Abstract
Background
Docetaxel plus cyclophosphamide (TC) has recently been established as a standard adjuvant chemotherapy regimen for HER2-negative (HER2−) operable breast cancer. However, the efficacy and tolerability of TC as neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) remain unclear. We, therefore, conducted a prospective study to evaluate the efficacy of TC NAC in HER2− primary breast cancer.
Methods
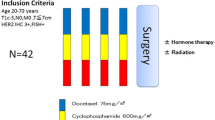
Patients who were diagnosed with HER2−, N0–N1, invasive breast cancer between July 2011 and February 2014 and had tumors measuring 1–7 cm were eligible. The subtypes were classified using a core-needle or vacuum-assisted breast biopsy. The efficacy and safety of NAC comprising TC (75 mg/m2 docetaxel and 600 mg/m2 cyclophosphamide, four cycles every 3 weeks) were investigated in a prospective study in patients with HER2− breast cancer.
Results
Fifty-two patients were enrolled. Of these, 94.2 % (49/52) completed four cycles of TC. The overall pCR rate was 16.3 % (8/49). The pCR rates for patients with luminal A-like breast cancer [estrogen receptor-positive (ER+), Ki67 index of <20 %, and HER2−], luminal B-like breast cancer (ER+, Ki67 index of >20 %, and HER2−), and triple-negative breast cancer [ER-negative (ER−) and HER2−] were 0 % (0/12), 4.3 % (1/23), and 50.0 % (7/14), respectively. Almost all pCRs occurred in triple-negative breast cancer patients.
Conclusions
The pCR rate of TC NAC was not very high despite the high completion rate. TC NAC was effective against the triple-negative subtype, resulting in a higher pCR rate. Therefore, our results indicated that TC NAC showed limited efficacy in luminal subtype breast cancer with the exception of the triple-negative subtype.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolmark N, Wnag J, Mamounas E, Bryant J, Fisher B. Prospective chemotherapy in patients with operable breast cancer: nine-year results from National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-18. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 2001;30:96–102.
Bear HD, Anderson S, Brown A, Smith R, Mamounas EP, Fisher B, et al. The effect on tumor response of adding sequential preoperative docetaxel to preoperative doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide: preliminary results from National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project Protocol B-27. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:4165–74.
Heys SD, Hutcheon AW, Sarkar TK, Ogston KN, Miller ID, Payne S, et al. Neoadjuvant docetaxel in breast cancer: 3-year survival results from the Aberdeen trial. Clin Breast Cancer. 2002;3(Suppl 2):S69–74.
Henderson IC, Berry DA, Demetri GD, Cirrincione CT, Goldstein LJ, Martino S, et al. Improved outcomes from adding sequential paclitaxel but not from escalating doxorubicin dose in an adjuvant chemotherapy regimen for patients with node-positive primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:976–83.
Jones S, Holmes FA, O’Shaughnessy J, Blum JL, Vukelja SJ, McIntyre KJ, et al. Docetaxel with cyclophosphamide is associated with an overall survival benefit compared with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide: 7-year follow-up of US Oncology Research Trial 9735. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:1177–83.
von Minckwitz G, Costa SD, Raab G, Blohmer JU, Eidtmann H, Hilfrich J, et al. Dose-dense doxorubicin, docetaxel, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor support with or without tamoxifen as preoperative therapy in patients with operable carcinoma of the breast: a randomized, controlled, open phase IIb study. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:3506–15.
Dieras V, Fumoleau P, Romieu G, Tubiana-Hulin M, Namer M, Mauriac L, et al. Randomized parallel study of doxorubicin plus paclitaxel and doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide as neoadjuvant treatment of patients with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:4958–65.
Buzdar AU. Preoperative chemotherapy treatment of breast cancer—a review. Cancer. 2007;110:2394–407.
von Minckwitz G, Untch M, Blohmer JU, Costa SD, Eidtmann H, Fasching PA, et al. Definition and impact of pathologic complete response on prognosis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in various intrinsic breast cancer subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:1796–804.
Carey LA, Dees EC, Sawyer L, Gatti L, Moore DT, Collichio F, et al. The triple negative paradox: primary tumor chemosensitivity of breast cancer subtypes. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:2329–34.
Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR, Andre F, Tordai A, Mejia JA, et al. Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:1275–81.
Toi M, Nakamura S, Kuroi K, Iwata H, Ohno S, Masuda N, et al. Phase II study of preoperative sequential FEC and docetaxel predicts of pathological response and disease free survival. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008;110:531–9.
Goldhirsch A, Winer EP, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thurlimann B, et al. Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2013. Ann Oncol. 2013;24:2206–23.
Cortazar P, Zhang L, Untch M, Mehta K, Costantino JP, Wolmark N, et al. Pathological complete response and long-term clinical benefit in breast cancer: the CTNeoBC pooled analysis. Lancet. 2014;384:164–72.
Fujii T, Le Du F, Xiao L, Kogawa T, Carlos H, et al. Effectiveness of an adjuvant chemotherapy regimen for early-stage breast cancer: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2015;1(9):1311–18.
Takabatake D, Taira N, Hara F, Sien T, Kiyoto S, Takashima S, et al. Feasibility study of docetaxel with cyclophosphamide as adjuvant chemotherapy for Japanese breast cancer patients. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2009;39:478–83.
Cortes JE, Pazdur R. Docetaxel. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13:2643–55.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Nakatsukasa, K., Koyama, H., Oouchi, Y. et al. Docetaxel and cyclophosphamide as neoadjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-negative primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer 24, 63–68 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-016-0666-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-016-0666-7