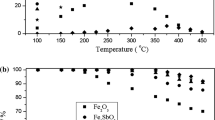
Abstract
Over recent years, catalytic materials of Fe-N-C species have been recognized being active for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). However, the identification of active site remains challenging as it generally involves a pyrolysis process and mixed components being obtained. Herein Fe3C/C and Fe2N/C samples were synthesized by temperature programmed reduction of Fe precursors in 15% CH4/H2 and pure NH3, respectively. By acid leaching of Fe2N/C sample, only single sites of FeN4 species were presented, providing an ideal model for identification of catalytic functions of the single sites of FeN4 in ORR. A correlation was conducted between the concentration of FeIIN4 in low spin state by Mössbauer spectra and the kinetic current density at 0.8 V in alkaline media, and such a structure-performance correlation assures the catalytic roles of low spin FeIIN4 species as highly active sites for the ORR.

Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Steele, B. C. H.; Heinzel, A. Materials for fuel-cell technologies. Nature 2001, 414 345–352.
Liang, H. W.; Wei, W.; Wu, Z. S.; Feng, X. L.; Müllen, K. Mesoporous metal-nitrogen-doped carbon electrocatalysts for highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135 16002–16005.
Cao, R. G.; Thapa, R.; Kim, H.; Xu, X. D.; Gyu Kim, M.; Li, Q.; Park, N.; Liu, M. L.; Cho, J. Promotion of oxygen reduction by a bio-inspired tethered iron phthalocyanine carbon nanotube-based catalyst. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4 2076.
Debe, M. K. Electrocatalyst approaches and challenges for automotive fuel cells. Nature 2012, 486 43–51.
Sun, T. T.; Li, Y. L.; Cui, T. T.; Xu, L. B.; Wang, Y. G.; Chen, W. X.; Zhang, P. P.; Zheng, T. Y.; Fu, X. Z.; Zhang, S. L. et al. Engineering of coordination environment and multiscale structure in single-site copper catalyst for superior electrocatalytic oxygen reduction. Nano Lett. 2020, 20 6206–6214.
Lefèvre, M.; Proietti, E.; Jaouen, F.; Dodelet, J. P. Iron-based catalysts with improved oxygen reduction activity in polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Science 2009, 324 71–74.
Li, X. Y.; Rong, H. P.; Zhang, J. T.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Modulating the local coordination environment of single-atom catalysts for enhanced catalytic performance. Nano Res. 2020, 13 1842–1855.
Cui, X. Y.; Yang, S. B.; Yan, X. X.; Leng, J. G.; Shuang, S.; Ajayan, P. M.; Zhang, Z. J. Pyridinic-nitrogen-dominated graphene aerogels with Fe-N-C coordination for highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26 5708–5717.
Chen, Y. Z.; Wang, C. M.; Wu, Z. Y.; Xiong, Y. J.; Xu, Q.; Yu, S. H.; Jiang, H. L. From bimetallic metal-organic framework to porous carbon: High surface area and multicomponent active dopants for excellent electrocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27 5010–5016.
Guan, B. Y.; Yu, L.; Lou, X. W. A dual-metal-organic-framework derived electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9 3092–3096.
Liang, H. W.; Zhuang, X. D.; Bruller, S.; Feng, X. L.; Müllen, K. Hierarchically porous carbons with optimized nitrogen doping as highly active electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5 4973.
Lee, S. H.; Kim, J.; Chung, D. Y.; Yoo, J. M.; Lee, H. S.; Kim, M. J.; Mun, B. S.; Kwon, S. G.; Sung, Y. E.; Hyeon, T. Design principle of Fe-N-C electrocatalysts: How to optimize multimodal porous structures? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141 2035–2045.
Chen, P. Z.; Zhou, T. P.; Xing, L. L.; Xu, K.; Tong, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhang, L. D.; Yan, W. S.; Chu, W. S.; Wu, C. Z. et al. Atomically dispersed iron-nitrogen species as electrocatalysts for bifunctional oxygen evolution and reduction reactions. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56 610–614.
You, B.; Jiang, N.; Sheng, M. L.; Drisdell, W. S.; Yano, J.; Sun, Y. J. Bimetal-organic framework self-adjusted synthesis of support-free nonprecious electrocatalysts for efficient oxygen reduction. ACS Catal. 2015, 5 7068–7076.
Wan, W. J.; Liu, X. J.; Li, H. Y.; Peng, X. Y.; Xi, D. S.; Luo, J. 3D carbon framework-supported CoNi nanoparticles as bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst for rechargeable Zn-air batteries. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2019, 240 193–200.
Jasinski, R. A new fuel cell cathode catalyst. Nature 1964, 201 1212–1213.
