Abstract
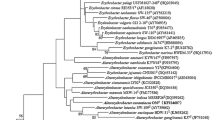
WS-10T–a Gram-negative, non-motile, and aerobic bacterial strain–was isolated from the sediment of a shallow stream in Korea. The optimum ranges of temperature and pH for growth were 20–40°C (optimum 28°C) and pH 6.0–8.0 (optimum pH 7.0), respectively. The DNA G+C content of strain WS-10T was 72.7 mol%. The major fatty acids (>5%) were summed feature 8 (C18:1 ω7c), summed feature 3 (C16:1 ω7c and/or C16:1 ω6c), C16:0, and C18:1 2-OH. The major polar lipids consisted of phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylethanolamine, and unidentified aminolipids. Q-10 was the predominant respiratory quinone. The highest similarities in the 16S rRNA gene sequence were shown with Paracraurococcus ruber (95.3%), Belnapia soli (95.3%), B. moabensis (95.1%), and B. rosea (95.0%). A phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequence comparisons showed that strain WS-10T formed a distinct line within a clade containing the genera Paracraurococcus, Craurococcus, and Belnapia in the family Acetobacteraceae. On the basis of polyphasic evidence, strain WS-10T represents a novel species of a new genus in the family Acetobacteraceae, for which the name Dankookia rubra gen. nov., sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain of the type species is WS-10T (= KACC 18533T = JCM 30602T).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alarico, S., Rainey, F.A., Empadinhas, N., Schumann, P., Nobre, M.F., and da Costa, M.S. 2002. Rubritepida flocculans gen. nov., sp. nov., a new slightly thermophilic member of the alpha-1 subclass of the Proteobacteria. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 25, 198–206.
Altschul, S.F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E.W., and Lipman, D.J. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215, 403–410.
Bernardet, J.F., Nakagawa, Y., and Holmes, B. 2002. Proposed minimal standards for describing new taxa of the family Flavobacteriaceae and emended description of the family. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 52, 1049–1070.
Collins, M.D. 1985. Analysis of isoprenoid quinone. In Gottschalk, G. (ed.), Methods in Microbiology, Vol. 18, pp. 329–366. Academic Press, London, UK.
Furuhata, K., Miyamoto, H., Goto, K., Kato, Y., Hara, M., and Fukuyama, M. 2008. Roseomonas stagni sp. nov., isolated from pond water in Japan. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 54, 167–171.
Gillis, M. 1978. Intra- and intergeneric similarities of the rRNA cistrons of Acetobacter and Gluconobacter. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 44, 117–118.
Gonzalez, J.M. and Saiz-Jimenez, C. 2002. A fluorimetric method for the estimation of G+C mol% content in microorganisms by thermal denaturation temperature. Environ. Microbiol. 4, 770–773.
Han, X.Y., Pham, A.S., Tarrand, J.J., Rolston, K.V., Helsel, L.O., and Levett, P.N. 2003. Bacteriologic characterization of 36 strains of Roseomonas species and proposal of Roseomonas mucosa sp nov and Roseomonas gilardii subsp rosea subsp nov. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 120, 256–264.
Jin, L., Lee, H.G., No, K.J., Ko, S.R., Kim, H.S., Ahn, C.Y., and Oh, H.M. 2013. Belnapia soli sp. nov., a proteobacterium isolated from grass soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 63, 1955–1959.
Jin, R., Su, J., Liu, H.Y., Wei, Y.Z., Li, Q.P., Zhang, Y.Q., and Yu, L.Y. 2012. Description of Belnapia rosea sp. nov. and emended description of the genus Belnapia Reddy et al. 2006. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 62, 705–709.
Kim, O.S., Cho, Y.J., Lee, K., Yoon, S.H., Kim, M., Na, H., Park, S.C., Jeon, Y.S., Lee J.H., Yi, H., et al. 2012. Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 62, 716–721.
Kim, W.H., Lee, S., and Ahn, T.Y. 2014. Flavihumibacter cheonanensis sp. nov., isolated from sediment of a shallow stream. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 64, 3235–3239.
Kolde, R. 2012. pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps. R package version 061.
Lane, D.J. 1991. 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics, pp. 115–175. In Stackebrandt, E. and Goodfellow, M. (eds.), Wiley, Chichester, UK.
Lee, S., Weon, H.Y., Han, K., and Ahn, T.Y. 2012. Flavobacterium dankookense sp. nov., isolated from a freshwater reservoir, and emended descriptions of Flavobacterium cheonanense, F. chungnamense, F. koreense and F. aquatile. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 62, 2378–2382.
Minnikin, D.E., O’Donnell, A.G., Goodfellow, M., Alderson, G., Athalye, M., Schaal, A., and Parlett, J.H. 1984. An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J. Microbiol. Methods 2, 233–241.
Nawrocki, E.P., Kolbe, D.L., and Eddy, S.R. 2009. Infernal 1.0: inference of RNA alignments. Bioinformatics 25, 1335–1337.
Perry, L.B. 1973. Gliding motility in some non-spreading flexibacteria. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 36, 227–232.
Reddy, G.S., Nagy, M., and Garcia-Pichel, F. 2006. Belnapia moabensis gen. nov., sp. nov., an alphaproteobacterium from biological soil crusts in the Colorado Plateau, USA. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 56, 51–58.
Rihs, J.D., Brenner, D.J., Weaver, R.E., Steigerwalt, A.G., Hollis, D.G., and Yu, V.L. 1993. Roseomonas, a new genus associated with bacteremia and other human infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42, 121–140.
Saitoh, S., Suzuki, T., and Nishimura, Y. 1998. Proposal of Craurococcus roseus gen. nov., sp. nov. and Paracraurococcus ruber gen. nov., sp. nov., novel aerobic bacteriochlorophyll a-containing bacteria from soil. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 48, 1043–1047.
Sasser, M. 1990. Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. MIDI Technical Note 101, MIDI Inc., Newark, DE, USA.
Skerman, V.B.D. 1967. A guide to the identification of the genera of bacteria, with methods and digests of generic characteristics. 2d edn. Williams & Wilkins Co., Baltimore, USA.
Smibert, R.M. and Krieg, N.R. 1994. Phenotypic characterization. In Gerhardt, P., Murray, R.G.E., Wood, W.A., and Krieg, N.R. (eds.), Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology, pp. 607–654. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC, USA.
Tamura, K., Dudley, J., Nei, M., and Kumar, S. 2007. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 24, 1596–1599.
Thompson, J.D., Higgins, D.G., and Gibson, T.J. 1994. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 22, 4673–4680.
Yurkov, V., Stackebrandt, E., Holmes, A., Fuerst, J.A., Hugenholtz, P., Golecki, J., Gad’on, N., Gorlenko, V.M., Kompantseva, E.I., and Drews, G. 1994. Phylogenetic positions of novel aerobic, bacteriochlorophyll a-containing bacteria and description of Roseococcus thiosulfatophilus gen. nov., sp. nov., Erythromicrobium ramosum gen. nov., sp. nov., and Erythrobacter litoralis sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 44, 427–434.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://www.springerlink.com/content/120956.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, WH., Kim, Dh., Kang, K. et al. Dankookia rubra gen. nov., sp. nov., an alphaproteobacterium isolated from sediment of a shallow stream. J Microbiol. 54, 420–425 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-016-6054-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-016-6054-3