Abstract
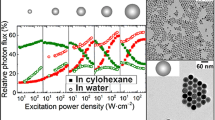
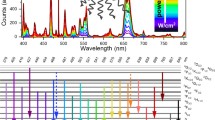
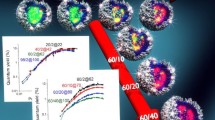
We assessed the influence of Yb3+ and Er3+ dopant concentration on the relative spectral distribution, quantum yield (ΦUC), and decay kinetics of the upconversion luminescence (UCL) and particle brightness (BUC) for similarly sized (33 nm) oleate-capped β-NaYF4:Yb3+,Er3+ upconversion (UC) nanoparticles (UCNPs) in toluene at broadly varied excitation power densities (P). This included an Yb3+ series where the Yb3+ concentration was varied between 11%-21% for a constant Er3+ concentration of 3%, and an Er3+ series, where the Er3+ concentration was varied between 1%-4% for a constant Yb3+ concentration of 14%. The results were fitted with a coupled rate equation model utilizing the UCL data and decay kinetics of the green and red Er3+ emission and the Yb3+ luminescence at 980 nm. An increasing Yb3+ concentration favors a pronounced triphotonic population of 4F9/2 at high P by an enhanced back energy transfer (BET) from the 4G11/2 level. Simultaneously, the Yb3+-controlled UCNPs absorption cross section overcompensates for the reduction in ΦUC with increasing Yb3+ concentration at high P, resulting in an increase in BUC. Additionally, our results show that an increase in Yb3+ and a decrease in Er3+ concentration enhance the color tuning range by P. These findings will pave the road to a deeper understanding of the energy transfer processes and their contribution to efficient UCL, as well as still debated trends in green-to-red intensity ratios of UCNPs at different P.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mader, H. S.; Kele, P.; Saleh, S. M.; Wolfbeis, O. S. Upconverting luminescent nanoparticles for use in bioconjugation and bioimaging. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010, 14, 582–596.
Goldschmidt, J. C.; Fischer, S. Upconversion for photovoltaics - a review of materials, devices and concepts for performance enhancement. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2015, 3, 510–535.
Chen, G. Y.; Ågren, H.; Ohulchanskyy, T. Y.; Prasad, P. N. Light upconverting core-shell nanostructures: Nanophotonic control for emerging applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1680–1713.
Resch-Genger, U.; Gorris, H. H. Perspectives and challenges of photonupconversion nanoparticles - Part I: Routes to brighter particles and quantitative spectroscopic studies. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 5855–5874.
Jaque, D.; Vetrone, F. Luminescence nanothermometry. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 4301–4326.
Zhou, B.; Shi, B. Y.; Jin, D. Y.; Liu, X. G. Controlling upconversion nanocrystals for emerging applications. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 924–936.
Chan, E. M. Combinatorial approaches for developing upconverting nanomaterials: High-throughput screening, modeling, and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1653–1679.
Haase, M.; Schafer, H. Upconverting nanoparticles. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5808–5829.
Liu, G. K. Advances in the theoretical understanding of photon upconversion in rare-earth activated nanophosphors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1635–1652.
Han, S. Y.; Deng, R. R.; Xie, X. J.; Liu, X. G. Enhancing luminescence in lanthanide-doped upconversion nanoparticles. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 11702–11715.
Wang, X. D.; Valiev, R. R.; Ohulchanskyy, T. Y.; Ågren, H.; Yang, C. H.; Chen, G. Y. Dye-sensitized lanthanide-doped upconversion nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4150–4167.
Pilch, A.; Würth, C.; Kaiser, M.; Wawrzyńczyk, D.; Kurnatowska, M.; Arabasz, S.; Prorok, K.; Samoć, M.; Strek, W.; Resch-Genger, U. et al. Shaping luminescent properties of Yb3+ and Ho3+ co-doped upconverting core-shell β-NaYF4 nanoparticles by dopant distribution and spacing. Small 2017, 13, 1701635.
Renero-Lecuna, C.; Martín-Rodríguez, R.; Valiente, R.; González, J.; Rodríguez, F.; Krämer, K. W.; Güdel, H. U. Origin of the high upconversion green luminescence efficiency in β-NaYF4:2%Er3+,20%Yb3+. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 3442–3448.
Anderson, R. B.; Smith, S. J.; May, P. S.; Berry, M. T. Revisiting the NIR-tovisible upconversion mechanism in β-NaYF4:Yb3+,Er3+. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 36–42.
Berry, M. T.; May, P. S. Disputed mechanism for NIR-to-red upconversion luminescence in NaYF4:Yb3+,Er+. J. Phys. Chem. A 2015, 119, 9805–9811.
