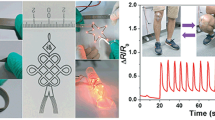
Abstract
Flexible strain sensors exhibit outstanding advantages in terms of sensitivity and stability by detecting changes in physical signals. It can be easily attached to human skin and clothed to achieve monitoring of human motion and health. However, general sensing materials shows low stretchability and cannot respond to signals under large deformation. In this work, a highly stretchable polymer composite was developed by adding small amount (0.17 wt.%) of silver nanowires (AgNWs) in stretchable conductive polymer materials. The conductivity of polymer/AgNWs composite is 1.3 S/m with the stretchability up to 500%. The stretchable strain sensor based on the polymer/AgNWs composite can respond to strain signals in real time, even for 1% strain response, and shows excellent stability over 1,000 loading/unloading cycles. Moreover, the strain sensor can be attached to human skin and clothed to monitor joints, throat and pulse of the human body. The human body electrocardiogram (ECG) signal was detected successfully with the polymer/AgNWs electrode, which is comparable to the signal obtained by the commercial electrode. Overall, the sensors enable monitoring of human movement and health. These advantages make it a potential application in wearable devices and electronic skin.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, C. Y.; Xia, K. L.; Wang, H. M.; Liang, X. P.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, Y. Y. Advanced carbon for flexible and wearable electronics. Adv. Mater.2019, 31, 1801072.
Ma, R. J.; Chou, S. Y.; Xie, Y.; Pei, Q. B. Morphological/nanostructural control toward intrinsically stretchable organic electronics. Chem. Soc. Rev.2019, 48, 1741–1786.
Yang, Y. R.; Gao, W. Wearable and flexible electronics for continuous molecular monitoring. Chem. Soc. Rev.2019, 48, 1465–1491.
Huang, S. Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, Z. F.; Guo, C. F. Flexible electronics: Stretchable electrodes and their future. Adv. Funct. Mater.2019, 29, 1805924.
Jayathilaka, W. A. D. M.; Qi, K.; Qin, Y. L.; Chinnappan, A.; Serrano-García, W.; Baskar, C.; Wang, H. B.; He, J. X.; Cui, S. Z.; Thomas, S. W. et al. Significance of nanomaterials in wearables: A review on wearable actuators and sensors. Adv. Mater.2019, 31, 1805921.
Liu, Y. H.; Pharr, M.; Salvatore, G. A. Lab-on-skin: A review of flexible and stretchable electronics for wearable health monitoring. ACS Nano2017, 11, 9614–9635.
Peng, Y. Y.; Xiao, S. G.; Yang, J. L.; Lin, J.; Yuan, W.; Gu, W. B.; Wu, X. Z.; Cui, Z. The elastic microstructures of inkjet printed polydimethylsiloxane as the patterned dielectric layer for pressure sensors. Appl. Phys. Lett.2017, 110, 261904.
Li, H. Y.; Guo, H.; Tong, S. C.; Huang, K. Q.; Zhang, C. J.; Wang, X. F.; Zhang, D.; Chen, X. H.; Yang, J. L. High-performance supercapacitor carbon electrode fabricated by large-scale roll-to-roll micro-gravure printing. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys.2019, 52, 115501.
Yao, S. S.; Zhu, Y. Wearable multifunctional sensors using printed stretchable conductors made of silver nanowires. Nanoscale2014, 6, 2345–2352.
Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q. C.; Cheng, W.; Wang, X. R.; Pan, L. J.; Xu, B. X.; Xu, H. X. A self-healable, highly stretchable, and solution processable conductive polymer composite for ultrasensitive strain and pressure sensing. Adv. Funct. Mater.2018, 28, 1705551.
Lee, J.; Pyo, S.; Kwon, D. S.; Jo, E.; Kim, W.; Kim, J. Ultrasensitive strain sensor based on separation of overlapped carbon nanotubes. Small2019, 15, 1805120.
Huang, G. W.; Xiao, H. M.; Fu, S. Y. Wearable electronics of silver-nanowire/poly(dimethylsiloxane) nanocomposite for smart clothing. Sci. Rep.2015, 5, 13971.
Kang, J.; Son, D.; Wang, G. J. N.; Liu, Y. X.; Lopez, J.; Kim, Y.; Oh, J. Y.; Katsumata, T.; Mun, J.; Lee, Y. et al. Tough and water-insensitive self-healing elastomer for robust electronic skin. Adv. Mater.2018, 30, 1706846.