Tang, H. L.; Zeng, Y.; Zeng, Y. X.; Wang, R.; Cai, S. C.; Liao, C.; Cai, H. P.; Lu, X. H.; Tsiakaras, P. Iron-embedded nitrogen doped carbon frameworks as robust catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction in microbial fuel cells. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2017, 202 550–556.
Yang, W. X.; Liu, X. J.; Yue, X. Y.; Jia, J. B.; Guo, S. J. Bamboolike carbon nanotube/Fe3C nanoparticle hybrids and their highly efficient catalysis for oxygen reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137 1436–1439.
Sebastián, D.; Serov, A.; Matanovic, I.; Artyushkova, K.; Atanassov, P.; Aricò, A. S.; Baglio, V. Insights on the extraordinary tolerance to alcohols of Fe-N-C cathode catalysts in highly performing direct alcohol fuel cells. Nano Energy 2017, 34 195–204.
Li, C. H.; Liu, H. X.; Yu, Z. Y. Novel and multifunctional inorganic mixing salt-templated 2D ultrathin Fe/Co-N/S-carbon nanosheets as effectively bifunctional electrocatalysts for Zn-air batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 241 95–103.
Hu, B. C.; Wu, Z. Y.; Chu, S. Q.; Zhu, H. W.; Liang, H. W.; Zhang, J.; Yu, S. H. SiO2-protected shell mediated templating synthesis of FeN-doped carbon nanofibers and their enhanced oxygen reduction reaction performance. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11 2208–2215.
Thorum, M. S.; Hankett, J. M.; Gewirth, A. A. Poisoning the oxygen reduction reaction on carbon-supported Fe and Cu electrocatalysts: Evidence for metal-centered activity. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2 295–298.
Xiao, M. L.; Zhu, J. B.; Feng, L. G.; Liu, C. P.; Xing, W. Meso/macroporous nitrogen-doped carbon architectures with iron carbide encapsulated in graphitic layers as an efficient and robust catalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction in both acidic and alkaline solutions. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27 2521–2527.
Wei, J.; Hu, Y. X.; Liang, Y.; Kong, B.; Zhang, J.; Song, J. C.; Bao, Q. L.; Simon, G. P.; Jiang, S. P.; Wang, H. T. Nitrogen-doped nanoporous carbon/graphene nano-sandwiches: Synthesis and application for efficient oxygen reduction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25 5768–5777.
Zhu, Y. S.; Zhang, B. S.; Liu, X.; Wang, D. W.; Su, D. S. Unravelling the structure of electrocatalytically active Fe-N complexes in carbon for the oxygen reduction reaction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53 10673–10677.
Li, Q. R.; Wan, G.; Zhao, H.; Pan, L. Y.; Wang, N.; Zhao, W. P.; Zhou, X. X.; Cui, X. Z.; Chen, H. R. Nitrogen-doped carbon vesicles with dual iron-based sites for efficient oxygen reduction. ChemSusChem 2017, 10 499–505.
Guan, B. Y.; Zhang, S. L.; Lou, X. W. D. Realization of walnut-shaped particles with macro-/mesoporous open channels through pore architecture manipulation and their use in electrocatalytic oxygen reduction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57 6176–6180.
Yuan, K.; Sfaelou, S.; Qiu, M.; Lützenkirchen-Hecht, D.; Zhuang, X. D.; Chen, Y. W.; Yuan, C.; Feng, X. L.; Scherf, U. Synergetic contribution of boron and Fe-Nx species in porous carbons toward efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3 252–260.
Lefèvre, M.; Dodelet, J. P.; Bertrand, P. Molecular oxygen reduction in PEM fuel cells: Evidence for the simultaneous presence of two active sites in Fe-based catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106 8705–8713.
Kabir, S.; Artyushkova, K.; Kiefer, B.; Atanassov, P. Computational and experimental evidence for a new TM-N3/C moiety family in non-PGM electrocatalysts. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17 17785–17789.
Jiang, W. J.; Gu, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L. J.; Wang, J. Q.; Hu, J. S.; Wei, Z. D.; Wan, L. J. Understanding the high activity of Fe-N-C electrocatalysts in oxygen reduction: Fe/Fe3C nanoparticles boost the activity of Fe-Nx. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138 3570–3578.
Ratso, S.; Sahraie, N. R.; Sougrati, M. T.; Käärik, M.; Kook, M.; Saar, R.; Paiste, P.; Jia, Q. Y.; Leis, J.; Mukerjee, S. et al. Synthesis of highly-active Fe-N-C catalysts for PEMFC with carbide-derived carbons. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6 14663–14674.