Würth, C.; Kaiser, M.; Wilhelm, S.; Grauel, B.; Hirsch, T.; Resch-Genger, U. Excitation power dependent population pathways and absolute quantum yields of upconversion nanoparticles in different solvents. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 4283–4294.
Kaiser, M.; Würth, C.; Kraft, M.; Hyppänen, I.; Soukka, T.; Resch-Genger, U. Power-dependent upconversion quantum yield of NaYF4:Yb3+,Er3+ nanoand micrometer-sized particles-measurements and simulations. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 10051–10058.
Wang, F.; Liu, X. G. Upconversion multicolor fine-tuning: Visible to nearinfrared emission from lanthanide-doped NaYF4 nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5642–5643.
Wang, J.; Deng, R. R.; MacDonald, M. A.; Chen, B. L.; Yuan, J. K.; Wang, F.; Chi, D. Z.; Andy Hor, T. S.; Zhang, P.; Liu, G. K. et al. Enhancing multiphoton upconversion through energy clustering at sublattice level. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 157–162.
Gao, D. L.; Zhang, X. Y.; Chong, B.; Xiao, G. Q.; Tian, D. P. Simultaneous spectra and dynamics processes tuning of a single upconversion microtube through Yb3+ doping concentration and excitation power. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 4288–4296.
Zhou, J.; Liu, Q.; Feng, W.; Sun, Y.; Li, F. Y. Upconversion luminescent materials: Advances and applications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 395–1465.
Xue, X. J.; Uechi, S.; Tiwari, R. N.; Duan, Z. C.; Liao, M. S.; Yoshimura, M.; Suzuki, T.; Ohishi, Y. Size-dependent upconversion luminescence and quenching mechanism of LiYF4: Er3+/Yb3+ nanocrystals with oleate ligand adsorbed. Opt. Mater. Express 2013, 3, 989–999.
Xu, C. T.; Zhan, Q. Q.; Liu, H. C.; Somesfalean, G.; Qian, J.; He, S. L.; Andersson-Engels, S. Upconverting nanoparticles for pre-clinical diffuse optical imaging, microscopy and sensing: Current trends and future challenges. Laser Photonics Rev. 2013, 7, 663–697.
Wei, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, R.; Goggi, J.; Ren, N.; Huang, L.; Bhakoo, K. K.; Sun, H. D.; Tan, T. T. Y. Cross relaxation induced pure red upconversion in activator- and sensitizer-rich lanthanide nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 5183–5186.
Wang, Y.; Liu, K.; Liu, X. M.; Dohnalová, K.; Gregorkiewicz, T.; Kong, X. G.; Aalders, M. C. G.; Buma, W. J.; Zhang, H. Critical shell thickness of core/shell upconversion luminescence nanoplatform for FRET application. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 2083–2088.
Wang, F.; Liu, X. G. Recent advances in the chemistry of lanthanide-doped upconversion nanocrystals. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 976–989.
Wang, F.; Han, Y.; Lim, C. S.; Lu, Y. H.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, H. Y.; Zhang, C.; Hong, M. H.; Liu, X. G. Simultaneous phase and size control of upconversion nanocrystals through lanthanide doping. Nature 2010, 463, 1061–1065.
Vetrone, F.; Naccache, R.; Mahalingam, V.; Morgan, C. G.; Capobianco, J. A. The active-core/active-shell approach: A strategy to enhance the upconversion luminescence in lanthanide-doped nanoparticles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 2924–2929.
Bogdan, N.; Vetrone, F.; Ozin, G. A.; Capobianco, J. A. Synthesis of ligandfree colloidally stable water dispersible brightly luminescent lanthanide-doped upconverting nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 835–840.
Arppe, R.; Hyppänen, I.; Perälä, N.; Peltomaa, R.; Kaiser, M.; Würth, C.; Christ, S.; Resch-Genger, U.; Schaferling, M.; Soukka, T. Quenching of the upconversion luminescence of NaYF4:Yb3+,Er3+ and NaYF4:Yb3+,Tm3+ nanophosphors by water: The role of the sensitizer Yb3+ in non-radiative relaxation. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 11746–11757.
Liu, L.; Jiang, H. L.; Chen, Y. J.; Zhang, X. L.; Zhang, Z. G.; Wang, Y. X. Power dependence of upconversion luminescence of Er3+ doped Yttria nanocrystals and their bulk counterpart. J. Lumin. 2013, 143, 423–431.
Mai, H. X.; Zhang, Y. W.; Sun, L. D.; Yan, C. H. Size- and phase-controlled synthesis of monodisperse NaYF4:Yb,Er nanocrystals from a unique delayed nucleation pathway monitored with upconversion spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 13730–13739.
