Abstract
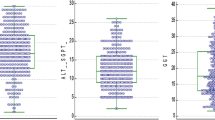
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) is the most common and cost effective screening test for asymptomatic liver disease. There is paucity of data on normal ALT among healthy individuals in India. An observational cross sectional study was conducted from January to July 2013 to estimate the upper limit of normal for ALT in healthy south Indian population. Adults undergoing voluntary or pre-employment health screening were included. Those with current and past alcoholism or smoking, acute illness or hospitalization during preceding 12 months, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory or over the counter medication use within a month, current or past intake of herbal medications, any chronic medical illness, abnormal body mass index (BMI), fatty liver in ultrasound, abnormality in haemoglobin, platelet count, blood sugar, creatinine, lipid profile and thyroid function test and positive serology (Hepatitis B, C or HIV) were excluded. A total of 2600 subjects were screened. 344 were included for analysis. Mean age was 35 years in men and 34.83 years in women, with a mean BMI of 22.2 kg/m2 in men and 21.8 kg/m2 in women. The mean ALT in men and women were 21.87 ± 2.9 (97.5th percentile 28 U/L) and 19.35 ± 3.3 (97.5th percentile 24 U/L) respectively. In conclusion, mean and upper limit of ALT (97.5th percentile) in south Indian men was 21.87 and 28 IU/L and women were 19.35 and 24 IU/L respectively. There is a need to re-consider ALT levels in our population for better detection of individuals at risk for liver disease.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lok AS, McMahon BJ. Chronic hepatitis B: update 2009. Hepatology. 2009;50(3):661–2.
Liaw YF, Kao JH, Piratvisuth T, Chan HL, Chien RN, Liu CJ, et al. Asian-Pacific consensus statement on the management of chronic hepatitis B: a 2012 update. Hepatol Int. 2012;6(3):531–61.
Tostmann A, Boeree MJ, Aarnoutse RE, de Lange WC, van der Ven AJ, Dekhuijzen R. Antituberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity: concise up-to-date review. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;23(2):192–202.
Prati D, Taioli E, Zanella A, Della Torre E, Butelli S, Del Vecchio E, et al. Updated definitions of healthy ranges for serum alanine aminotransferase levels. Ann Intern Med. 2002;137(1):1–10.
Lee JK, Shim JH, Lee HC, Lee SH, Kim KM, Lim YS, et al. Estimation of the healthy upper limits for serum alanine aminotransferase in Asian populations with normal liver histology. Hepatology. 2010;51(5):1577–83.
Park HN, Sinn DH, Gwak GY, Kim JE, Rhee SY, Eo SJ, et al. Upper normal threshold of serum alanine aminotransferase in identifying individuals at risk for chronic liver disease. Liver Int. 2012;32(6):937–44.
Zheng MH, Shi KQ, Fan YC, Liu WY, Lin XF, Li LF, et al. Upper limits of normal for serum alanine aminotransferase levels in Chinese Han population. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e43736.
Kumar S, Amarapurkar A, Amarapurkar D. Serum aminotransferase levels in healthy population from western India. Indian J Med Res. 2013;138(6):894–9.
Furruqh S, Anitha D, Venkatesh T. Estimation of reference values in liver function test in health plan individuals of an urban south Indian population. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2004;19(2):72–9.
Yadav D, Mishra S, Gupta M, John PJ, Sharma P. Establishment of reference interval for liver specific biochemical parameters in apparently healthy north Indian population. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2013;28(1):30–7.
Maksane SN, Dandekar SP, Shukla A, Bhatia S. Hepatic enzyme’s reference intervals and their modulating factors in Western Indian population. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2016;31(1):108–16.
Piton A, Poynard T, Imbert Bismut F, Khalil L, Delattre J, Pelissier E, et al. Factors associated with serum alanine transaminase activity in healthy subjects: consequences for the definition of normal values for selection of blood donors and for patients with chronic hepatitis C. MULTIVIRC Group. Hepatology. 1998;27:1213–9.
Dong MH, Bettencourt R, Barrett-Connor E, Loomba R. Alanine aminotransferase decreases with age: the Rancho Bernardo Study. PLoS One. 2010;5(12):e14254.
Kim HC, Nam CM, Jee SH, Han KH, Oh DK, Suh I. Normal serum aminotransferase concentration and risk of mortality from liver diseases: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2004;328:983.
Lai M, Hyatt BJ, Nasser I, Curry M, Afdhal NH. The clinical significance of persistently normal ALT in chronic hepatitis B infection. J Hepatol. 2007;47:760–7.
Kyrlagkitsis I, Portmann B, Smith H, O’Grady J, Cramp ME. Liver histology and progression of fibrosis in individuals with chronic hepatitis C and persistently normal ALT. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98(7):1588–93.
Boccato S, Pistis R, Noventa F, Guido M, Benvegnu L, Alberti A. Fibrosis progression in initially mild chronic hepatitis C. J Viral Hepat. 2006;13:297–302.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohan, P., Sundar, V., Bhaskar, E. et al. Estimation of Upper Limit of Normal for Serum Alanine Transaminase in Healthy South Indian Population. Ind J Clin Biochem 32, 337–342 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-016-0616-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-016-0616-3