Liu, Z. J.; Yu, J.; Li, X. Y.; Zhang, L. X.; Luo, D.; Liu, X. H.; Liu, X. W.; Liu, S. B.; Feng, H. B.; Wu, G. L. et al. Facile synthesis of N-doped carbon layer encapsulated Fe2N as an efficient catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Carbon 2018, 127 636–642.
Huang, X. X.; Yang, Z. Y.; Dong, B.; Wang, Y. Z.; Tang, T. Y.; Hou, Y. L. In situ Fe2N@N-doped porous carbon hybrids as superior catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Nanoscale 2017, 9 8102–8106.
Zhu, A. Q.; Qiao, L. L.; Tan, P. F.; Ma, Y. J.; Zeng, W. X.; Dong, R.; Ma, C.; Pan, J. Iron-nitrogen-carbon species for oxygen electro-reduction and Zn-air battery: Surface engineering and experimental probe into active sites. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2019, 254 601–611.
Yu, Y.; Xiao, D. J.; Ma, J.; Chen, C. L.; Li, K.; Ma, J.; Liao, Y.; Zheng, L. R.; Zuo, X. The self-template synthesis of highly efficient hollow structure Fe/N/C electrocatalysts with Fe-N coordination for the oxygen reduction reaction. RSC Adv. 2018, 8 24509–24516.
Jiao, L.; Wan, G.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, H.; Yu, S. H.; Jiang, H. L. From metal-organic frameworks to single-atom Fe implanted N-doped porous carbons: Efficient oxygen reduction in both alkaline and acidic media. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57 8525–8529.
Zhang, J.; Zheng, C. Y.; Zhang, M. L.; Qiu, Y. J.; Xu, Q.; Cheong, W. C.; Chen, W. X.; Zheng, L. R.; Gu, L.; Hu, Z. P. et al. Controlling N-doping type in carbon to boost single-atom site Cu catalyzed transfer hydrogenation of quinoline. Nano Res., in press, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-2977-4.
Xu, P.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, G. P.; Hassan, F.; Choi, J. Y.; Fu, X. G.; Zamani, P.; Yang, L. J.; Banham, D.; Ye, S. Y. et al. Embellished hollow spherical catalyst boosting activity and durability for oxygen reduction reaction. Nano Energy 2018, 51 745–753.
Wu, Z. Y.; Xu, X. X.; Hu, B. C.; Liang, H. W.; Lin, Y.; Chen, L. F.; Yu, S. H. Iron carbide nanoparticles encapsulated in mesoporous Fe-N-doped carbon nanofibers for efficient electrocatalysis. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54 8179–8183.
Jiang, R.; Li, L.; Sheng, T.; Hu, G. F.; Chen, Y. G.; Wang, L. Y. Edge-site engineering of atomically dispersed Fe-N4 by selective C-N bond cleavage for enhanced oxygen reduction reaction activities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140 11594–11598.
Li, J. S.; Chen, J. J.; Wan, H.; Xiao, J.; Tang, Y. G.; Liu, M.; Wang, H. Y. Boosting oxygen reduction activity of Fe-N-C by partial copper substitution to iron in Al-air batteries. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2019, 242 209–217.
Liu, W. G.; Zhang, L. L.; Liu, X.; Liu, X. Y.; Yang, X. F.; Miao, S.; Wang, W. T.; Wang, A. Q.; Zhang, T. Discriminating catalytically active FeNx species of atomically dispersed Fe-N-C catalyst for selective oxidation of the C-H bond. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139 10790–10798.
Li, Q. H.; Chen, W. X.; Xiao, H.; Gong, Y.; Li, Z.; Zheng, L. R.; Zheng, X. S.; Yan, W. S.; Cheong, W. C.; Shen, R. A. et al. Fe isolated single atoms on S, N codoped carbon by copolymer pyrolysis strategy for highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30 1800588.
Yi, J. D.; Xu, R.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, T.; Zang, K. T.; Luo, J.; Liang, Y. L.; Huang, Y. B.; Cao, R. Atomically dispersed iron-nitrogen active sites within porphyrinic triazine-based frameworks for oxygen reduction reaction in both alkaline and acidic media. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3 883–889.
Chen, Y. J.; Ji, S. F.; Wang, Y. G.; Dong, J. C.; Chen, W. X.; Li, Z.; Shen, R. A.; Zheng, L. R.; Zhuang, Z. B.; Wang, D. S. et al. Isolated single iron atoms anchored on N-doped porous carbon as an efficient electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56 6937–6941.
An, S. F.; Zhang, G. H.; Wang, T. W.; Zhang, W. N.; Li, K. Y.; Song, C. S.; Miller, J. T.; Miao, S.; Wang, J. H.; Guo, X. W. High-density ultra-small clusters and single-atom Fe sites embedded in graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) for highly efficient catalytic advanced oxidation processes. ACS Nano 2018, 12 9441–9450.