Amjadi, M.; Pichitpajongkit, A.; Lee, S.; Ryu, S.; Park, I. Highly stretchable and sensitive strain sensor based on silver nanowire-elastomer nanocomposite. ACS Nano2014, 8, 5154–5163.
Lan, L. Y.; Yin, T. H.; Jiang, C. M.; Li, X. J.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qu, S. X.; Ye, Z. Z.; Ping, J. F.; Ying, Y. B. Highly conductive 1D-2D composite film for skin-mountable strain sensor and stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy2019, 62, 319–328.
Duan, S. S.; Wang, Z. H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Li, C. Z. A highly stretchable, sensitive, and transparent strain sensor based on binary hybrid network consisting of hierarchical multiscale metal nanowires. Adv. Mater. Technol.2018, 3, 1800020.
Kim, K. H.; Jang, N. S.; Ha, S. H.; Cho, J. H.; Kim, J. M. Highly sensitive and stretchable resistive strain sensors based on microstructured metal nanowire/elastomer composite films. Small2018, 14, 1704232.
Hou, C. Y.; Huang, T.; Wang, H. Z.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Q. H.; Li, Y. G. A strong and stretchable self-healing film with self-activated pressure sensitivity for potential artificial skin applications. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3138.
Wang, X. X.; Song, W. Z.; You, M. H.; Zhang, J.; Yu, M.; Fan, Z. Y.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y. Z. Bionic single-electrode electronic skin unit based on piezoelectric nanogenerator. ACS Nano2018, 12, 8588–8596.
Parida, K.; Kumar, V.; Wang, J. X.; Bhavanasi, V.; Bendi, R.; Lee, P. S. Highly transparent, stretchable, and self-healing ionic-skin triboelectric nanogenerators for energy harvesting and touch applications. Adv. Mater.2017, 29, 1702181.
Huang, J. Y.; Li, D. W.; Zhao, M.; Mensah, A.; Lv, P. F.; Tian, X. J.; Huang, F. L.; Ke, H. Z.; Wei, Q. F. Highly sensitive and stretchable CNT-bridged AgNP strain sensor based on TPU electrospun membrane for human motion detection. Adv. Elect. Mater.2019, 5, 1900241.
Amjadi, M.; Kyung, K. U.; Park, I.; Sitti, M. Stretchable, skin-mountable, and wearable strain sensors and their potential applications: A review. Adv. Funct. Mater.2016, 26, 1678–1698.
Ho, M. D.; Ling, Y. Z.; Yap, L. W.; Wang, Y.; Dong, D. S.; Zhao, Y. M.; Cheng, W. L. Percolating network of ultrathin gold nanowires and silver nanowires toward “invisible” wearable sensors for detecting emotional expression and apexcardiogram. Adv. Funct. Mater.2017, 27, 1700845.
Yang, K.; Yin, F. X.; Xia, D.; Peng, H. F.; Yang, J. Z.; Yuan, W. J. A highly flexible and multifunctional strain sensor based on a network-structured MXene/polyurethane mat with ultra-high sensitivity and a broad sensing range. Nanoscale2019, 11, 9949–9957.
Zhao, S. F.; Li, J. H.; Cao, D. X.; Zhang, G. P.; Li, J.; Li, K.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Jin, Y. F.; Sun, R. et al. Recent advancements in flexible and stretchable electrodes for electromechanical sensors: Strategies, materials, and features. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces2017, 9, 12147–12164.
Kim, S. J.; Mondal, S.; Min, B. K.; Choi, C. G. Highly sensitive and flexible strain-pressure sensors with cracked paddy-shaped MoS2/ graphene foam/ecoflex hybrid nanostructures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces2018, 10, 36377–36384.
Tao, L. Q.; Zhang, K. N.; Tian, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D. Y.; Chen, Y. Q.; Yang, Y.; Ren, T. L. Graphene-paper pressure sensor for detecting human motions. ACS Nano2017, 11, 8790–8795.
Pang, Y.; Zhang, K. N.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Ju, Z. Y.; Li, Y. X.; Wang, X. F.; Wang, D. Y.; Jian, M. Q.; Zhang, Y. Y. et al. Epidermis microstructure inspired graphene pressure sensor with random distributed spinosum for high sensitivity and large linearity. ACS Nano2018, 12, 2346–2354.
Shi, J. D.; Li, X. M.; Cheng, H. Y.; Liu, Z. J.; Zhao, L. Y.; Yang, T. T.; Dai, Z. H.; Cheng, Z. G.; Shi, E. Z.; Yang, L. et al. Graphene reinforced carbon nanotube networks for wearable strain sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater.2016, 26, 2078–2084.