Xu, D. K.; Liu, C. F.; Yan, J. W.; Yang, S. H.; Zhang, Y. L. Understanding energy transfer mechanisms for tunable emission of Yb3+-Er3+ codoped GdF3 nanoparticles: Concentration-dependent luminescence by near-infrared and violet excitation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 6852–6860.
Liao, J. S.; Nie, L. L.; Liu, S. H.; Liu, B.; Wen, H. R. Yb3+ concentration dependence of upconversion luminescence in Y2Sn2O7:Yb3+/Er3+ nanophosphors. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 6081–6086.
Shen, B.; Cheng, S. M.; Gu, Y. Y.; Ni, D. R.; Gao, Y. L.; Su, Q. Q.; Feng, W.; Li, F. Y. Revisiting the optimized doping ratio in core/shell nanostructured upconversion particles. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 1964–1971.
Zhao, J. W.; Sun, Y. J.; Kong, X. G.; Tian, L. J.; Wang, Y.; Tu, L. P.; Zhao, J. L.; Zhang, H. Controlled synthesis, formation mechanism, and great enhancement of red upconversion luminescence of NaYF4:Yb3+,Er3+ nanocrystals/submicroplates at low doping level. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 15666–15672.
Zhu, H. Y.; Lin, M.; Jin, G. R.; Lu, T. J.; Xu, F. A modified energy transfer model for determination of upconversion emission of β-NaYF4:Yb,Er: Role of self-quenching effect. J. Lumin. 2017, 185, 292–297.
Li, D. G.; Qin, W. P.; Zhao, D.; Aidilibike, T.; Chen, H.; Liu, S. H.; Zhang, P.; Wang, L. L. Tunable green to red upconversion fluorescence of water-soluble hexagonal-phase core-shell CaF2@NaYF4 nanocrystals. Opt. Mater. Express 2016, 6, 270–278.
Kraft, M.; Würth, C.; Muhr, V.; Hirsch, T.; Resch-Genger, U. Particle-sizedependent upconversion luminescence of NaYF4: Yb, Er nanoparticles in organic solvents and water at different excitation power densities. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 6360–6374.
Fischer, S.; Bronstein, N. D.; Swabeck, J. K.; Chan, E. M.; Alivisatos, A. P. Precise tuning of surface quenching for luminescence enhancement in core-shell lanthanide-doped nanocrystals. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 7241–7247.
Hossan, M. Y.; Hor, A.; Luu, Q.; Smith, S. J.; May, P. S.; Berry, M. T. Explaining the nanoscale effect in the upconversion dynamics of β-NaYF4:Yb3+, Er3+ core and core-shell nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 16592–16606.
Homann, C.; Krukewitt, L.; Frenzel, F.; Grauel, B.; Würth, C.; Resch- Genger, U.; Haase, M. NaYF4:Yb,Er/NaYF4 core/shell nanocrystals with high upconversion luminescence quantum yield. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 8765–8769.
Würth, C.; Fischer, S.; Grauel, B.; Alivisatos, A. P.; Resch-Genger, U. Quantum yields, surface quenching, and passivation efficiency for ultrasmall core/shell upconverting nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 4922–4928.
Zhao, J. B.; Lu, Z. D.; Yin, Y. D.; McRae, C.; Piper, J. A.; Dawes, J. M.; Jin, D. Y.; Goldys, E. M. Upconversion luminescence with tunable lifetime in NaYF4:Yb,Er nanocrystals: Role of nanocrystal size. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 944–952.
Wilhelm, S.; Kaiser, M.; Würth, C.; Heiland, J.; Carrillo-Carrion, C.; Muhr, V.; Wolfbeis, O. S.; Parak, W. J.; Resch-Genger, U.; Hirsch, T. Water dispersible upconverting nanoparticles: Effects of surface modification on their luminescence and colloidal stability. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 1403–1410.
Hudry, D.; Busko, D.; Popescu, R.; Gerthsen, D.; Abeykoon, A. M. M.; Kübel, C.; Bergfeldt, T.; Richards, B. S. Direct evidence of significant cation intermixing in upconverting core@shell nanocrystals: Toward a new crystallochemical model. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 9238–9246.
Dühnen, S.; Haase, M. Study on the intermixing of core and shell in NaEuF4/NaGdF4 core/shell nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 8375–8386.
Zuo, J.; Sun, D. P.; Tu, L. P.; Wu, Y. N.; Cao, Y. H.; Xue, B.; Zhang, Y. L.; Chang, Y. L.; Liu, X. M.; Kong, X. G. et al. Precisely tailoring upconversion dynamics via energy migration in core-shell nanostructures. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3054–3058.