Xiong, Y.; Sun, W. M.; Xin, P. Y.; Chen, W. X.; Zheng, X. S.; Yan, W. S.; Zheng, L. R.; Dong, J. C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D. S. et al. Gram-scale synthesis of high-loading single-atomic-site Fe catalysts for effective epoxidation of styrene. Adv. Mater., in press, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202000896.
Kramm, U. I.; Herranz, J.; Larouche, N.; Arruda, T. M.; Lefèvre, M.; Jaouen, F.; Bogdanoff, P.; Fiechter, S.; Abs-Wurmbach, I.; Mukerjee, S. et al. Structure of the catalytic sites in Fe/N/C-catalysts for O2-reduction in PEM fuel cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14 11673–11688.
Jia, Q. Y.; Ramaswamy, N.; Tylus, U.; Strickland, K.; Li, J. K.; Serov, A.; Artyushkova, K.; Atanassov, P.; Anibal, J.; Gumeci, C. et al. Spectroscopic insights into the nature of active sites in iron-nitrogen-carbon electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction in acid. Nano Energy 2016, 29 65–82.
Li, X. N.; Zhu, K. Y.; Pang, J. F.; Tian, M.; Liu, J. Y.; Rykov, A. I.; Zheng, M. Y.; Wang, X. D.; Zhu, X. F.; Huang, Y. Q. et al. Unique role of Mössbauer spectroscopy in assessing structural features of heterogeneous catalysts. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2018, 224 518–532.
Varnell, J. A.; Tse, E. C. M.; Schulz, C. E.; Fister, T. T.; Haasch, R. T.; Timoshenko, J.; Frenkel, A. I.; Gewirth, A. A. Identification of carbon-encapsulated iron nanoparticles as active species in non-precious metal oxygen reduction catalysts. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7 12582.
Park, J. C.; Yeo, S. C.; Chun, D. H.; Lim, J. T.; Yang, J. I.; Lee, H. T.; Hong, S.; Lee, H. M.; Kim, C. S.; Jung, H. Highly activated K-doped iron carbide nanocatalysts designed by computational simulation for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2 14371–14379.
Ferrandon, M.; Kropf, A. J.; Myers, D. J.; Artyushkova, K.; Kramm, U.; Bogdanoff, P.; Wu, G.; Johnston, C. M.; Zelenay, P. Multitechnique characterization of a polyaniline-iron-carbon oxygen reduction Catalyst. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116 16001–16013.
Zitolo, A.; Goellner, V.; Armel, V.; Sougrati, M. T.; Mineva, T.; Stievano, L.; Fonda, E.; Jaouen, F. Identification of catalytic sites for oxygen reduction in iron- and nitrogen-doped graphene materials. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14 937–942.
Kramm, U. I.; Lefèvre, M.; Larouche, N.; Schmeisser, D.; Dodelet, J. P. Correlations between mass activity and physicochemical properties of Fe/N/C catalysts for the ORR in PEM fuel cell via 57Fe Mössbauer spectroscopy and other techniques. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136 978–985.
Zang, C.; Liu, Y. G.; Xu, Z. J.; Tse, C. W.; Guan, X. G.; Wei, J. H.; Huang, J. S.; Che, C. M. Highly enantioselective iron-catalyzed cis-dihydroxylation of alkenes with hydrogen peroxide oxidant via an FeIII-OOH reactive intermediate. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55 10253–10257.
Kramm, U. I.; Herrmann-Geppert, I.; Behrends, J.; Lips, K.; Fiechter, S.; Bogdanoff, P. On an easy way to prepare metal-nitrogen doped carbon with exclusive presence of MeN4-type sites active for the ORR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138 635–640.
Chen, Y. F.; Li, Z. J.; Zhu, Y. B.; Sun, D. M.; Liu, X. E.; Xu, L.; Tang, Y. W. Atomic Fe dispersed on N-doped carbon hollow nanospheres for high-efficiency electrocatalytic oxygen reduction. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31 1806312.
Mechler, A. K.; Sahraie, N. R.; Armel, V.; Zitolo, A.; Sougrati, M. T.; Schwämmlein, J. N.; Jones, D. J.; Jaouen, F. Stabilization of iron-based fuel cell catalysts by non-catalytic platinum. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165 F1084.
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2017YFA0700103), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21932002, 21872014, 21707015, 21902018, and 21577013), the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (Nos. 2019T120210, 2018M641687) and the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (No. 2019-MS-053).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, H., Chen, B., Zhang, X. et al. Highly active sites of low spin FeIIN4 species: The identification and the ORR performance. Nano Res. 14, 122–130 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-3054-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-3054-8