MH, Mukherjee S, Guo S, Zhang S, Kobayashi T, Schoonmaker JA, Ebert BL, Al-Shahrour F, Hasserjian RP, Scadden EO, Aung Z, Matza M, Merkenschlager M, Lin C, Rommens JM, Scadden DT (2010) Bone progenitor dysfunction induces myelodysplasia and secondary leukaemia. Nature 464:852–857
Bissell MJ, Hines WC (2011) Why don't we get more cancer? A proposed role of the microenvironment in restraining cancer progression. Nat Med 17:320–329
Xu WR, Lin HS, Chen XY, Zhang Y (2011) Yin-yang balance therapy on regulating cancer stem cells. J Tradit Chin Med 31:158–160
Shang B, Cao Z, Zhou Q (2012) Progress in tumor vascular normalization for anticancer therapy: challenges and perspectives. Front Med 6(1):67–78
Ebos JM, Kerbel RS (2011) Antiangiogenic therapy: impact on invasion, disease progression, and metastasis. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 8:210–221
Van Cutsem E, Lambrechts D, Prenen H, Jain RK, Carmeliet P (2011) Lessons from the adjuvant bevacizumab trial on colon cancer: what next? J Clin Oncol 29:1–4
Miles D, Harbeck N, Escudier B, Hurwitz H, Saltz L, Van Cutsem E, Cassidy J, Mueller B, Sirzen F (2011) Disease course patterns after discontinuation of bevacizumab: pooled analysis of randomized phase III trials. J Clin Oncol 29:83–88
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2011) Principles and mechanisms of vessel normalization for cancer and other angiogenic diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10:417–427
Goel S, Duda DG, Xu L, Munn LL, Boucher Y, Fukumura D, Jain RK (2011) Normalization of the vasculature for treatment of cancer and other diseases. Physiol Rev 91:1071–1121
Sato Y (2011) Persistent vascular normalization as an alternative goal of anti-angiogenic cancer therapy. Cancer Sci 102:1253–1256
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 30971138), Chinese Academy of Science Special National Strategic Leader Project (No. XDA01040200), Suzhou City Scientific Research Funds (No. SWG0904, SS201004, and SS201138), and a project funded by the priority academic program development (PAPD) of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shang, B., Zhang, G., Pan, Y. et al. Deciphering the Key Features of Malignant Tumor Microenvironment for Anti-cancer Therapy. Cancer Microenvironment 5, 211–223 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12307-012-0108-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12307-012-0108-9