Abstract
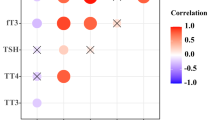
Dependence on alcohol, nicotine and duration of alcohol consumption are known to alter thyroid function tests. This study was conducted to assess the effect of interaction between the duration of alcohol consumption and alcohol dependence on TFT. The subjects consisted of 38 male patients with alcohol dependent syndrome co morbid with nicotine dependent syndrome, 33 male patients with alcohol dependent syndrome and 30 male normal healthy volunteers. Liver function tests, haematological parameters and thyroid function tests were assayed. Two way multivariate ANOVA was used to assess the interaction effect by SPSS 21 package. Multivariate analysis of combined TFT levels revealed no significant (P = .078) difference amongst groups based on alcohol dependence, significant difference (P = .001) amongst groups based on duration of alcohol consumption and no significant (P = .604) interaction effect between duration of alcohol consumption and alcohol dependence. Tests of between subject effects for individual TFT revealed significant (P = .014) difference in T3 between groups based on alcohol dependence, significant difference in the levels of fT4 (P = .001), T3 (P = .07) and T4 (P < .001) between groups based on duration of alcohol consumption was observed. Interaction between the effect of duration of alcohol consumption and alcohol dependence for individual TFT did not reveal any significance. fT4, TSH and T4 levels were significantly low in persons consuming alcohol for more than 20 years. TSH levels were significantly low in ADS compared to controls. Significant decrease in the levels of thyroid hormones was observed as the duration of alcohol consumption increased.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kendler KS, Ohlsson H, Sundquist J, Sundquist K. Alcohol use disorder and mortality across the lifespan: a longitudinal cohort and co-relative analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016;73(6):575–81.
Grant BF, Goldstein RB, Saha TD, Chou SP, Jung J, Zhang H, et al. Epidemiology of DSM-5 alcohol use disorder: results from the national epidemiologic survey on alcohol and related conditions III. JAMA Psychiatry. 2015;72(8):757–66.
Murthy P, Manjunatha N, Subody BN, Chand PK, Benegal V. Substance use and addiction research in India. Indian J Psychiatry. 2010;52(Suppl 1):S189–99.
True WR, Xian H, Scherrer JF, Madden PA, Bucholz KK, Heath AC, et al. Common genetic vulnerability for nicotine and alcohol dependence in men. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1999;56(7):655–61.
Balhara YP, Deb KS. Impact of alcohol use on thyroid function. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2013;17(4):580–7.
Zoeller RT, Fletcher DL, Simonyl A, Rudeen PK. Chronic ethanol treatment reduces the responsiveness of the hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid axis to central stimulation. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1996;20(5):954–60.
Hermann D, Heinz A, Mann K. Dysregulation of the hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid axis in alcoholism. Addiction. 2002;97(11):1369–81.
Skinner HA, Allen BA. Alcohol dependence syndrome: measurement and validation. J Abnorm Psychol. 1982;91(3):199–209.
Deshpande SN, Mathur MN, Das SK, Bhatia T, Sharma S, Nimgaonkar VL. A Hindi version of the diagnostic interview for genetic studies. Schizophr Bull. 1998;24:489–93.
Gornall AG, Bardawill CJ, David MM. Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J Biol Chem. 1949;177(2):751–66.
Doumas BT, Peters T Jr. Serum and urine albumin: a progress report on their measurement and clinical significance. Clin Chim Acta. 1997;258(1):3–20.
Bergmeyer HU, Horder M, Rej R. International federation of clinical chemistry (IFCC) scientific committee, analytical section: approved recommendation (1985) on IFCC methods for the measurement of catalytic concentration of enzymes. Part 3. IFCC methods for alanine aminotransferase (l-alanine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase, EC 2.6.1.2). J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1986;24(7):481–95.
Bergmeyer HU, Horder M, Rej R. International federation of clinical chemistry (IFCC) scientific committee, analytical section: approved recommendation (1985) on IFCC methods for the measurement of catalytic concentration of enzymes. Part 2. IFCC methods for aspartate aminotransferase (l-aspartate:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase, EC 2.6.1.1). J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1986;24(7):497–510.
McComb RB, Bowers GN Jr. Study of optimum buffer conditions for measuring alkaline phosphatase activity in human serum. Clin Chem. 1972;18(2):97–104.
