Abstract
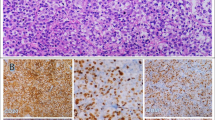
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most frequent, complex and heterogeneous lymphoma of adulthood. Heterogeneity is expressed at clinical, genetic, and molecular levels. It is known that BCL-6 expression is a favorable prognostic factor in DLBCL. However, the underlying mechanisms of BCL-6 expression in DLBCL relapse are not yet elucidated. Here, we present so far undescribed clinical phenomenon of switching BCL-6+ protein expression into BCL-6− expression in 19 of 41 relapsed DLBCL patients. The switch in relapsed DLBCL was associated with more aggressive clinical course of the disease. Bone marrow infiltration and high IPI risk were more often present in BCL-6− patients. Significantly increased biochemical parameters, such as LDH, beta-2 macroglobulin, CRP, and ferritin have been found, as well as significantly decreased serum Fe, TIBC, and hemoglobin. A Ki-67 proliferation marker was considerably high in relapsed DLBCL, but without significant differences between BCL-6+ and BCL-6− groups of patients. Thus, switching of the positive into negative BCL-6 expression during DLBCL relapse could be used as a prognostic factor and a valuable criterion for treatment decision.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lossos IS, Jones CD, Warnke R et al (2001) Expression of a single gene, BCL-6, strongly predicts survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 98:945–951
Sehn LH, Berry B, Chhanabhai M et al (2007) The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood 109:1857–1861
Shustik J, Han G, Farinha P et al (2010) Correlations between BCL6 rearrangement and outcome in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with CHOP or R-CHOP. Haematologica 95:96–101
Pasqualucci L, Migliazza A, Basso K et al (2003) Mutations of the BCL6 proto-oncogene disrupt its negative autoregulation in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 101:2914–2923
Lenz G, Wright GW, Emre NCT et al (2008) Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma arise by distinct genetic pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:13520–13525
Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC et al (2004) Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 103:275–282
Kerckaert JP, Deweindt C, Tilly H et al (1993) LAZ3, a novel zinc-finger encoding gene, is disrupted by recurring chromosome 3q27 translocations in human lymphomas. Nat Genet 5:66–70
Ye BH, Chaganti S, Chang CC et al (1995) Chromosomal translocations cause deregulated BCL6 expression by promoter substitution in B cell lymphoma. EMBO J 14:6209–6217
Winter JN, Weller EA, Horning SJ et al (2006) Prognostic significance of Bcl-6 protein expression in DLBCL treated with CHOP or R-CHOP: a prospective correlative study. Blood 107:4207–4213
The International Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project (1993) A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med 329:987–994
Wagner SD, Ahearne M, Ferrigno PK (2011) The role of BCL6 in lymphomas and routes to therapy. Br J Haematol 152:3–12
Iqbal J, Greiner TC, Patel K et al (2007) Distinctive patterns of BCL6 molecular alterations and their functional consequences in different subgroups of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 21:2332–2343
Van Etten RA (2011) BCL6 a novel target for therapy of Ph+ B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell 20:3–5
Lo Coco F, Ye BH, Lista F et al (1994) Rearrangements of the BCL6 gene in diffuse large cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Blood 83:1757–1759
Baron BW, Stanger RR, Hume E et al (1995) BCL6 encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Genes Chromosom Cancer 13:221–224
Takeda N, Arima M, Tsuruoka N et al (2003) Bcl6 is a transcriptional repressor for the IL-18 gene. J Immunol 171:426–431
Ye BH, Cattoretti G, Shen Q et al (1997) The BCL-6 proto-oncogene controls germinal-centre formation and Th2-type inflammation. Nat Genet 16:161–170
Fukuda T, Yoshida T, Okada S et al (1997) Disruption of the Bcl6 gene results in an impaired germinal center formation. J Exp Med 186:439–448
Ye BH, Lista F, Lo Coco F et al (1993) Alterations of a zinc finger-encoding gene, BCL-6, in diffuse large-cell lymphoma. Science 262:747–750
Akasaka T, Ueda C, Kurata M et al (2000) Nonimmunoglobulin (non-Ig)/BCL6 gene fusion in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma results in worse prognosis than Ig/BCL6. Blood 96:2907–2909
Choi SY, Kim SJ, Kim WS et al (2011) Aggressive B cell lymphomas of the gastrointestinal tract: clinicopathologic and genetic analysis. Virchows Arch 459:495–502
Avilés A, Narváez BR, Díaz-Maqueo JC et al (1993) Value of serum beta 2 microglobulin as an indicator of early relapse in diffuse large cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 9:377–380
Pavlidis AN, Kalef-Ezra J, Bourantas LC et al (1993) Serum tumor markers in non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Int J Biol Mark 8:14–20
Lim ST, Tao M, Cheung YB et al (2005) Can patients with early-stage diffuse large B-cell lymphoma be treated without bone marrow biopsy? Ann Oncol 16:215–258
Loeb JN (1972) The influence of temperature on the solubility of monosodium urate. Arthritis Rheum 15:189–192
Radisavljevic Z (2008) AKT as locus of fragility in robust cancer system. J Cell Biochem 104:2071–2077
Radisavljevic Z (2003) Nitric oxide suppression triggers apoptosis through the FKHRL1 (FOXO3a)/ROCK kinase pathway in human breast carcinoma cells. Cancer 97:1358–1363
Tilly H, Dreyling M (2010) ESMO Guidelines Working Group. Diffuse large B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 21(Suppl 5):172–174
Acknowledgments
This work was supported from the Ministry of Science of Serbia (Project No 41004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Todorović, M., Balint, B., Andjelic, B. et al. Switching to BCL-6 Negativity in Relapsed Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma Correlated with More Aggressive Disease Course. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus 30, 269–274 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-014-0346-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-014-0346-8