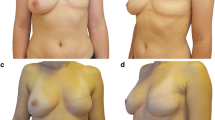
Abstract
Background
The use of post-mastectomy radiotherapy (PMRT) following immediate breast reconstruction has increased recently, and its safety is becoming a major concern. We aimed to evaluate the complication rates of PMRT to immediate tissue-expander/permanent implant (TE/PI)-based reconstructions for breast cancer and its association with radiotherapy timing (irradiation to TE or PI).
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the cases of breast cancer patients who underwent mastectomy, immediate TE/PI reconstruction, and PMRT between January 2003 and December 2014. The rates of complications including reconstruction failure, re-operation, and infection were estimated by Kaplan–Meier analysis. The risk factors including radiotherapy timing were analyzed by log-rank test and multivariate Cox proportional hazard model.
Results
A total of 81 patients were included. Median follow-up was 32 months (range 2–120 months). Radiotherapy consisted of 50 Gy to the reconstructed breast and supraclavicular region in most cases. Total reconstruction failure, re-operation, and infection rates were 12.3, 13.6, and 11.1%, and 5-year cumulative reconstruction failure, re-operation, and infection rates were 16.7, 16.6, and 12.2%, respectively. No significant differences were observed in complication rates with respect to radiotherapy timing. In multivariate analysis, age 55 years and older was a significant risk factor for complications (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
There were no significant differences in rates of reconstruction failure, re-operation, or infection with regard to radiotherapy timing. PMRT to reconstructed breasts of older patients aged 55 years or over can be expected to result in more complications than in younger patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kummerow KL, Du L, Penson DF, Shyr Y, Hooks MA. Nationwide trends in mastectomy for early-stage breast cancer. JAMA Surg. 2015;150:9–16.
Jagsi R, Jiang J, Momoh AO, Alderman A, Giordano SH, Buchholz TA, et al. Trends and variation in use of breast reconstruction in patients with breast cancer undergoing mastectomy in the United States. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:919–26.
Kurebayashi J, Miyoshi Y, Ishikawa T, Saji S, Sugie T, Suzuki T, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of breast cancer and trends in the management of breast cancer patients in Japan: based on the Breast Cancer Registry of the Japanese Breast Cancer Society between 2004 and 2011. Breast Cancer. 2015;22:235–44.
Reefy S, Patani N, Anderson A, Burgoyne G, Osman H, Mokbel K. Oncological outcome and patient satisfaction with skin-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction: a prospective observational study. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:171.
Clarke M, Collins R, Darby S, Davies C, Elphinstone P, Evans V, et al. Effects of radiotherapy and of differences in the extent of surgery for early breast cancer on local recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005;366:2087–106.
EBCTCG (Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group), McGale P, Taylor C, Correa C, Cutter D, Duane F, et al. Effect of radiotherapy after mastectomy and axillary surgery on 10-year recurrence and 20-year breast cancer mortality: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 8135 women in 22 randomised trials. Lancet. 2014;383:2127–35.
Network NCC. NCCN Web site. NCCN Practice Guidelines in Oncology—v.2.2017: Breast cancer. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast.pdf. Accessed 16 June 2017.
Senkus E, Kyriakides S, Ohno S, Penault-Llorca F, Poortmans P, Rutgers E, et al. Primary breast cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2015;26(Suppl 5):v8–30.
Frasier LL, Holden S, Holden T, Schumacher JR, Leverson G, Anderson B, et al. Temporal trends in postmastectomy radiation therapy and breast reconstruction associated with changes in national comprehensive cancer network guidelines. JAMA Oncol. 2015;2:1–7.
Barry M, Kell MR. Radiotherapy and breast reconstruction: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;127:15–22.
Lam TC, Hsieh F, Boyages J. The effects of postmastectomy adjuvant radiotherapy on immediate two-stage prosthetic breast reconstruction: a systematic review. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;132:511–8.
Cordeiro PG, Albornoz CR, McCormick B, Hudis CA, Hu Q, Heerdt A, et al. What is the optimum timing of postmastectomy radiotherapy in two-stage prosthetic reconstruction: radiation to the tissue expander or permanent implant? Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;135:1509–17.
Lentz R, Ng R, Higgins SA, Fusi S, Matthew M, Kwei SL. Radiation therapy and expander-implant breast reconstruction: an analysis of timing and comparison of complications. Ann Plast Surg. 2013;71:269–73.
Center for disease control and prevention. CDC/NHSN surveillance definitions for specific types of infections. January 2017. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/nhsn/pdfs/pscmanual/17pscnosinfdef_current.pdf. Accessed 15 June 2017.
Nava MB, Pennati AE, Lozza L, Spano A, Zambetti M, Catanuto G. Outcome of different timings of radiotherapy in implant-based breast reconstructions. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;128:353–9.
Baschnagel AM, Shah C, Wilkinson JB, Dekhne N, Arthur DW, Vicini FA. Failure rate and cosmesis of immediate tissue expander/implant breast reconstruction after postmastectomy irradiation. Clin Breast Cancer. 2012;12:428–32.