Pearlman FC, Lee RT. Detection and measurement of total bilirubin in serum, with use of surfactants as solubilizing agents. Clin Chem. 1974;20(4):447–53.
Bretaudiere JP, Phung HT, Bailly M. Direct enzymatic determination of urea in plasma and urine with a centrifugal analyzer. Clin Chem. 1976;22(10):1614–7.
Larsen K. Creatinine assay by a reaction-kinetic principle. Clin Chim Acta. 1972;41:209–17.
Mason GA, Noonan LR, Garbutt JC, Caldwell JD, Shimoda K, Walker CH, et al. Effects of ethanol and control liquid diets on the hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid axis of male Fischer-344rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1992;16(6):1130–7.
Baumgartner A, Heyne A, Campos-Barros A, Kohler R, Muller F, Meinhold H, et al. Hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid axis in chronic alcoholism. II. Deiodinase activities and thyroid hormone concentrations in brain and peripheral tissues of rats chronically exposed to ethanol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1994;18(2):295–304.
Garbutt JC, Mayo JP, Little KY, Gillette GM, Mason GA, Dew B, et al. Dose-response studies with thyrotropin-releasing hormone: evidence for differential pituitary responses in men with major depression, alcoholism, or no psychopathology. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1996;20(4):717–22.
Liappas I, Piperi C, Malitas PN, Tzavellas EO, Zisaki A, Liappas AI, et al. Interrelationship of hepatic function, thyroid activity and mood status in alcohol-dependent individuals. Vivo. 2006;20(2):293–300.
Shimizu Y, Nakazato M, Sekita Y, Kadota K, Arima K, Yamasaki H, et al. Free thyroxine (FT4) and anemia in relation to drinking status of Japanese men: the Nagasaki islands study. Endocr J. 2013;60(9):1029–34.
Valeix P, Faure P, Bertrais S, Vergnaud AC, Dauchet L, Hercberg S. Effects of light to moderate alcohol consumption on thyroid volume and thyroid function. Clin Endocrinol. 2008;68(6):988–95.
Hegedus L, Rasmussen N, Ravn V, Kastrup J, Krogsgaard K, Aldershvile J. Independent effects of liver disease and chronic alcoholism on thyroid function and size: the possibility of a toxic effect of alcohol on the thyroid gland. Metabolism. 1988;37(3):229–33.
Heinz A, Bauer M, Kuhn S, Kruger F, Graf KJ, Rommelspacher H, et al. Long-term observation of the hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid (HPT) axis in alcohol-dependent patients. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1996;93(6):470–6.
Baumgartner A, Rommelspacher H, Otto M, Schmidt LG, Kurten I, Graf KJ, et al. Hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid (HPT) axis in chronic alcoholism. I. HPT axis in chronic alcoholics during withdrawal and after 3 weeks of abstinence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1994;18(2):284–94.
Majumdar SK, Shaw GK, Thomson AD. Thyroid status in chronic alcoholics. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1981;7(1):81–4.
Aoun EG, Lee MR, Haass-Koffler CL, Swift RM, Addolorato G, Kenna GA, et al. Relationship between the thyroid axis and alcohol craving. Alcohol Alcohol. 2015;50(1):24–9.
Valimaki M, Pelkonen R, Harkonen M, Ylikahri R. Hormonal changes in noncirrhotic male alcoholics during ethanol withdrawal. Alcohol Alcohol. 1984;19(3):235–42.
Ozsoy S, Esel E, Izgi HB, Sofuoglu S. Thyroid function in early and late alcohol withdrawal: relationship with aggression, family history, and onset age of alcoholism. Alcohol Alochol. 2006;41(5):515–21.
Acknowledgements
All the authors wish to thank the authority of Father Muller Medical College for providing infrastructure and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
J. B. Honnamurthy, A. R. Shivashankara, S. S. Avinash, P. John Mathai, and M. Malathi declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Standard
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study was approved by Father Muller Institutional ethics committee (FMMC/FMIEC/2039/2014).
Informed Consent
All authors declare that written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Honnamurthy, J.B., Shivashankara, A.R., Avinash, S.S. et al. Effect of Interaction Between Duration of Alcohol Consumption and Alcohol Dependence on Thyroid Function Test: Cross Sectional Observational Study. Ind J Clin Biochem 33, 61–68 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-017-0645-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-017-0645-6