Yang, Y. N.; Shi, L. J.; Cao, Z. R.; Wang, R. R.; Sun, J. Strain sensors with a high sensitivity and a wide sensing range based on a Ti3C2Tx (MXene) nanoparticle-nanosheet hybrid network. Adv. Funct. Mater.2019, 29, 1807882.
Cai, Y. C.; Shen, J.; Ge, G.; Zhang, Y. Z.; Jin, W. Q.; Huang, W.; Shao, J. J.; Yang, J.; Dong, X. C. Stretchable Ti3C2Tx MXene/carbon nanotube composite based strain sensor with ultrahigh sensitivity and tunable sensing range. ACS Nano2018, 12, 56–62.
Shi, X. L.; Wang, H. K.; Xie, X. T.; Xue, Q. W.; Zhang, J. Y.; Kang, S. Q.; Wang, C. H.; Liang, J. J.; Chen, Y. S. Bioinspired ultrasensitive and stretchable MXene-based strain sensor via nacre-mimetic microscale “brick-and-mortar” architecture. ACS Nano2019, 13, 649–659.
Gao, Y.; Fang, X. L.; Tan, J. P.; Lu, T.; Pan, L. K.; Xuan, F. Z. Highly sensitive strain sensors based on fragmentized carbon nanotube/ polydimethylsiloxane composites. Nanotechnology2018, 29, 235501.
Zheng, Y. J.; Li, Y. L.; Dai, K.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, G. Q.; Liu, C. T.; Shen, C. Y. A highly stretchable and stable strain sensor based on hybrid carbon nanofillers/polydimethylsiloxane conductive composites for large human motions monitoring. Compos. Sci. Technol.2018, 156, 276–286.
Xu, F.; Zhu, Y. Highly conductive and stretchable silver nanowire conductors. Adv. Mater.2012, 24, 5117–5122.
Yin, F. Q.; Lu, H. J.; Pan, H.; Ji, H. J.; Pei, S.; Liu, H.; Huang, J. Y.; Gu, J. H.; Li, M. Y.; Wei, J. Highly sensitive and transparent strain sensors with an ordered array structure of AgNWs for wearable motion and health monitoring. Sci. Rep.2019, 9, 2403.
Hu, W. L.; Niu, X. F.; Zhao, R.; Pei, Q. B. Elastomeric transparent capacitive sensors based on an interpenetrating composite of silver nanowires and polyurethane. Appl. Phys. Lett.2013, 102, 083303.
Yang, Y.; Ding, S.; Araki, T.; Jiu, J. T.; Sugahara, T.; Wang, J.; Vanfleteren, J.; Sekitani, T.; Suganuma, K. Facile fabrication of stretchable Ag nanowire/polyurethane electrodes using high intensity pulsed light. Nano Res.2016, 9, 401–414.
Liang, J. J.; Tong, K.; Pei, Q. B. A water-based silver-nanowire screen-print ink for the fabrication of stretchable conductors and wearable thin-film transistors. Adv. Mater.2016, 28, 5986–5996.
Zhu, S. E.; Ghatkesar, M. K.; Zhang, C.; Janssen, G. C. A. M. Graphene based piezoresistive pressure sensor. Appl. Phys. Lett.2013, 102, 161904.
Zheng, Q. B.; Liu, X.; Xu, H. R.; Cheung, M. S.; Choi, Y. W.; Huang, H. C.; Lei, H. Y.; Shen, X.; Wang, Z. Y.; Wu, Y. et al. Sliced graphene foam films for dual-functional wearable strain sensors and switches. Nanoscale Horiz.2018, 3, 35–44.
Liu, X.; Liu, D.; Lee, J. H.; Zheng, Q. B.; Du, X. H.; Zhang, X. Y.; Xu, H. R.; Wang, Z. Y.; Wu, Y.; Shen, X. et al. Spider-web-inspired stretchable graphene woven fabric for highly sensitive, transparent, wearable strain sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces2019, 11, 2282–2294.
Li, L.; Lou, Z.; Chen, D.; Jiang, K.; Han, W.; Shen, G. Z. Recent advances in flexible/stretchable supercapacitors for wearable electronics. Small2018, 14, 1702829.