Fowble B, Park C, Wang F, Peled A, Alvarado M, Ewing C, et al. Rates of reconstruction failure in patients undergoing immediate reconstruction with tissue expanders and/or implants and postmastectomy radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015;92:634–41.
McCarthy CM, Mehrara BJ, Riedel E, Davidge K, Hinson A, Disa JJ, et al. Predicting complications following expander/implant breast reconstruction: an outcomes analysis based on preoperative clinical risk. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;121:1886–92.
Fischer JP, Nelson JA, Serletti JM, Wu LC. Peri-operative risk factors associated with early tissue expander (TE) loss following immediate breast reconstruction (IBR): a review of 9305 patients from the 2005–2010 ACS-NSQIP datasets. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2013;66:1504–12.
Berry T, Brooks S, Sydow N, Djohan R, Nutter B, Lyons J, et al. Complication rates of radiation on tissue expander and autologous tissue breast reconstruction. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17(Suppl 3):202–10.
Brooks S, Djohan R, Tendulkar R, Nutter B, Lyons J, Dietz J. Risk factors for complications of radiation therapy on tissue expander breast reconstructions. Breast J. 2012;18:28–34.
Leong SP, Shen ZZ, Liu TJ, Agarwal G, Tajima T, Paik NS, et al. Is breast cancer the same disease in Asian and Western countries? World J Surg. 2010;34:2308–24.
Santosa KB, Chen X, Qi J, Ballard TN, Kim HM, Hamill JB, et al. Postmastectomy radiation therapy and two-stage implant-based breast reconstruction: is there a better time to irradiate? Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;138:761–9.
Anderson PR, Freedman G, Nicolaou N, Sharma N, Li T, Topham N, et al. Postmastectomy chest wall radiation to a temporary tissue expander or permanent breast implant—Is there a difference in complication rates? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;74:81–5.
Collier P, Williams J, Edhayan G, Kanneganti K, Edhayan E. The effect of timing of postmastectomy radiation on implant-based breast reconstruction: a retrospective comparison of complication outcomes. Am J Surg. 2014;207:408–11.
Yan C, Fischer JP, Freedman GM, Basta MN, Kovach SJ, Serletti JM, et al. The timing of breast irradiation in two-stage expander/implant breast reconstruction. Breast J. 2016;22:322–9.
Langstein HN, Cheng MH, Singletary SE, Robb GL, Hoy E, Smith TL, et al. Breast cancer recurrence after immediate reconstruction: patterns and significance. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003;111:712–20.
Stralman K, Mollerup CL, Kristoffersen US, Elberg JJ. Long-term outcome after mastectomy with immediate breast reconstruction. Acta Oncol. 2008;47:704–8.
Medina-Franco H, Vasconez LO, Fix RJ, Heslin MJ, Beenken SW, Bland KI, et al. Factors associated with local recurrence after skin-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction for invasive breast cancer. Ann Surg. 2002;235:814–9.
Nedumpara T, Jonker L, Williams MR. Impact of immediate breast reconstruction on breast cancer recurrence and survival. Breast. 2011;20:437–43.
Gieni M, Avram R, Dickson L, Farrokhyar F, Lovrics P, Faidi S, et al. Local breast cancer recurrence after mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction for invasive cancer: a meta-analysis. Breast. 2012;21:230–6.
Damast S, Beal K, Ballangrud A, Losasso TJ, Cordeiro PG, Disa JJ, et al. Do metallic ports in tissue expanders affect postmastectomy radiation delivery? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;66:305–10.
Chen SA, Ogunleye T, Dhabbaan A, Huang EH, Losken A, Gabram S, et al. Impact of internal metallic ports in temporary tissue expanders on postmastectomy radiation dose distribution. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;85:630–5.
Vu TT, Pignol JP, Rakovitch E, Spayne J, Paszat L. Variability in radiation oncologists’ opinion on the indication of a bolus in post-mastectomy radiotherapy: an international survey. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2007;19:115–9.
Thomas K, Rahimi A, Spangler A, Anderson J, Garwood D. Radiation practice patterns among United States radiation oncologists for postmastectomy breast reconstruction and oncoplastic breast reduction. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2014;4:466–71.
Chen SA, Hiley C, Nickleach D, Petsuksiri J, Andic F, Riesterer O, et al. Breast reconstruction and post-mastectomy radiation practice. Radiat Oncol. 2013;8:45.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have declared no conflicts of interest. No funding was received for this article.
Additional information
This study was approved by the institutional review board at our institution (IRB code: 15-R089).
About this article
Cite this article
Ogita, M., Nagura, N., Kawamori, J. et al. Risk factors for complications among breast cancer patients treated with post-mastectomy radiotherapy and immediate tissue-expander/permanent implant reconstruction: a retrospective cohort study. Breast Cancer 25, 167–175 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-017-0808-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-017-0808-6