Shalav, A.; Richards, B. S.; Trupke, T.; Krämer, K. W.; Güdel, H. U. Application of NaYF4:Er3+ up-converting phosphors for enhanced near-infrared silicon solar cell response. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 86, 013505.
Ivaturi, A.; MacDougall, S. K. W.; Martín-Rodríguez, R.; Quintanilla, M.; Marques-Hueso, J.; Krämer, K. W.; Meijerink, A.; Richards, B. S. Optimizing infrared to near infrared upconversion quantum yield of β-NaYF4:Er3+ in fluoropolymer matrix for photovoltaic devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 013505.
Vetrone, F.; Boyer, J. C.; Capobianco, J. A.; Speghini, A.; Bettinelli, M. Effect of Yb3+ codoping on the upconversion emission in nanocrystalline Y2O3:Er3+. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 1107–1112.
Gao, D. L.; Zhang, X. Y.; Zheng, H. R.; Gao, W.; He, E. J. Yb3+/Er3+ codoped β-NaYF4 microrods: Synthesis and tuning of multicolor upconversion. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 554, 395–399.
Zhang, H. X.; Jia, T. Q.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y. C.; Zhang, S. A.; Feng, D. H.; Sun, Z. R.; Qiu, J. R. Depleted upconversion luminescence in NaYF4:Yb3+,Tm3+ nanoparticles via simultaneous two-wavelength excitation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 17756–17764.
Strohhöfer, C.; Polman, A. Absorption and emission spectroscopy in Er3+-Yb3+ doped aluminum oxide waveguides. Opt. Mater. 2003, 21, 705–712.
Wen, S. H.; Zhou, J. J.; Zheng, K. Z.; Bednarkiewicz, A.; Liu, X. G.; Jin, D. Y. Advances in highly doped upconversion nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2415.
Gargas, D. J.; Chan, E. M.; Ostrowski, A. D.; Aloni, S.; Altoe, M. V. P.; Barnard, E. S.; Sanii, B.; Urban, J. J.; Milliron, D. J.; Cohen, B. E. et al. Engineering bright sub-10-nm upconverting nanocrystals for single-molecule imaging. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 300–305.
Ylihärsilä, M.; Harju, E.; Arppe, R.; Hattara, L.; Hölsä, J.; Saviranta, P.; Soukka, T.; Waris, M. Genotyping of clinically relevant human adenoviruses by array-in-well hybridization assay. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 551–557.
Würth, C.; Grabolle, M.; Pauli, J.; Spieles, M.; Resch-Genger, U. Comparison of methods and achievable uncertainties for the relative and absolute measurement of photoluminescence quantum yields. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 3431–3439.
Würth, C.; Pauli, J.; Lochmann, C.; Spieles, M.; Resch-Genger, U. Integrating sphere setup for the traceable measurement of absolute photoluminescence quantum yields in the near infrared. Anal. Chem, 2012, 84, 1345–1352.
Hatami, S.; Würth, C.; Kaiser, M.; Leubner, S.; Gabriel, S.; Bahrig, L.; Lesnyak, V.; Pauli, J.; Gaponik, N.; Eychmüller, A. et al. Absolute photoluminescence quantum yields of IR26 and IR-emissive Cd1- xHgxTe and PbS quantum dots - method- and material-inherent challenges. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 133–143.
Resch-Genger, U.; Bremser, W.; Pfeifer, D.; Spieles, M.; Hoffmann, A.; DeRose, P. C.; Zwinkels, J. C.; Gauthier, F.; Ebert, B.; Taubert, R. D. et al. State-of-the art comparability of corrected emission spectra. 2. Field laboratory assessment of calibration performance using spectral fluorescence standards. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 3899–3907.
Würth, C.; Grabolle, M.; Pauli, J.; Spieles, M.; Resch-Genger, U. Relative and absolute determination of fluorescence quantum yields of transparent samples. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1535–1550.
Acknowledgments
Synthesis of the UCNPs by Emilia Palo and performance of the ICP-OES measurements by MSc. Melissa Monks is gratefully acknowledged. URG acknowledges financial support by research grants RE 1203/18-1 (German research council; DFG), RE 1203/20-1 (project NANOHYPE; DFG and M-Eranet) and TS from Tekes, the Finnish Funding Agency for Innovation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2019_2450_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Explaining the influence of dopant concentration and excitation power density on the luminescence and brightness of β-NaYF4:Yb3+,Er3+ nanoparticles: Measurements and simulations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaiser, M., Würth, C., Kraft, M. et al. Explaining the influence of dopant concentration and excitation power density on the luminescence and brightness of β-NaYF4:Yb3+,Er3+ nanoparticles: Measurements and simulations. Nano Res. 12, 1871–1879 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-019-2450-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-019-2450-4