Lee, M. S.; Lee, K.; Kim, S. Y.; Lee, H.; Park, J.; Choi, K. H.; Kim, H. K.; Kim, D. G.; Lee, D. Y.; Nam, S. et al. High-performance, transparent, and stretchable electrodes using graphene-metal nanowire hybrid structures. Nano Lett.2013, 13, 2814–2821.
Sun, J. M.; Pu, X.; Liu, M. M.; Yu, A. F.; Du, C. H.; Zhai, J. Y.; Hu, W. G.; Wang, Z. L. Self-healable, stretchable, transparent triboelectric nanogenerators as soft power sources. ACS Nano2018, 12, 6147–6155.
Li, H. Y.; Guo, H.; Huang, K. Q.; Liu, B.; Zhang, C. J.; Chen, X. H.; Xu, X. W.; Yang, J. L. Carbon electrode with conductivity improvement using silver nanowires for high-performance supercapacitor. Appl. Phys. A2018, 124, 763.
Xu, X. W.; Liu, Z. F.; He, P.; Yang, J. L. Screen printed silver nanowire and graphene oxide hybrid transparent electrodes for long-term electrocardiography monitoring. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys.2019, 52, 455401.
Wang, Y.; Zhu, C. X.; Pfattner, R.; Yan, H. P.; Jin, L. H.; Chen, S. C.; Molina-Lopez, F.; Lissel, F.; Liu, J.; Rabiah, N. I. et al. A highly stretchable, transparent, and conductive polymer. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1602076.
Shi, L.; Zhu, T. X.; Gao, G. X.; Zhang, X. Y.; Wei, W.; Liu, W. F.; Ding, S. J. Highly stretchable and transparent ionic conducting elastomers. Nat. Commun.2018, 9, 2630.
Zhou, Y.; Wan, C. J.; Yang, Y. S.; Yang, H.; Wang, S. C.; Dai, Z. D.; Ji, K. J.; Jiang, H.; Chen, X. D.; Long, Y. Highly stretchable, elastic, and ionic conductive hydrogel for artificial soft electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater.2019, 29, 1806220.
Lee, S.; Shin, S.; Lee, S.; Seo, J.; Lee, J.; Son, S.; Cho, H. J.; Algadi, H.; Al-Sayari, S.; Kim, D. E. et al. Ag nanowire reinforced highly stretchable conductive fibers for wearable electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater.2015, 25, 3114–3121.
Hu, W. L.; Niu, X. F.; Li, L.; Yun, S.; Yu, Z. B.; Pei, Q. B. Intrinsically stretchable transparent electrodes based on silver-nanowire-crosslinked-polyacrylate composites. Nanotechnology2012, 23, 344002.
Chen, S.; Wei, Y.; Yuan, X.; Lin, Y.; Liu, L. A highly stretchable strain sensor based on a graphene/silver nanoparticle synergic conductive network and a sandwich structure. J. Mater. Chem. C2016, 4, 4304–4311.
Lu, L. J.; Wei, X. D.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, G. Q.; Dai, K.; Liu, C. T.; Shen, C. Y. A flexible and self-formed sandwich structure strain sensor based on AgNW decorated electrospun fibrous mats with excellent sensing capability and good oxidation inhibition properties. J. Mater. Chem. C2017, 5, 7035–7042.
Lee, C. J.; Park, K. H.; Han, C. J.; Oh, M. S.; You, B.; Kim, Y. S.; Kim, J. W. Crack-induced Ag nanowire networks for transparent, stretchable, and highly sensitive strain sensors. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7959.
Song, Y. X.; Xu, W. M.; Rong, M. Z.; Zhang, M. Q. A sunlight self-healable transparent strain sensor with high sensitivity and durability based on a silver nanowire/polyurethane composite film. J. Mater. Chem. A2019, 7, 2315–2325.
Zhu, Y.; Qin, Q. Q.; Xu, F.; Fan, F. R.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wiley, B. J.; Wang, Z. L. Size effects on elasticity, yielding, and fracture of silver nanowires: In situ experiments. Phys. Rev. B2012, 85, 045443.
Myers, A. C.; Huang, H.; Zhu, Y. Wearable silver nanowire dry electrodes for electrophysiological sensing. RSC Adv.2015, 5, 11627–11632.
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51673214 and 61804185), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2017YFA0206600), the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (No. 2019JJ50804), and the Free Exploration and Innovation Project of Central South University (No. 2019zzts427).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., He, P., Luo, M. et al. Highly stretchable polymer/silver nanowires composite sensor for human health monitoring. Nano Res. 13, 919–926 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-2730-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-2730-z